AZATHIOPRINE Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
When do Azathioprine patents expire, and what generic alternatives are available?
Azathioprine is a drug marketed by Alkem Labs Ltd, Amneal, Rising, Zydus Pharms Usa, and Hikma. and is included in five NDAs.
The generic ingredient in AZATHIOPRINE is azathioprine sodium. There are sixteen drug master file entries for this compound. One supplier is listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the azathioprine sodium profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Litigation and Generic Entry Outlook for Azathioprine
A generic version of AZATHIOPRINE was approved as azathioprine sodium by HIKMA on March 31st, 1995.
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for AZATHIOPRINE?
- What are the global sales for AZATHIOPRINE?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for AZATHIOPRINE?
Summary for AZATHIOPRINE
| US Patents: | 0 |
| Applicants: | 5 |
| NDAs: | 5 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 11 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 1 |
| Clinical Trials: | 357 |
| Patent Applications: | 4,391 |
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for AZATHIOPRINE |
| DailyMed Link: | AZATHIOPRINE at DailyMed |
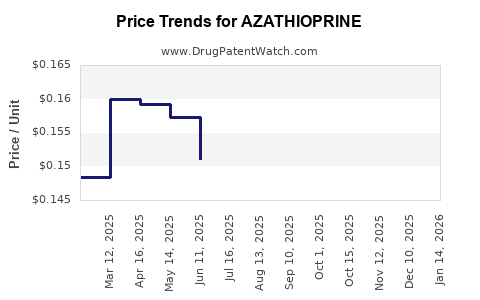
See drug prices for AZATHIOPRINE
Recent Clinical Trials for AZATHIOPRINE
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| NovelMed Therapeutics | PHASE2 |
| University Hospital Schleswig-Holstein | PHASE4 |
| First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University | PHASE3 |
Pharmacology for AZATHIOPRINE
| Drug Class | Purine Antimetabolite |
| Mechanism of Action | Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors |
Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) Categories for AZATHIOPRINE
Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classes for AZATHIOPRINE
US Patents and Regulatory Information for AZATHIOPRINE
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkem Labs Ltd | AZATHIOPRINE | azathioprine | TABLET;ORAL | 208687-001 | Mar 27, 2020 | AB | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Amneal | AZATHIOPRINE | azathioprine | TABLET;ORAL | 074069-003 | Nov 2, 2021 | AB | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Alkem Labs Ltd | AZATHIOPRINE | azathioprine | TABLET;ORAL | 208687-004 | Mar 27, 2020 | AB | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Zydus Pharms Usa | AZATHIOPRINE | azathioprine | TABLET;ORAL | 077621-004 | Sep 5, 2008 | AB | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Rising | AZATHIOPRINE | azathioprine | TABLET;ORAL | 075568-001 | Dec 13, 1999 | AB | RX | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
EU/EMA Drug Approvals for AZATHIOPRINE
| Company | Drugname | Inn | Product Number / Indication | Status | Generic | Biosimilar | Orphan | Marketing Authorisation | Marketing Refusal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nova Laboratories Ireland Limited | Jayempi | azathioprine | EMEA/H/C/005055Jayempi is indicated in combination with other immunosuppressive agents for the prophylaxis of transplant rejection in patients receiving allogenic kidney, liver, heart, lung or pancreas transplants. Azathioprine is indicated in immunosuppressive regimens as an adjunct to immunosuppressive agents that form the mainstay of treatment (basis immunosuppression).Jayempi is used as an immunosuppressant antimetabolite either alone or, more commonly, in combination with other agents (usually corticosteroids) and/ or procedures which influence the immune response.Jayempi is indicated in patients who are intolerant to glucocorticosteroids or if the therapeutic response is inadequate despite treatment with high doses of glucocorticosteroids, in the following diseases:severe active rheumatoid arthritis (chronic polyarthritis) that cannot be kept under control by less toxic agents (disease-modifying anti-rheumatic -medicinal products – DMARDs)auto-immune hepatitis systemic lupus erythematosusdermatomyositispolyarteritis nodosapemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoidBehçet’s diseaserefractory auto-immune haemolytic anaemia, caused by warm IgG antibodieschronic refractory idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpuraJayempi is used for the treatment of moderately severe to severe forms of chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis) in patients in whom glucocorticosteroid therapy is necessary, but where glucocorticosteroids are not tolerated, or in whom the disease is untreatable with other common means of first choice.It is also indicated in adult patients in relapsing multiple sclerosis, if an immunomodulatory therapy is indicated but beta interferon therapy is not possible, or a stable course has been achieved with previous treatment with azathioprine. 3Jayempi is indicated for the treatment of generalised myasthenia gravis. Depending on the severity of the disease, Jayempi should be given in combination with glucocorticosteroids because of slow onset of action at the beginning of treatment and the glucocorticosteroid dose should be gradually reduced after several months of treatment. | Authorised | no | no | no | 2021-06-21 | |
| >Company | >Drugname | >Inn | >Product Number / Indication | >Status | >Generic | >Biosimilar | >Orphan | >Marketing Authorisation | >Marketing Refusal |
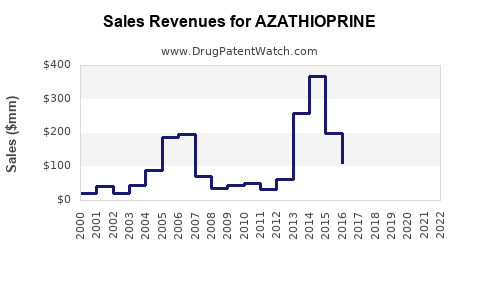
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for the Pharmaceutical Drug: Azathioprine
More… ↓
