Last updated: August 1, 2025
Introduction
VISTARIL (hydroxyzine) stands as a longstanding antihistamine with dual utility in allergy relief and anxiolytic applications. Originally developed in the mid-20th century, VISTARIL has maintained relevance in clinical practice, though its market dynamics and financial trajectories are undergoing significant shifts owing to evolving regulatory landscapes, generational therapeutic preferences, and emerging competition. This analysis delineates the current and future market environment for VISTARIL, assessing factors influencing its commercial performance, and offering insights for stakeholders.
Historical and Regulatory Overview
VISTARIL, known generically as hydroxyzine, was first approved by the FDA in 1956. It functions as a first-generation antihistamine—crossing the blood-brain barrier to exert sedative effects—making it suitable for allergy management, preoperative sedation, and anxiety relief. Despite its long history, the patent for hydroxyzine expired decades ago, leaving multiple generic competitors in the U.S. and international markets. Consequently, market pricing pressures and commoditization influence its revenue streams.
Regulatory norms have evolved with increased emphasis on safety profiles; hydroxyzine's sedative properties and potential central nervous system (CNS) side effects have prompted scrutiny, especially regarding off-label use. Nonetheless, approval for specific indications remains intact, and off-label prescribing sustains demand.
Market Dynamics
1. Competitive Landscape
The hydroxyzine market is saturated with generics, prompting intense price competition. Key competitors include generic versions from major pharmaceutical manufacturers such as Teva Pharmaceuticals, Mylan, and Sandoz. The available alternatives—antihistamines like diphenhydramine, loratadine, and cetirizine—offer similar efficacy with improved safety profiles and fewer sedative effects, leading to passive market erosion.
2. Therapeutic Shift and Prescribing Trends
Modern therapeutics favor second-generation antihistamines for allergy management due to their minimal sedative properties. This shift has scaled back VISTARIL's role primarily to niche indications and cases where control of anxiety and sedation are prioritized. Notably, the use of hydroxyzine for anxiety has persisted in hospital and psychiatric settings, particularly in the U.S.
3. Regulatory and Reimbursement Factors
Healthcare payers and regulatory bodies increasingly favor drugs with favorable safety profiles and economic value. The cost-effectiveness of second-generation antihistamines diminishes the relative attractiveness of hydroxyzine, especially as newer, less sedating drugs gain market share. Reimbursement policies further influence prescribing habits, often favoring established, cost-effective generics but with a growing preference for newer agents with better safety profiles.
4. Impact of Off-Label Use and Customer Demographics
Despite declining mainstream usage, hydroxyzine remains prescribed off-label for insomnia, anxiety, and pruritus. Such off-label applications sustain some revenue streams, largely in inpatient and specialty care settings. The aging population with increased comorbidities and medication needs may sustain demand, although the overall volume is limited compared to historical levels.
5. Emerging Market Opportunities
Expanding into emerging markets presents potential growth avenues due to limited access to newer, often costlier antihistamines. Countries with less stringent regulatory environments and high prevalence of allergy and anxiety disorders could represent underserved niches for hydroxyzine.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
1. Revenue Trends
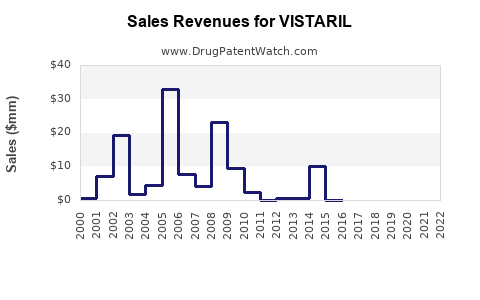
Industry reports indicate that VISTARIL’s revenues have experienced a consistent decline over the past decade. U.S. prescriptions for hydroxyzine have decreased approximately 15-20% annually, driven by competitive pressures and changing clinical guidelines. The expiration of patent protections globally contributed to a price erosion of 30-40%, translating directly into revenue declines.
2. Profitability and Cost Dynamics
The commoditized nature of hydroxyzine generics results in narrow profit margins. Manufacturers’ manufacturing costs have declined due to automation and global supply chains; however, intense price competition caps profit potential. Marginal gains are likely limited unless patent protection or formulation innovations introduce differentiation.
3. Investment Trends and R&D Outlook
In light of diminishing revenue prospects, most companies have deprioritized R&D investments in hydroxyzine. Research efforts focus instead on novel therapeutics with distinct mechanisms of action. This shift suggests limited potential for pipeline innovations, constraining future financial upside.
4. Market Exit and Consolidation
Market analyses indicate a trend toward consolidation among manufacturers of hydroxyzine and similar generics, with smaller players exiting due to marginal returns. Larger pharmaceutical firms may diversify their portfolios or focus on proprietary formulations with patent lock-in to sustain profitability.
Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations
Given current market dynamics, the financial trajectory for VISTARIL appears subdued in mature markets. However, niche applications and emerging markets could mitigate some decline. Strategic opportunities include:
- Formulation Differentiation: Developing sustained-release formulations or combination products to capture niche segments.
- Regulatory Expansion: Seeking approval for additional indications or optimizing existing labeling in emerging markets.
- Market Penetration: Targeting regions with limited access to newer therapies, emphasizing cost advantages.
- Partnership and Licensing: Engaging in licensing agreements or partnerships for formulations with improved safety profiles, aiming to extend lifecycle value.
Key Takeaways
- Market Saturation and Competition: The global hydroxyzine market is highly commoditized with significant price competition, pressuring revenue streams.
- Therapeutic Shift: Preference for second-generation antihistamines and safety concerns reduce hydroxyzine's overarching market share.
- Niche and Off-Label Prescribing: Demand derived from specific niche uses and off-label indications sustain minimal revenue levels, especially in specialized care settings.
- Emerging Market Potential: Untapped emerging markets present growth opportunities, contingent upon regulatory, economic, and clinical factors.
- Limited R&D Investment: Innovation efforts are minimal, with most manufacturers focusing on cost control and market retention strategies.
FAQs
Q1: What is the primary driver of declining revenues for VISTARIL?
A: The main factors are the expiration of patent protections, the proliferation of cheaper generics, and the shift towards newer antihistamines with better safety profiles reducing demand.
Q2: Can VISTARIL regain market share through formulation innovation?
A: While possible, the high costs and limited success of such strategies in saturated markets mean only incremental gains are likely. Formulation differentiation may help niche applications but is unlikely to reverse overall declines.
Q3: What role do emerging markets play in VISTARIL’s future?
A: Emerging markets offer growth potential due to lower competition and high unmet therapeutic needs; however, success depends on regulatory approval and local prescribing practices.
Q4: Are there regulatory hurdles for expanding VISTARIL’s indications?
A: Yes, any new indication requires rigorous clinical trials and approval processes, though historically, hydroxyzine’s safety profile accelerates certain regulatory pathways.
Q5: How does the off-label use of hydroxyzine impact its market?
A: Off-label prescribing helps sustain demand in specific niches, particularly in inpatient settings, but it does not significantly influence overall market growth.
Sources:
[1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Hydroxyzine product label.
[2] IQVIA. National prescription data for antihistamines, 2012-2022.
[3] MarketResearch.com. Global antihistamine market analysis, 2022.
[4] Pharma Intelligence. Patent expirations and generic competition analysis, 2023.
[5] CDC. Trends in allergy medication prescribing patterns, 2015–2022.