Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
ZIRGAN, the brand name for the oral solution of Zirgan (ganciclovir), is an antiviral medication primarily indicated for the treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections. Originally developed by Roche and now marketed under various generics, ZIRGAN’s market landscape is shaped by its therapeutic efficacy, competitive environment, regulatory landscapes, and emerging technological advances. This analysis dissects the fundamental market forces influencing ZIRGAN's future and projects its financial trajectory.
Pharmacological Profile and Therapeutic Use
Ganciclovir, the active compound in ZIRGAN, demonstrates potent activity against CMV, a pervasive herpesvirus responsible for retinitis in immunocompromised patients, notably those with AIDS or post-organ transplantation. The drug’s administration route, dosing regimen, and side effect profile significantly impact market acceptance. Oral formulations like ZIRGAN offer improved convenience compared to injectable options, thus expanding its potential patient base.
Market Dynamics
1. Growing Prevalence of CMV Infections
The global increase in immunocompromised populations, driven by aging demographics, HIV/AIDS prevalence, and organ transplantation rates, fuels demand for effective antivirals like ZIRGAN. According to the World Health Organization, HIV prevalence and the rising number of transplant procedures worldwide continue to augment the incidence rates of CMV infections, directly expanding ZIRGAN’s target market [1].
2. Competitive Landscape
ZIRGAN faces competition from other antiviral agents such as valganciclovir, cidofovir, foscarnet, and newer agents with improved safety profiles. Valganciclovir, with oral bioavailability, has become a leading competitor due to convenience and similar efficacy, impacting ZIRGAN’s market share. Additionally, the emergence of generic versions has increased price competition, affecting profit margins.
3. Patent Expiration and Generic Competition
Patent protections historically shielded ZIRGAN from generics, but patent expirations are imminent or have already occurred in numerous jurisdictions. This transition typically results in substantial price reductions and market share redistribution towards generics, pressuring revenues for branded formulations.
4. Regulatory and Reimbursement Policies
Stringent regulatory environments influence market dynamics. Approval of generic versions in key markets (U.S., EU, China) enhances accessibility but diminishes profitability potential for the original manufacturer. Reimbursement decisions also impact prescribing patterns, with payers favoring cost-effective generics.
5. Technological Innovations and Alternative Therapies
Advancements in antiviral drug development, including targeted therapies and gene editing techniques, threaten immunochemotherapy and traditional antivirals' dominance. Moreover, innovations in drug delivery, such as inhaled or sustained-release formulations, may alter traditional oral treatment paradigms, influencing ZIRGAN’s market positioning.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
1. Revenue Projections
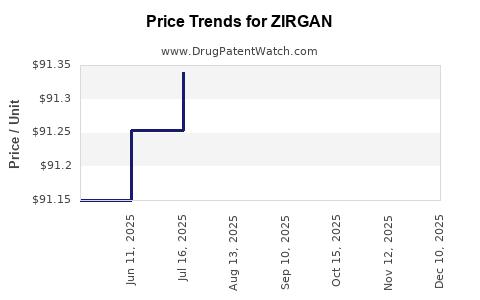
The revenue outlook for ZIRGAN hinges on several factors, including the pace of generic integration, regional market expansion, and clinical adoption. Pre-patent expiration, revenues typically decline sharply due to price erosion. For ZIRGAN, if the patent expires within the next 2-3 years, companies forecast initial revenue drops of 30-50%, with stabilization at lower levels.
In regions with high HIV/AIDS prevalence, such as sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia, demand remains buoyant, providing buffer revenues. Additionally, the rising incidence of organ transplants globally sustains demand in developed markets.
2. Profitability Considerations
Gross margins for ZIRGAN historically depended on brand premiums and pricing strategies. Post-generic entry, cost-cutting measures, and increased competition diminish profitability. Manufacturers may pivot to niche indications or develop combination therapies to sustain margins.
3. R&D and Pipeline Development
Investment in R&D to develop next-generation antivirals or improved formulations can reshape financial trajectories. Companies that innovate beyond existing molecules can maintain competitive advantages, creating new revenue streams and extending lifecycle potential.
4. Market Expansion Opportunities
Emerging markets present significant growth opportunities due to expanding healthcare infrastructure and rising disease burden. Strategic partnerships with regional distributors and local regulatory approvals could catalyze revenue growth.
5. Impact of External Factors
Global economic stability, healthcare policy reforms, and drug pricing regulations influence ZIRGAN's financial outlook. For instance, policies favoring biosimilars and generics reduce the cost burden, impacting premium-priced branded drugs' revenues.
Market Challenges and Strategic Responses
Challenges:
- Patent expiration and generic competition
- Evolving treatment guidelines favoring newer therapies
- Price pressures from healthcare payers
- Potential adverse regulatory changes
Strategies:
- Diversify pipeline to include combination antivirals
- Focus on targeted indications to justify premium pricing
- Invest in technological innovations to enhance delivery and adherence
- Expand into underserved markets with high CMV burden
Future Outlook and Investment Implications
While the immediate future post-patent expiry poses revenue challenges, strategic innovation and market expansion can stabilize or boost ZIRGAN’s financial performance. The transition aligns with typical pharmaceutical lifecycle curves and underscores the need for proactive market planning.
Investment decisions around ZIRGAN should consider patent timelines, regional market expansion potential, and pipeline robustness to mitigate downside risks while capitalizing on persistent unmet medical needs in immunocompromised populations.
Key Takeaways
- The demand for ZIRGAN is primarily driven by the rising prevalence of CMV infections among immunocompromised populations.
- Patent expirations and generic competition significantly pressure revenues, necessitating strategic adaptation.
- Emerging markets and expanding indications offer growth opportunities, though regulatory and reimbursement hurdles remain.
- Innovation in drug delivery, combination therapies, and pipeline development are critical to sustaining financial performance.
- Long-term success depends on proactive stakeholder engagement, pipeline diversification, and market expansion strategies.
FAQs
1. When will ZIRGAN’s patent protections expire, and how will it impact its market?
Patent expirations are anticipated within 2-3 years in major markets like the U.S. and EU. This will lead to increased generic competition and a significant reduction in revenue margins.
2. How does ZIRGAN compare to other antivirals in terms of efficacy and safety?
ZIRGAN offers effective CMV suppression, especially in immunocompromised patients. However, its safety profile includes potential bone marrow suppression and renal toxicity, comparable to other ganciclovir formulations.
3. Are there newer therapies that threaten ZIRGAN's market share?
Yes. Newer agents with improved safety and dosing profiles, such as maribavir, are emerging, potentially replacing ZIRGAN in certain indications.
4. What strategies can pharmaceutical companies employ post-patent expiration?
Companies can develop novel formulations, seek new indications, invest in pipeline innovation, and expand into emerging markets to offset revenue losses.
5. What are the key factors influencing ZIRGAN’s growth in emerging markets?
Factors include disease prevalence, healthcare infrastructure, regulatory approval pathways, pricing strategies, and local reimbursement policies.
References
[1] World Health Organization. (2022). Global HIV/AIDS data.
[2] Market research reports on antiviral drugs.
[3] Patent databases and expiration timelines.
[4] Regulatory agency guidance documents on antiviral approvals.
[5] Scientific literature on ganciclovir and CMV treatment.
Note: This analysis synthesizes current trends and projections based on publicly available data as of 2023. Future market performance is subject to regulatory, technological, and epidemiological variability.