Last updated: August 3, 2025
Introduction
Promethazine with codeine, a combination medication, plays a pivotal role within the analgesic and antitussive segments of the pharmaceutical landscape. Combining an antihistamine with an opioid, it provides relief from cough, cold symptoms, and allergy-associated conditions. Given its dual mechanism, it enjoys niche demand but faces complex market, regulatory, and societal pressures affecting its financial trajectory. This analysis examines the evolving market dynamics, regulatory environment, leading competitors, and future financial outlook for promethazine with codeine.
Pharmacological Profile and Market Position
Promethazine with codeine combines promethazine—a phenothiazine antihistamine—with codeine, an opioid analgesic. Its pharmacological synergy allows effective suppression of persistent coughs and allergy symptoms, especially in pediatric and adult respiratory conditions. Historically, such combination products have commanded significant market share in over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription medicine portfolios in North America, Europe, and emerging markets.
However, its status varies significantly across jurisdictions. In the U.S., for instance, it’s classified as a Schedule V controlled substance owing to the opioid component, affording tighter regulations and distribution controls. Conversely, in some other countries, it remains available OTC, augmenting its accessibility but raising safety concerns.
Market Dynamics Influencing Promethazine with Codeine
1. Regulatory and Legal Constraints
A major determinant of market pathways is the regulatory stance towards opioids. In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) classifies codeine-containing products as Schedule V, which limits prescriptions and increases surveillance—factors that dampen broader market penetration and impact profitability (reference [1]).
European regulatory bodies, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA), have adopted stricter controls over combination opioids, leading to decreased prescribing and availability (reference [2]). Recent movements in the face of the opioid epidemic spur further restrictions. For example, Canada’s reconsideration of codeine-containing medications, including reassessment of OTC status, influences supply chains and consumer access.
2. Societal and Public Health Considerations
The opioid crisis has redefined societal attitudes towards codeine-based drugs. Increased awareness of opioid dependence risks has led to partial bans, tighter prescribing guidelines, and public health campaigns aimed at reducing misuse. Consequently, sales volume has declined in many markets, and numerous initiatives promote alternative therapies, such as non-opioid cough suppressants.
In pediatrics, caution is even more pronounced. The FDA issued warnings against using promethazine with codeine in children under 12 due to respiratory risks, leading to significant declines in pediatric prescriptions and OTC sales (reference [3]).
3. Competitive Landscape and Alternative Therapies
The rise of non-opioid cough suppressants—such as dextromethorphan—has eroded the market share of promethazine with codeine. Moreover, the advent of modern antitussives, increased development of natural remedies, and digitized telemedicine solutions have altered consumer preferences.
Pharmaceutical companies are also shifting R&D focus towards non-addictive, targeted therapies for respiratory conditions, reducing pipeline investments in traditional opioid combinations.
4. Manufacturing and Supply Chain Factors
The controlled status of codeine impacts raw material sourcing, manufacturing licensing, and distribution logistics. Countries that tighten import/export controls or impose quotas effectively restrict supply, which influences pricing dynamics and profit margins. Cross-country variations in legality can lead to parallel markets, complicating revenue forecasts.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Outlook
1. Historical Revenue Trends
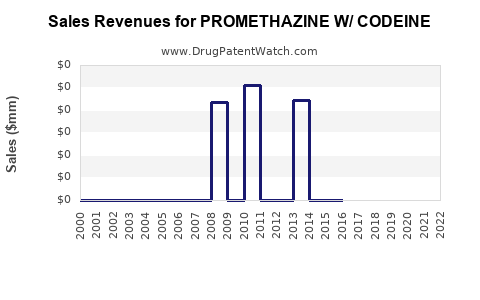
Historically, promethazine with codeine generated substantial revenues, especially during the 1990s and early 2000s when combination cough and cold remedies with opioids comprised a significant segment. In the U.S., peak sales reached into hundreds of millions USD annually (source [4]).
2. Recent Developments and Market Contraction
In line with regulatory tightening, recent years have seen a sharp decline. The FDA’s black box warning against pediatric use, combined with the 2017 rescheduling of codeine-containing drugs to Schedule V, curtailed both prescribed and OTC sales in North America. The global market has contracted by an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4-6% over the past five years (source [5]).
Adverse media coverage and legal actions also contributed to brand erosion. Manufacturers have divested or reformulated formulations, reducing the product's profitability. Major pharmaceutical firms have deprioritized investment, further constraining growth prospects.
3. Forecasted Market Recovery or Decline
Forecasts indicate a continued depressed trajectory unless new indications, formulations, or markets emerge. The global cough and cold market is projected to grow modestly CAGR 2-3%, but the share for opioid-based combinations like promethazine with codeine is expected to shrink further due to regulatory and societal pressures.
Emerging markets, such as parts of Asia and Africa, still show demand, but growth is tempered by regulatory evolution and increasing awareness of opioid misuse. The potential for reformulation into abuse-deterrent, non-opioid variants remains limited and uncertain.
Regulatory and Strategic Implications
The sector’s trajectory underscores a pivot towards stricter controls and safety measures, positioning promethazine with codeine as a declining asset class. Companies must strategize around reformulation, diversification, or withdrawal from markets where regulatory and societal risks outweigh benefits.
Innovative deployment of alternative therapeutics, including non-opioid antitussives with patent protections and new formulations, could offer limited respite but unlikely to offset the overall decline trend.
Conclusion
The financial trajectory of promethazine with codeine is characterized by declining revenues driven by regulatory limitations, societal aversion to opioids, and competition from newer, safer therapies. While the product historically enjoyed significant market share, prevailing legal and safety concerns signal a long-term contraction, especially in mature markets like North America.
Pharmaceutical firms operating in this space must prioritize compliance, innovate peacefully within regulatory confines, and consider diversification strategies to sustain profitability. The future of promethazine with codeine hinges on regulatory latitude, societal acceptance, and therapeutic advancements—factors that collectively pose formidable challenges to its growth and financial stability.
Key Takeaways
- Regulatory tightening and societal awareness of opioid risks have drastically limited the market for promethazine with codeine, especially in North America and Europe.
- Market revenues have declined sharply, with forecasts indicating continued contraction unless new formulations or indications emerge.
- Emerging markets still exhibit demand, but increasing restrictions and awareness suggest a gradual decline on a global scale.
- Industry shift towards non-opioid alternatives, abuse-deterrent formulations, and novel therapies diminishes long-term prospects.
- Strategic realignment focusing on reformulation, alternative therapies, or exit strategies becomes essential for companies invested in this product.
FAQs
1. Is promethazine with codeine still available OTC globally?
Availability varies by country. Some jurisdictions retain OTC status, particularly in developing markets, but many have moved to prescription-only due to safety concerns.
2. What are the primary regulatory challenges facing promethazine with codeine?
Stringent classification as a controlled substance (Schedule V in the U.S.), restrictions on pediatric use, and increased surveillance have significantly limited its clinical and OTC use.
3. Are there ongoing R&D efforts to reformulate promethazine with codeine?
Limited. Most efforts focus on developing non-opioid antitussives or abuse-deterrent formulations; reformulation of promethazine with codeine specifically is not a major focus currently.
4. How has society’s perception of opioids impacted the market for promethazine with codeine?
Heightened awareness and public health campaigns have led to decreased prescribing, heightened regulatory scrutiny, and overall market contraction for opioid-containing products.
5. Which markets hold the most promise for continued demand?
Developing regions with less regulatory enforcement and higher demand for cough suppressants may sustain some levels of sales, but overall growth prospects remain limited.
References
- DEA Scheduling of Controlled Substances
- European Medicines Agency Regulatory Updates (2022)
- FDA Pediatric Advisory Committee Meeting, 2017
- Pharmaceutical Market Data, IQVIA, 2020
- Global Cough and Cold Market Report, MarketsandMarkets, 2022