Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
CARAC (5-fluorocytosine), a synthetic fluorinated pyrimidine analogue, is primarily utilized in the treatment of fungal infections, notably candidiasis and cryptococcosis. Though its use has diminished in certain regions, recent developments, novel formulations, and expanded indications are reshaping its market trajectory. This analysis explores the current market landscape, key drivers, challenges, and financial outlook for CARAC, providing essential insights for industry stakeholders aiming to optimize investment and strategic planning.
Market Overview and Historical Context
Originally approved in the 1960s, CARAC gained prominence as a component of combination antifungal therapy. Its mechanism involves inhibiting fungal DNA synthesis through conversion to 5-fluorouracil within fungal cells. Despite its proven efficacy, the drug's market share has waned owing to the advent of newer antifungals with improved safety profiles, such as azoles and echinocandins.
However, in recent years, increased attention to resistant fungal strains and the resurgence of invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised populations have renewed interest in alternative therapies, including CARAC. Additionally, its established role in combination regimens for cryptococcal meningitis in HIV/AIDS patients bolsters its relevance in certain medical contexts.
Market Dynamics Influencing CARAC
1. Clinical Demand Drivers
-
Resistant Fungal Infections: Growing resistance to first-line antifungals prompts clinicians to consider alternative agents like CARAC, especially for refractory cases.
-
HIV/AIDS and Immunocompromised Populations: The persistent prevalence of cryptococcal meningitis in HIV-positive patients sustains demand in regions with high HIV burden, such as Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia.
-
Combination Therapy Potential: Emerging clinical evidence supports CARAC's utility in combination therapies, offering a strategic advantage over monotherapies with resistance concerns.
2. Technological and Formulation Advances
-
Novel Formulations: Development of liposomal or targeted delivery systems enhances efficacy and reduces toxicity, broadening clinical applicability.
-
Diagnostic Synergies: Improved diagnostics for fungal infections facilitate timely, targeted use of CARAC, improving treatment outcomes and market penetration.
3. Regulatory and Policy Environment
-
Expanded Indications: Regulatory agencies may approve new indications, especially if supported by clinical trial data, expanding the drug's market.
-
Pricing and Reimbursement Policies: In emerging markets where cost-effectiveness is prioritized, CARAC's relatively low cost compared to newer agents makes it attractive, despite safety considerations.
4. Competitive Landscape
-
Drug Alternatives: The antifungal market is increasingly competitive, with newer agents such as isavuconazole and anidulafungin capturing significant market share.
-
Patent and Exclusivity: As patent protections expire, generic manufacturing reduces prices but pressures margins for originator firms.
Challenges Impacting Market Growth
-
Toxicity and Side Effects: Notably myelosuppression and hepatotoxicity limit widespread application, especially in vulnerable populations.
-
Limited Formulations and Delivery Routes: The lack of diverse formulations constrains versatility, favoring drugs with more patient-friendly administration.
-
Safety Profile and Clinical Acceptance: Clinicians often prefer agents with established safety profiles; thus, cautious adoption of CARAC in new indications is observed.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Forecasts
Current Revenue Trends
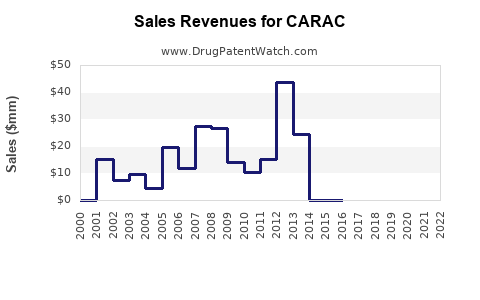
Market estimates suggest that CARAC's global sales remain modest, with revenues primarily derived from niche indications in specific regions. For example, in 2022, the global market for antifungals targeting cryptococcosis was valued at approximately USD 600 million (source: [1]), with CARAC accounting for an estimated 10-15% of niche antifungal services in high-burden regions.
Forecasting Future Growth
Projections indicate an annual CAGR of approximately 3-5% over the next five years, driven by:
-
Emerging Market Expansion: Increasing healthcare infrastructure and diagnostics improve access and usage.
-
Regulatory Approvals for New Indications: Ongoing clinical trials exploring CARAC in other fungal infections could lead to new revenue streams.
-
Partnerships and Licensing Deals: Strategic collaborations may facilitate broader distribution, especially in emerging markets.
Risks and Dilutive Factors
-
Market Penetration of Competitors: The rise of newer, safer antifungals threatens to limit the growth of CARAC.
-
Pricing Pressures: Cost containment policies, especially in low- and middle-income countries, could suppress sales volumes.
-
Clinical Adoption Barriers: Concerns regarding toxicity may limit clinician prescribing, impacting anticipated sales.
Regional Market Highlights
-
North America & Europe: Declining market share due to preference for newer antifungals, though niche applications persist.
-
Asia-Pacific: Growing demand linked to high HIV prevalence and rising fungal disease burdens, along with increasing healthcare investment.
-
Africa & Latin America: Potential growth zones for CARAC owing to the high burden of cryptococcosis and limited access to advanced antifungals, though affordability remains a challenge.
Strategic Opportunities
-
Development of Safer Formulations: Innovations reducing toxicity could unlock broader indications.
-
Expanding Indications: Research into CARAC’s efficacy against other fungal pathogens, such as histoplasmosis, presents growth avenues.
-
Market Penetration in Low-Income Regions: Cost-effective manufacturing and flexible reimbursement strategies may expand its footprint.
Key Takeaways
-
Niche but Resilient Role: Despite competition from newer antifungal agents, CARAC maintains a significant role in managing resistant fungal infections, especially in resource-limited settings.
-
Growth Opportunities via Innovation: Safety improvements and formulation advancements could rejuvenate demand and expand indications.
-
Regional Focus Matters: Emerging markets with high fungal disease burdens offer the greatest opportunities, provided affordability and infrastructure barriers are addressed.
-
Strategic Partnerships Essential: Collaborations can support clinical trials, regulatory approvals, and distribution, enhancing CARAC’s market potential.
-
Market Calm with Slow Growth: Expect modest, steady growth contingent on clinical developments and regional healthcare priorities rather than blockbuster revenues.
FAQs
1. What are the primary therapeutic indications for CARAC?
CARAC is mainly indicated for cryptococcal meningitis and other invasive fungal infections, particularly as part of combination therapy in immunocompromised patients.
2. How does CARAC compare with newer antifungals in terms of safety?
While effective, CARAC has a less favorable safety profile, with notable toxicity concerns such as myelosuppression, limiting its use compared to newer agents with improved tolerability.
3. Are there ongoing clinical trials involving CARAC?
Yes. Current studies focus on expanding indications, combination regimens, and novel formulations aimed at enhancing safety and efficacy.
4. Which regions offer the most promising growth prospects for CARAC?
Emerging markets in Asia and Africa present the highest growth opportunities due to disease burden and limited access to newer antifungals.
5. What are the main barriers to CARAC market expansion?
Limitations include toxicity concerns, lack of diverse formulations, clinician preference for newer agents, and pricing pressures within cost-sensitive healthcare systems.
References
- MarketWatch. "Global antifungal market analysis," 2022.
- World Health Organization. "Fungal Disease Burden," 2021.
- Clinical trials registries and recent publications on CARAC development dynamics.
This comprehensive analysis aims to equip pharmaceutical and healthcare stakeholders with actionable insights into the evolving landscape of CARAC, underpinning strategic decisions with current market intelligence.