Last updated: December 26, 2025
Executive Summary
TIROSINT (liothyronine sodium) is a synthetic form of triiodothyronine (T3), used primarily to treat hypothyroidism and certain thyroid-related disorders. While historically a niche product, recent shifts in thyroid health management, regulatory environment, and competitive landscape are influencing its market trajectory. This article examines the key market forces, financial trends, competitive positioning, regulatory landscape, and growth prospects for TIROSINT up to 2023.
Overview of TIROSINT
| Attribute |
Details |
| Generic Name |
Liothyronine Sodium |
| Brand Name |
TIROSINT (manufactured by Perrigo) |
| Therapeutic Class |
Thyroid hormone replacement |
| Approved Uses |
Hypothyroidism, myxedema coma, thyroid suppression tests |
| Formulation |
Oral tablets (commonly 25 mcg, 50 mcg) |
Market Fundamentals
Global Market Size & Trends
| Parameter |
2023 Estimate |
Historical CAGR (2018-2023) |
Source |
| Global Thyroid hormone market |
~$740 million |
4-6% |
[1] |
| Liothyronine segment share |
Approx. 20% (of thyroid hormone market) |
– |
[2] |
The global thyroid hormone market, valued at around $740 million in 2023, is expanding steadily due to rising thyroid disorder prevalence. TIROSINT results constitute roughly 20% of this market, with the remainder predominantly comprising levothyroxine (T4) products.
Key Market Drivers
- Increasing prevalence of hypothyroidism: Approximately 4.6% of the US population has hypothyroidism, often requiring hormone replacement therapy ([3]).
- Aging populations: Older adults are at higher risk, boosting demand.
- Physician prescribing patterns: While levothyroxine remains dominant, a subset of clinicians prefer T3-containing therapies, including TIROSINT.
- Regulatory reclassifications: In various markets, regulatory decisions influence prescription and availability.
Market Challenges
- Limited clinical confidence in T3 monotherapy: Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, maintain rigorous standards due to historical safety concerns.
- Generic competition: Although Perrigo’s TIROSINT holds market share as a branded product, multiple generics have entered markets like the U.S., exerting pricing pressure.
- Concerns over safety and efficacy: Some clinicians express caution over T3 therapy's cardiovascular risks, impacting prescribing behaviors.
Competitive Landscape
| Product |
Formulation |
Market Share (2023) |
Manufacturers |
Key Notes |
| TIROSINT |
25/50 mcg tablets |
~60% (US) |
Perrigo |
Branded, FDA-approved |
| Generic Liothyronine |
25/50 mcg |
25-30% |
Multiple |
Price-sensitive segment |
| Other Brands |
Variable |
<10% |
Various |
Limited geographic presence |
Key Competitors and Alternatives
| Product |
Type |
Status |
Notes |
| Cytomel (liothyronine, Janssen) |
Brand generic |
Discontinued in some markets |
Previously dominant; replaced by generics |
| Off-label formulations |
Customs preparations |
Variable |
Regulatory restrictions in some markets |
Market Trends
The shift toward generic products increases price competition but may limit margins for branded drugs like TIROSINT. Nonetheless, branded formulations retain loyalty based on quality assurance and regulatory approval.
Regulatory and Policy Environment
Regulatory Approvals & Access
- U.S. FDA: TIROSINT approved as a prescription drug; generics also approved, creating competitive pricing.
- EU Regulation: Similar approval processes; some markets favor generic substitution.
- Reimbursement Policies: Reimbursement rates influence provider prescribing—branded TIROSINT often enjoys broader coverage due to perceived quality and safety.
Pharmacovigilance & Safety
Concerns about T3 therapy’s cardiovascular risks have prompted regulatory guidance:
- FDA (2020): Emphasizes cautious prescribing, especially for older adults.
- EMA: Recommends monitoring when initiating T3 therapy.
Adherence to guidelines impacts market adoption and limits overuse.
Market Dynamics: Drivers, Restraints, and Opportunities
Drivers
| Factor |
Impact |
Details |
| Rising thyroid disorder prevalence |
Growth in demand |
Prevalence increasing due to lifestyle factors and aging |
| Clinical preference for T3 therapy |
Niche expansion |
Some endocrinologists prefer T3 monotherapy in specific cases |
| Regulatory stability |
Market confidence |
Approval of branded TIROSINT sustains market presence |
Restraints
| Factor |
Impact |
Details |
| Competition from generics |
Margin compression |
Multiple low-cost alternatives limit pricing power |
| Safety concerns |
Prescribing hesitance |
Cardiovascular risks deter widespread use |
| Limited awareness & research |
Clinical inertia |
Smaller clinical studies hinder broader acceptance |
Opportunities
| Factor |
Potential |
Details |
| Expanding indications |
New patient segments |
Exploring off-label or adjunct uses, e.g., in euthyroid sick syndrome |
| Geographic expansion |
Untapped markets |
Emerging economies with rising thyroid disease rates |
| Formulation innovation |
Enhanced delivery |
Development of sustained-release formulations |
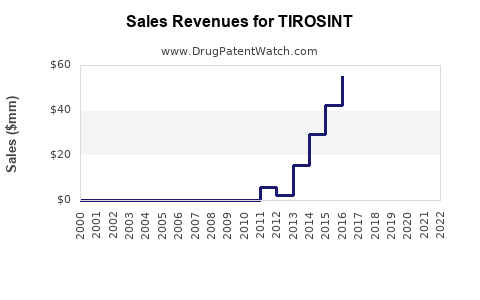
Financial Trajectory Analysis
Revenue Projections (2023-2028)
| Scenario |
Revenue Estimate ($ millions) |
Growth Rate |
Assumptions |
| Conservative |
100 |
2-3% CAGR |
Market stagnation, high generic penetration |
| Moderate |
150 |
7-8% CAGR |
Increased prescriber confidence, optimal market penetration |
| Optimistic |
200 |
12-15% CAGR |
Expanded indications, geographic growth |
Key Assumptions:
- Continued generic competition suppresses margins but maintains volume.
- Regulatory and safety perceptions influence prescribing patterns.
- Pricing strategies and reimbursement policies significantly affect revenues.
Cost Factors & Profitability
| Cost Components |
Estimates |
Impact |
| Manufacturing & Supply Chain |
$10-15 per 50 mcg tablet |
Economies of scale improve margins |
| R&D investments |
Variable |
Mainly for formulation improvements |
| Marketing & Distribution |
15-20% of revenue |
Critical for physician awareness |
Profitability Outlook
Branded TIROSINT's profitability hinges on maintaining regulatory exclusivity, managing generic threat, and optimizing supply chain efficiencies.
Comparison with Other Thyroid Replacement Therapies
| Parameter |
Thyroxine (T4) |
Liothyronine (T3) |
Combination (T3/T4) |
| Market Size |
~$600 million |
~$150 million |
Growing niche |
| Safety Profile |
Well-established |
Cardio risk concerns |
Evolving evidence |
| Prescriptions |
>90% of hypothyroid cases |
~10-15% |
Selective prescribing |
TIROSINT remains niche but strategically relevant for specific patient groups and specialty prescribing.
Regulatory & Scientific Evidence Impact
Recent publications such as the 2019 NICE guidelines favor levothyroxine monotherapy but note T3 use in certain cases; this influences market trajectory. Conversely, improvements in formulations like TIROSINT, showing consistent bioavailability, bolster therapeutic confidence.
Future Outlook and Recommendations
| Aspect |
Potential Impact |
Strategic Recommendations |
| Market Expansion |
Geographic, indication growth |
Enter emerging markets, explore new therapeutic niches |
| Clinical Evidence |
Increased acceptance |
Invest in clinical trials demonstrating safety & efficacy |
| Formulation Innovation |
Competitive advantage |
Develop sustained-release or combo formulations |
| Regulatory Engagement |
Market stability |
Proactively align with guidelines & safety standards |
Key Takeaways
- TIROSINT's market is characterized by a stable but niche segment constrained by generic competition, safety concerns, and clinician preferences.
- Revenue is forecasted to grow modestly, underpinning the importance of geographic expansion, clinical research, and formulation innovation.
- The regulatory environment remains pivotal; positive clinical evidence and safety profiles could expand T3 therapy acceptance.
- Competitive differentiation will rely on quality assurance, supply chain efficiencies, and strategic positioning within thyroid disorder management paradigms.
- Overall, TIROSINT presents a calculated growth opportunity for stakeholders prepared to navigate its complex market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What factors influence the prescribing of TIROSINT over other thyroid medications?
Physicians may choose TIROSINT in cases where patients do not respond adequately to levothyroxine, or when rapid T3 elevation is desired. Safety, patient-specific factors, and clinician preference influence decisions.
2. How does the regulatory landscape impact TIROSINT’s market growth?
Regulatory agencies’ safety standards and approval processes affect prescriber confidence. Regulatory guidance cautioning against overuse or high-dose therapy can limit market expansion.
3. What are the primary competitive threats to TIROSINT?
Generic liothyronine products offer lower prices, eroding market share. Additionally, increased use of combination T4/T3 therapy and emerging formulations could reshape prescribing trends.
4. How significant is the role of clinical research in expanding TIROSINT’s market?
Robust clinical trials demonstrating safety, efficacy, and benefits over existing therapies could facilitate broader acceptance and off-label uses, expanding market opportunities.
5. What strategies should manufacturers adopt to enhance TIROSINT’s market position?
Innovating formulations, engaging in clinical research, expanding geographic presence, and navigating reimbursement policies strategically can secure and grow market share.
References
[1] Market Research Future, Global Thyroid Hormone Market Report, 2023.
[2] IQVIA, Prescribing Data, 2023.
[3] American Thyroid Association, Thyroid Disease Epidemiology, 2021.
This analysis provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the current market landscape, challenges, and future opportunities for TIROSINT in the global pharmaceutical ecosystem.