Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Perphenazine, a first-generation antipsychotic medication belonging to the phenothiazine class, has maintained a significant position within the therapeutic landscape for schizophrenia and psychotic disorders. Developed during the mid-20th century, its pharmacological profile targets positive symptoms of psychosis through dopamine D2 receptor antagonism. Despite the advent of atypical antipsychotics, perphenazine continues to influence market dynamics owing to its cost-effectiveness, familiarity, and established efficacy. This analysis examines the current market environment, emerging trends, and financial prospects surrounding perphenazine, providing a comprehensive outlook for stakeholders.
Historical and Regulatory Context
Perphenazine was first introduced in the United States in the 1950s, rapidly becoming a staple in psychiatric treatment. Its generic formulations have contributed notably to its widespread use. Regulatory considerations have primarily centered on safety profiles, including potential extrapyramidal symptoms and sedation, which have prompted comparative assessments with newer agents.
While the drug's patent expired decades ago, allowing for broad generics manufacture, regulatory pathways remain pivotal, especially concerning quality control of generic versions. The absence of specific patent protection has made market entry more accessible for generic manufacturers, intensifying competition and exerting downward pressure on prices.
Market Dynamics
1. Competitive Landscape
The global psychiatric medication market is characterized by intense competition, where first-generation antipsychotics like perphenazine compete primarily on cost, established clinical use, and clinician familiarity. The proliferation of second-generation ("atypical") antipsychotics, such as risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole, has shifted prescriber preferences toward drugs with improved side effect profiles.
However, perphenazine maintains a niche in low-resource settings and for patients intolerant to atypicals, due to its affordability. Generic manufacturers dominate its supply chain, which reduces pricing and limits margins but sustains high-volume sales.
2. Regional Market Variations
Developing economies rely heavily on generics, including perphenazine, for treatment affordability. Countries like India, China, and parts of Africa report stable or increasing usage owing to economic constraints on healthcare budgets. Conversely, in refined healthcare markets like North America and Western Europe, perphenazine's use has declined, supplanted by newer agents with improved tolerability.
3. Prescriber Trends and Clinical Guidelines
Clinical guidelines influence prescribing behavior considerably. While some psychiatric practitioners still favor perphenazine for acute cases or maintenance therapy, many guidelines recommend atypical antipsychotics for their lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms and metabolic side effects. Nevertheless, the drug's entrenched role in long-standing treatment protocols sustains a baseline demand.
4. Regulatory and Safety Concerns
Safety concerns, especially regarding motor side effects and cardiovascular risks, impact market confidence. Regulatory agencies have issued updates and warnings, although none have led to major restrictions on its use. Ongoing pharmacovigilance is essential to maintain regulatory approval and market stability.
Financial Trajectory
1. Revenue Trends
The global market for first-generation antipsychotics, including perphenazine, has seen a gradual decline in revenue due to competitive pressures from second-generation drugs. However, the low-cost formulations preserve a steady revenue stream, especially in price-sensitive markets.
Forecasts suggest modest growth in these regions, driven by increasing mental health awareness and expanding healthcare access. Conversely, in high-income markets, revenue from perphenazine is expected to diminish further, with manufacturers consolidating their portfolios around newer, patent-protected agents.
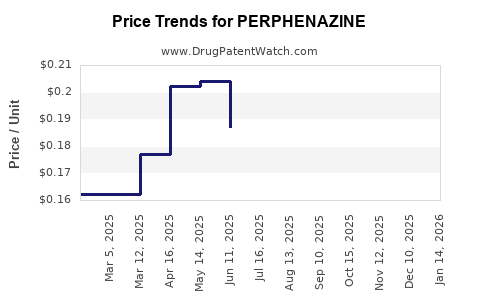
2. Pricing and Cost Dynamics
Manufacturers of generic perphenazine benefit from low production costs, enabling competitive pricing. Price erosion has been accentuated by herbicide market competition, leading to razor-thin margins but high sales volumes. Future pricing strategies will likely depend on regulatory costs and regional price controls.
3. Investment in R&D and Market Expansion
Current investments tend to favor reformulations or combination therapies with improved safety profiles rather than new formulations of perphenazine. Market expansion efforts focus predominantly on emerging economies where demand persists.
4. Impact of Patent and Regulatory Environment
While the loss of patent protection diminishes exclusivity, regulatory frameworks emphasizing quality and safety standards influence future market prospects. Any new formulations or delivery methods (e.g., depot injections, transdermal patches) could open revenue avenues, though R&D investments for such innovations are minimal relative to newer drugs.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Market
- Shift Toward Atypical Antipsychotics: Prescribing patterns favor drugs with fewer side effects, reducing perphenazine's market share.
- Cost-Sensitive Markets: Persistent demand in developing countries sustains its relevance.
- New Formulation Development: Limited pipeline activity focuses on enhancing safety or delivery, with little innovation specific to perphenazine.
- Generic Consolidation: Larger players dominating supply can influence pricing stability and distribution channels.
Conclusion and Outlook
Perphenazine's market dynamics are emblematic of a classic first-generation antipsychotic transitioning into a primarily generic-driven segment. Its financial trajectory is characterized by stable revenue in low-cost markets, offset by declines in premium segments favoring newer agents. The therapeutic landscape's evolution, driven by safety concerns and prescriber preferences, underscores a gradual decline in its global prominence.
Nonetheless, in regions with constrained healthcare budgets and established treatment protocols, perphenazine will likely sustain a niche market. Manufacturers focusing on cost efficiency and regional distribution channels will benefit from this persistent demand. Future growth may hinge on targeted formulations or strategic partnerships that optimize its clinical utility within specific niches.
Key Takeaways
- Market Position: Perphenazine remains relevant in low-resource settings due to cost advantages; its role in high-income markets diminishes.
- Revenue Outlook: Expect gradual decline in premium markets; stable or modest growth in emerging economies.
- Competitive Landscape: Intensified competition from second-generation antipsychotics influences prescriber preferences.
- Regulatory Environment: Safety concerns and quality standards shape ongoing market access; innovation is limited.
- Strategic Focus: Manufacturers should explore niche formulations and regional partnerships to sustain profitability.
FAQs
1. Why has the use of perphenazine declined in Western countries?
The adoption of second-generation antipsychotics with improved side effect profiles has led to decreased reliance on perphenazine, especially given concerns about extrapyramidal symptoms and metabolic effects associated with first-generation drugs.
2. In which markets does perphenazine still generate significant revenue?
Primarily in low- and middle-income countries like India, China, and parts of Africa, where affordability and existing clinical protocols sustain demand.
3. Are there ongoing innovations or reformulations of perphenazine?
Current efforts are minimal; most focus on generic manufacturing efficiency. Some exploratory research considers new delivery methods, but these are not commercially widespread.
4. How do regulatory challenges affect perphenazine’s market?
Regulatory agencies emphasize safety and quality. While no major restrictions exist, safety warnings influence prescriber confidence, impacting demand in certain regions.
5. What strategies can manufacturers employ to maintain profitability?
Leveraging regional distribution, optimizing cost efficiencies, and exploring niche formulations or combination therapies can help sustain revenues amidst declining global demand.
Sources:
[1] MarketWatch. "Global Antipsychotic Drugs Market."
[2] WHO. "Mental Health and Psychotropic Medication Use."
[3] IMS Health Reports. "Trends in Antipsychotic Prescriptions."
[4] Clinical Pharmacology. "Perphenazine: Pharmacology and Safety Profile."
[5] IQVIA. "Generic Drug Market Data."