Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Trimethoprim, a broad-spectrum antifolate antibiotic primarily used to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), remains a critical player in the antimicrobial landscape. Since its inception in the 1960s, trimethoprim's market trajectory has been shaped by evolving antimicrobial resistance, regulatory considerations, and competitive dynamics. This analysis explores the current market environment, key drivers, emerging challenges, and forecasted financial outlooks for trimethoprim, with a focus on strategic implications for industry stakeholders.
Market Overview and Evolution
Trimethoprim was first introduced in the early 1960s, marketed as a standalone treatment and later in combination formulations—most notably with sulfamethoxazole as co-trimoxazole (e.g., Bactrim, Septra)—to combat resistant bacterial strains and improve efficacy. Its mechanism, inhibiting bacterial dihydrofolate reductase, underpins its broad-spectrum activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens.
Over decades, the drug's utilization has experienced fluctuations. Initially favored due to its potency and oral administration advantages, trimethoprim's standing has been challenged by rising antimicrobial resistance (AMR), regulatory shifts favoring stewardship programs, and the advent of newer, targeted antibiotics.
Despite these challenges, trimethoprim remains on essential medicines lists worldwide, especially in resource-constrained settings where alternative therapies may be less accessible or affordable.
Current Market Dynamics
Demand Drivers
-
Prevalence of UTIs: UTIs are among the most common bacterial infections globally, with an estimated 150 million cases annually [1]. Trimethoprim's efficacy, oral route, and cost-effectiveness sustain its demand as a first-line agent, particularly in outpatient settings.
-
Antimicrobial Stewardship: Increasing emphasis on stewardship programs has led to a preference for narrow-spectrum agents like trimethoprim in uncomplicated UTIs, reducing unnecessary broad-spectrum antibiotic use and curtailing resistance development.
-
Global Health Policies: Many health authorities, including WHO, endorse trimethoprim as part of standardized antibiotics in primary care, bolstering demand.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Dynamics
-
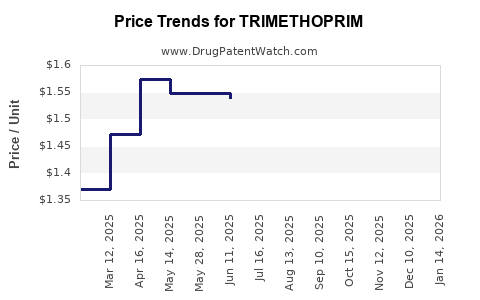
Generic Market Dominance: The patent expiry of brand-name formulations in many regions has prompted a surge in generic manufacturers, reducing prices and increasing supply efficiency.
-
Manufacturing Concerns: Quality control and regulatory hurdles, especially in low-income regions, influence supply consistency. Regulatory authorities' tightening standards have prompted manufacturers to upgrade compliant facilities, impacting production costs.
Pricing and Reimbursement Landscape
-
Cost Sensitivity: In developing markets, trimethoprim remains a low-cost antibiotic, supported by governmental procurement programs.
-
Reimbursement Policies: In some developed markets, reimbursement policies favor combination products or newer antibiotics, constraining fiscal support for standalone trimethoprim formulations.
Resistance and Prescribing Trends
-
Rising Resistance: Increased resistance, particularly via plasmid-mediated mechanisms, diminishes clinical efficacy, prompting shifts toward alternative therapies [2].
-
Prescribing Practices: Clinicians are increasingly cautious, balancing efficacy against resistance concerns, which influences volume and formulation choices.
Regulatory Environment
-
Approval and Reclassification: Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA have maintained ongoing evaluations, with some regions reclassifying trimethoprim due to resistance patterns or safety concerns related to folate deficiency.
-
Combination Approvals: Regulatory approval of combination formulations (e.g., with pyrimethamine) varies, influencing market choices.
Emerging Challenges and Opportunities
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
AMR remains the foremost threat to trimethoprim's market viability. Resistance rates vary geographically, with some regions experiencing resistance levels exceeding 20-30%, especially in parts of Asia and Africa [3].
Innovative stewardship efforts and molecular surveillance can prolong trimethoprim's utility, especially with tailored prescribing protocols.
Development of Formulations and Derivatives
-
Combination Products: Continued development of improved combinations aiming to mitigate resistance and augment efficacy may enhance the drug's attractiveness.
-
New Derivatives: Research into next-generation dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors could reframe therapeutic options, though market entry hurdles and high R&D costs pose risks.
Generic Competition and Pricing Strategies
Generic manufacturers benefit from entrenched market positions but face pressure to reduce prices amid global competition. Strategic alliances and optimized manufacturing can sustain margins.
Market Expansion in Low-Income Countries
Regionally prioritized initiatives for essential medicines could expand trimethoprim's access, underpinning growth in emerging markets.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Addressing safety profiles—particularly concerning folate deficiency, hematological adverse effects, and contraindications—remains vital for maintaining regulatory compliance and prescriber confidence.
Financial Trajectory and forecasts (2023–2030)
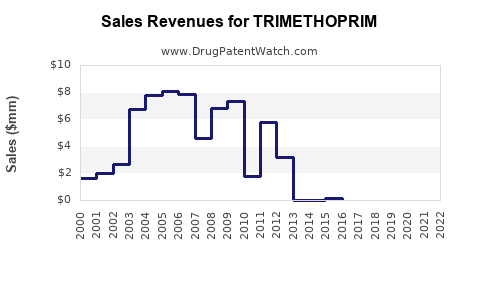
The global trimethoprim market is projected to experience modest growth, driven predominantly by demand in developing regions. A compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 2-4% is anticipated over the next decade, contingent on resistance trends and regulatory interventions [4].
Key factors influencing this trajectory include:
-
Demand stability in resource-limited settings: Further integration into essential medicine lists and national drug formularies.
-
Resistance-driven demand fluctuations: Potential declines where resistance becomes widespread; conversely, increases where resistance management strategies succeed.
-
Introduction of improved formulations: Such as combination therapies with lower resistance propensity, to recapture clinical efficacy.
-
Impact of newer antibiotics: As newer agents gain market share, trimethoprim’s relative market share may decrease unless repositioned within treatment guidelines.
Strategic Implications for Industry Stakeholders
-
Investment in Resistance Surveillance: Real-time resistance data collection enables adaptive prescribing and market positioning.
-
Product Development: Focused R&D on formulations that mitigate resistance and improve safety could rejuvenate market relevance.
-
Market Diversification: Expansion into underserved regions with tailored cost-effective formulations can sustain volume growth.
-
Regulatory Engagement: Active collaboration with authorities to streamline approvals of new combinations or formulations responsive to resistance patterns.
Key Takeaways
-
The global market for trimethoprim is characterized by steady demand driven by its role in UTIs and essential medicine status, despite rising resistance challenges.
-
Generic manufacturing and strategic alliances are central to maintaining competitive pricing and supply stability.
-
Resistance evolution notably influences prescribing trends and formulary inclusion, necessitating rigorous stewardship and surveillance.
-
Growth prospects hinge on technological innovation, regional expansion, and effective resistance management, with a forecasted CAGR of 2-4% through 2030.
-
Industry players should prioritize R&D for advanced formulations, foster partnerships with health authorities, and invest in global access initiatives.
FAQs
1. How is antimicrobial resistance affecting trimethoprim's market?
Rising resistance rates, particularly in developing regions, are diminishing clinical efficacy, leading to decreased prescribing and prompting the development of new formulations and stewardship efforts to preserve its utility.
2. What role do generics play in the trimethoprim market?
Generics dominate the market post patent expiry, providing cost-effective options that support global accessibility and supply sustainability. Pricing competition among generics influences profit margins but enhances affordability.
3. Are there upcoming formulations or combinations that could extend trimethoprim's market lifespan?
Yes, ongoing research focuses on combination antibiotics combining trimethoprim with agents that combat resistance mechanisms, potentially restoring efficacy and expanding indications.
4. Which regions present the most growth opportunities for trimethoprim?
Emerging markets in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, where essential medicines are prioritized and healthcare infrastructure is expanding, offer significant growth potential.
5. How do regulatory policies influence the future of trimethoprim?
Regulatory agencies impact market access through approval processes, safety requirements, and resistance management strategies, all of which can accelerate or hinder product development and dissemination.
Sources
[1] Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership (GARP). "Antibiotic Use and Resistance in Urinary Tract Infections." 2020.
[2] World Health Organization. "Antibacterial agents in clinical development: an analysis of the antibacterial pipeline." 2022.
[3] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. "Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States," 2019.
[4] Market Research Future. "Global Trimethoprim Market Analysis." 2022.