Last updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
Hydroxyzine, marketed under the brand name ATARAX, is a first-generation antihistamine widely used for its anxiolytic, sedative, antiemetic, and antiallergic properties. Since its introduction in the mid-20th century, ATARAX has maintained a significant presence in both prescription and over-the-counter drug markets. Its market dynamics, driven by evolving medical guidelines, regulatory factors, and consumer preferences, influence its financial trajectory. This comprehensive analysis explores current market trends, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and future growth prospects of ATARAX within the pharmaceutical sector.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Clinical Applications
Introduced by Pfizer in the 1950s, hydroxyzine quickly gained popularity for its efficacy in treating allergies, anxiety, nausea, and sleep disorders. Its broad therapeutic profile made it a versatile option for clinicians, especially before the advent of newer agents with improved safety profiles. Despite the development of second-generation antihistamines, hydroxyzine remains a valuable drug owing to its sedative and anxiolytic effects, particularly in hospital settings, outpatient clinics, and for specific patient populations where alternative options are limited.
Market Size and Adoption
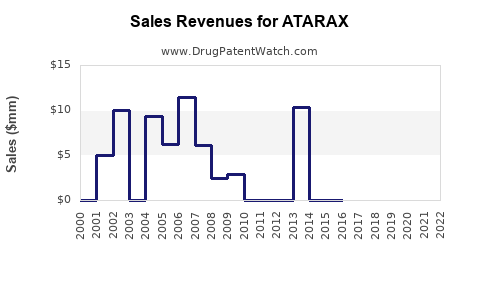
Global pharmaceutical databases estimate the hydroxyzine market, predominantly driven by the ATARAX formulation, to be valued at approximately USD 300-400 million annually, with North America accounting for nearly 50% of the consumption. The demand persists owing to ATARAX’s utility in treating chronic allergic conditions, anxiety disorders, and insomnia, especially in regions with limited access to newer pharmacological agents.
The prevalence of allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and anxiety disorders significantly influences the market size. For instance, the CDC reports over 50 million Americans suffer from allergic rhinitis alone, corroborating the steady demand for antihistamines like hydroxyzine [1].
Competitive Landscape
While ATARAX faces competition from second-generation antihistamines such as loratadine, cetirizine, and fexofenadine, its unique sedative and anti-anxiety properties maintain its clinical niche. Nonetheless, the proliferation of over-the-counter (OTC) alternatives and the rise of non-sedating antihistamines exert pressure on sales volumes.
The pharmaceutical market also includes generics, which dominate the hydroxyzine segment, often leading to price reductions and affecting profit margins for branded formulations. Notably, Teva, Mylan, and other generic manufacturers supply hydroxyzine globally, influencing market pricing and availability.
Regulatory Environment and Market Drivers
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
Hydroxyzine's patent expiration in the early 2000s marked a pivotal shift, accelerating generic adoption and truncating revenue streams for branded ATARAX. This phenomenon underscores the importance of patent management and innovative drug development as strategic imperatives for market sustainment.
Regulatory Approvals and Off-Label Uses
Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have not issued new approvals for ATARAX in recent years, but off-label usages—like its application in managing opioid withdrawal symptoms—have expanded its clinical utility, albeit with limited official endorsement. These off-label indications can influence prescribing patterns and market flows.
Pharmacovigilance and Safety Profile
Hydroxyzine's side effect profile, characterized by sedation, anticholinergic effects, and potential for misuse, necessitates ongoing pharmacovigilance. Stricter prescribing guidelines and increased awareness of adverse effects can temper demand and impact the drug's trajectory.
Financial Trajectory and Future Outlook
Revenue Trends
The influence of generic competition has resulted in downward pressure on ATARAX's pricing and sales revenues over the past decade. Nonetheless, its entrenched position in hospital formularies and specialized treatment settings sustains a baseline revenue, estimated at approximately USD 100-150 million annually in key markets.
Market Growth Opportunities
Emerging markets present substantial growth potential due to increasing allergy prevalence and limited access to newer medications. China and India, with rapidly expanding healthcare infrastructure, could drive increased demand for hydroxyzine, especially in its generic form.
In addition, expanding off-label uses in anesthesia and psychiatry may offer marginal revenue enhancements, provided safety and efficacy profiles support regulatory acceptance.
Challenges and Risks
Key risks include:
- Increasing utilization of non-sedating, second-generation antihistamines.
- Regulatory constraints owing to safety concerns, especially across aging populations vulnerable to anticholinergic effects.
- Price erosion due to intensified generic competition.
- Shifting prescriber preferences favoring newer, better-tolerated agents.
Strategic Considerations
To sustain competitiveness, pharmaceutical companies should explore:
- Development of improved formulations (e.g., extended release).
- Expansion of approved indications.
- Strategic partnerships to enhance market penetration.
- Cost-effective manufacturing to maintain margins amid price erosion.
Conclusion
The market dynamics for ATARAX are characterized by mature, competitive pressures and regulatory factors that shape its financial trajectory. While generic competition constrains revenue growth, sustained demand stemming from established clinical utility ensures stability. Opportunities in emerging markets and off-label applications offer avenues for growth, contingent upon regulatory and safety considerations. Long-term profitability hinges on strategic innovation, footprint expansion, and adaptation to evolving prescriber preferences.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroxyzine (ATARAX) remains relevant in specific therapeutic niches despite intense generic competition and the advent of newer antihistamines.
- Market growth is primarily driven by demand in emerging economies, but overall revenues face downward pressure due to price erosion and evolving clinical guidelines.
- Strategic focus on formulation innovation and expanding indications could help sustain revenues and regional market share.
- Regulatory and safety concerns necessitate ongoing pharmacovigilance, influencing prescribing practices and product positioning.
- Operators should explore partnerships, local market adaptation, and cost efficiencies to enhance financial sustainability.
FAQs
1. How does ATARAX compare to second-generation antihistamines in clinical practice?
While second-generation antihistamines like loratadine are preferred for chronic allergy management due to fewer sedative effects, ATARAX's sedative and anxiolytic properties make it valuable for specific indications such as anxiety and sleep disorders.
2. What is the impact of generic hydroxyzine on the ATARAX market?
Generic hydroxyzine's entry post-patent expiry has significantly reduced branded ATARAX's market share and price points, leading to decreased revenues but ensuring wider accessibility.
3. Are there upcoming regulatory developments affecting ATARAX?
Currently, no significant regulatory changes are anticipated. However, safety concerns related to anticholinergic burden, especially in the elderly, could influence prescribing guidelines.
4. What are the main opportunities for growth in the hydroxyzine market?
Emerging markets offer expansion potential, alongside exploring off-label applications and potential new formulations that could improve tolerability and compliance.
5. How can pharmaceutical companies differentiate ATARAX in a competitive market?
Focusing on formulation improvements, expanding approved indications, and developing targeted marketing strategies tailored to regions with high allergy prevalence can enhance market position.
References
[1] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). “Allergic Rhinitis Data and Statistics.” CDC.gov. 2022.