XTORO Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
When do Xtoro patents expire, and what generic alternatives are available?
Xtoro is a drug marketed by Fonseca Biosciences and is included in one NDA. There are four patents protecting this drug.
This drug has forty-two patent family members in eighteen countries.
The generic ingredient in XTORO is finafloxacin. Additional details are available on the finafloxacin profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Generic Entry Outlook for Xtoro
Xtoro was eligible for patent challenges on December 17, 2018.
By analyzing the patents and regulatory protections it appears that the earliest date
for generic entry will be July 2, 2030. This may change due to patent challenges or generic licensing.
Indicators of Generic Entry
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for XTORO?
- What are the global sales for XTORO?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for XTORO?
Summary for XTORO
| International Patents: | 42 |
| US Patents: | 4 |
| Applicants: | 1 |
| NDAs: | 1 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 44 |
| DailyMed Link: | XTORO at DailyMed |
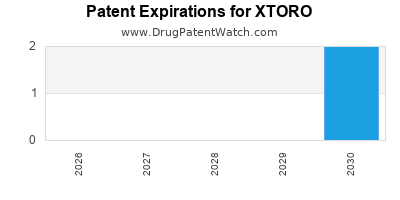
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Loss of Exclusivity (LOE) Date for XTORO
Generic Entry Date for XTORO*:
Constraining patent/regulatory exclusivity:
NDA:
Dosage:
SUSPENSION/DROPS;OTIC |
*The generic entry opportunity date is the latter of the last compound-claiming patent and the last regulatory exclusivity protection. Many factors can influence early or later generic entry. This date is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source.
US Patents and Regulatory Information for XTORO
XTORO is protected by four US patents.
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the earliest date for a generic version of XTORO is ⤷ Get Started Free.
This potential generic entry date is based on patent ⤷ Get Started Free.
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fonseca Biosciences | XTORO | finafloxacin | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OTIC | 206307-001 | Dec 17, 2014 | DISCN | Yes | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| Fonseca Biosciences | XTORO | finafloxacin | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OTIC | 206307-001 | Dec 17, 2014 | DISCN | Yes | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Fonseca Biosciences | XTORO | finafloxacin | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OTIC | 206307-001 | Dec 17, 2014 | DISCN | Yes | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Fonseca Biosciences | XTORO | finafloxacin | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OTIC | 206307-001 | Dec 17, 2014 | DISCN | Yes | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
Expired US Patents for XTORO
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | Patent No. | Patent Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fonseca Biosciences | XTORO | finafloxacin | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OTIC | 206307-001 | Dec 17, 2014 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Fonseca Biosciences | XTORO | finafloxacin | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OTIC | 206307-001 | Dec 17, 2014 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration |
International Patents for XTORO
When does loss-of-exclusivity occur for XTORO?
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the following patents block generic entry in the countries listed below:
Argentina
Patent: 7372
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y METODOS PARA TRATAR INFECCIONES OFTALMICAS OTICAS O NASALES
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Australia
Patent: 10266120
Patent: Compositions comprising finafloxacin and methods for treating ophthalmic, otic, or nasal infections
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Brazil
Patent: 1016257
Patent: composições compreendendo finafloxacino e métodos para tratar infecções oftálmicas, ópticas ou nasais
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Canada
Patent: 65852
Patent: COMPOSITIONS COMPRENANT DE LA FINAFLOXACINE ET METHODES DE TRAITEMENT D'INFECTIONS OPHTALMIQUES, OTIQUES OU NASALES (COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING FINAFLOXACIN AND METHODS FOR TREATING OPHTHALMIC, OTIC, OR NASAL INFECTIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Chile
Patent: 11003327
Patent: Composicion farmaceutica que comprende finafloxacina y un agente antiinflamatorio; uso en el tratamiento de infecciones oftalmicas, oticas o nasales.
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
China
Patent: 2470139
Patent: Compositions comprising finafloxacin and methods for treating ophthalmic, otic, or nasal infections
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 5687111
Patent: 用于治疗眼、耳或鼻感染的包含非那沙星的组合物和方法 (Compositions and methods for treating ophthalmic, otic, or nasal infections)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
European Patent Office
Patent: 48587
Patent: COMPOSITIONS COMPRENANT DE LA FINAFLOXACINE ET MÉTHODES DE TRAITEMENT D'INFECTIONS OPHTALMIQUES, OTIQUES OU NASALES (COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING FINAFLOXACIN AND METHODS FOR TREATING OPHTHALMIC, OTIC, OR NASAL INFECTIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Japan
Patent: 84012
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 12532115
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 15134827
Patent: 眼、耳または鼻の感染症を処置するためのフィナフロキサシンを含む組成物および方法 (COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING FINAFLOXACIN AND METHODS FOR TREATING OPHTHALMIC, OTIC, OR NASAL INFECTIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Mexico
Patent: 12000136
Patent: COMPOSICIONES QUE COMPRENDEN FINAFLOXACINA Y METODOS PARA TRATAR INFECCIONES OFTALMICAS, OTICAS, O NASALES. (COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING FINAFLOXACIN AND METHODS FOR TREATING OPHTHALMIC, OTIC, OR NASAL INFECTIONS.)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Russian Federation
Patent: 70731
Patent: КОМПОЗИЦИИ, ВКЛЮЧАЮЩИЕ ФИНАФЛОКСАЦИИ, И СПОСОБЫ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ ОФТАЛЬМОЛОГИЧЕСКИХ, УШНЫХ ИЛИ НАЗАЛЬНЫХ ИНФЕКЦИЙ (FINAFLOXACIN-INCLUDING COMPOSITIONS, AND METHODS OF TREATING OPHTHALMOLOGICAL, AURAL AND NASAL INFECTIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 12103458
Patent: КОМПОЗИЦИИ, ВКЛЮЧАЮЩИЕ ФИНАФЛОКСАЦИИ, И СПОСОБЫ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ ОФТАЛЬМОЛОГИЧЕСКИХ, УШНЫХ ИЛИ НАЗАЛЬНЫХ ИНФЕКЦИЙ
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Africa
Patent: 1109492
Patent: COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING FINAFLOXACIN AND METHODS FOR TREATING OPHTHALMIC,OTIC,OR NASAL INFECTIONS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Korea
Patent: 1541823
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 120114211
Patent: COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING OPHTHALMIC, OTIC, OR NASAL INFECTIONS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Spain
Patent: 94775
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Taiwan
Patent: 60181
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1102395
Patent: Compositions and methods for treating ophthalmic, otic, or nasal infections
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Uruguay
Patent: 758
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y MÉTODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE INFECCIONES ÓPTICAS, NASALES U OFTÁLMICAS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
See the table below for additional patents covering XTORO around the world.
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 104869999 | Finafloxacin suspension compositions | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| South Korea | 20150090045 | 피나플록사신 현탁 조성물 (FINAFLOXACIN SUSPENSION COMPOSITIONS) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| European Patent Office | 0946176 | UTILISATION DE DERIVES D'ACIDE 7-(2-OXY-5,8-DIAZABICYCLO 4.3.0]NON-8-YL)QUINOLEONE ET NAPHTYRIDONECARBOXYLIQUE POUR L'OBTENTION D'UN MEDICAMENT DESTINE AU TRAITEMENT D'INFECTIONS PAR HELICOBACTER PYLORI ET DES MALADIES GASTRO-DUODENALES QUI Y SONT ASSOCIEES (THE USE OF 7-(2-OXA-5,8-DIAZABICYCLO 4.3.0]NON-8-YL)-QUINOLONE CARBOXYLIC ACID AND NAPHTHYRIDON CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES FOR MANUFACTURE OF A MEDICAMENT FOR THE TREATMENT OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTIONS AND ASSOCIATED GASTRODUODENAL DISEASES) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Slovakia | 14962000 | Použitie derivátov 7-(2-oxa-5,8-diazabicyklo[4.3.0] non-8-yl)- chinolónkarboxylovej a -naftyridónkarboxylovej kyseliny na výrobu liečiv na terapiu infekcií spôsobených Helicobacter pylori a ním asociovaných gastroduodenálnych ochorení a zlúčenina tohto typu (The use of 7-(2-oxa-5,8-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-8-yl)-quinolone carboxylic acid and naphthyridon carboxylic acid derivatives for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infections and associated gastroduodenal diseases) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for the Pharmaceutical Drug: XTORO
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
