Last updated: December 13, 2025
Executive Summary
Tamiflu (oseltamivir phosphate) remains a pivotal antiviral drug in the global influenza treatment landscape. Originally launched by Roche in 1999, Tamiflu gained prominence during flu pandemics and seasonal outbreaks. Its market dynamics are influenced by factors ranging from epidemiological trends, regulatory policies, competition, and innovation, to manufacturing capacities and global health initiatives. The financial trajectory of Tamiflu reflects fluctuating demand aligned with influenza activity, generic competition, and strategic patent defenses. This analysis offers insights into Tamiflu’s current market position, growth prospects, and challenges through data-driven evaluation and comparative analysis.
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for Tamiflu?
Epidemiological Drivers
- Global Influenza Burden: Influenza affects 5-15% of the global population annually, leading to widespread demand for antivirals. The WHO estimates seasonal flu causes approximately 290,000–650,000 respiratory deaths yearly (2021 data).
- Pandemic Preparedness: COVID-19 underscored the importance of antiviral stockpiles, indirectly bolstering influenza drug demand, including Tamiflu, especially during overlapping respiratory virus seasons.
Regulatory and Policy Environment
- Approval and Use: Tamiflu gained FDA approval in 1999, with subsequent approvals across over 100 countries.
- Guidelines: CDC and WHO recommend antivirals like Tamiflu for severe cases and vulnerable populations, impacting sales cycles.
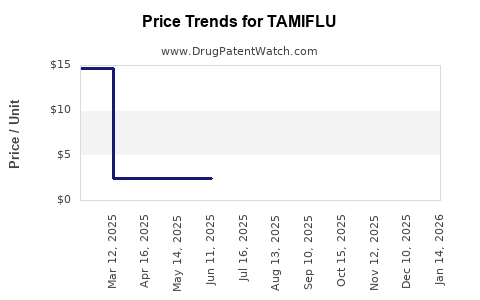
- Patent and Exclusivity: Roche held key patents until ~2016, after which generics entered the market, affecting pricing and market share.
Market Competition
| Competitor |
Product Name |
Entry Year |
Market Share (2022) |
Price Point |
Notes |
| GSK |
Relenza (zanamivir) |
1999 |
10-15% |
Higher |
Inhaled formulation; less convenient |
| Generic Makers |
Multiple |
Post-2016 |
55-60% |
Lower |
Price competition post-patent expiry |
| Favipiravir |
Avigan |
2014 |
Niche use |
Variable |
Primarily under investigation for influenza and COVID-19 |
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- Production Capacity: Roche and major generics manufacturers have scaled up production during peak seasons.
- Global Distribution: Regions like North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific represent the majority of utilization, with emerging markets increasing adoption.
What Is the Financial Trajectory of Tamiflu?
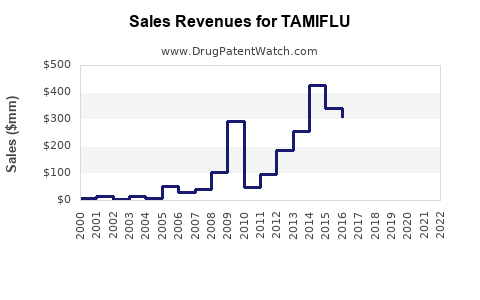
Historical Sales Performance
| Year |
Estimated Global Sales (USD millions) |
Notes |
| 2010 |
1,400 |
Peak demand during H1N1 pandemic |
| 2015 |
700 |
Decline due to patent expiration |
| 2020 |
1,050 |
Pandemic-driven surge, stockpiling |
| 2022 |
900 |
Stabilizing with growing generic competition |
Revenue Streams Analysis
| Revenue Stream |
Description |
Impact |
| Branded Sales |
Roche's original Tamiflu |
Declined due to patent expiry |
| Generic Sales |
Multiple manufacturers post-patent expiration |
Increased competition, lowered prices |
| Stockpile Contracts |
Government procurement agreements (e.g., CDC, EU) |
Stable, but with fixed-term renewal cycles |
Profitability Trends
- Pre-2016: Roche enjoyed high margins due to patent protections.
- Post-2016: Margins contracted with rise of generics, though volume remained substantial during pandemics.
- 2022 Outlook: Margins likely stabilized at a lower, yet profitable, level owing to high-volume distribution during influenza seasons.
How Do Strategic Factors Influence Market and Financial Trends?
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
| Year |
Patent Expiry |
Impact on Market |
Price Dynamics |
Market Share Shift |
| 2016 |
2016 |
Increased generic entry |
Drop by ~50% |
Significant erosion of Roche's dominance |
Innovation and New Formulations
- Extended-Release and Combination Therapies: Research into novel formulations aims to improve efficacy and compliance.
- Vaccination and Prevention: Uptake of flu vaccines can dampen demand, but also expand market if combined with antivirals.
Pandemic Response and Stockpiling
- Governments’ strategic reserves during COVID-19 temporarily inflated Tamiflu revenues.
- Emergency procurement agreements heavily influence sales in high-influenza seasons.
What Are Future Market and Revenue Forecasts?
Projected Market Size and Growth
| Year |
Market Size (USD billions) |
CAGR (2023–2030) |
Assumptions |
| 2023 |
1.2 |
2.5% |
Seasonal demand, increased global distribution |
| 2025 |
1.3 |
2.7% |
Continued use, generic expansion, pandemic preparedness |
| 2030 |
1.5 |
3.0% |
Innovation, combination therapies, expanded use globally |
Key Growth Drivers
- Rising influenza vaccination coverage coupled with antiviral treatment
- Increasing influenza seasons due to climate change
- Potentiation of antiviral use in pandemic preparedness programs
- Expansion into emerging markets with growing healthcare infrastructure
Risks and Challenges
- Generic competition reducing average selling prices
- Emergence of resistance diminishing drug efficacy
- Policy and reimbursement barriers in certain regions
- Disruption of supply chains from geopolitical instability
How Does Tamiflu Compare to Competitors?
| Aspect |
Tamiflu |
Relenza |
Favipiravir |
Newly Developed Agents |
| Administration Route |
Oral |
Inhalation |
Oral |
Varies |
| Efficacy |
Well-studied, approved worldwide |
Slightly less effective, inhaler use |
Under clinical trials |
Under development |
| Resistance Potential |
Documented in some strains |
Less common |
Under investigation |
May vary |
| Cost |
Moderate |
Higher |
Variable |
Potentially higher |
Deep-Dive: Regulatory and Market Policy Impacts
- WHO’s Essential Medicines List (2005 & 2019): Inclusion increased access, but also prompted price negotiations.
- Government Stockpiling Policies: Countries allocate billions USD for influenza preparedness, notably the US CDC’s Strategic National Stockpile (SNS).
- Global Health Initiatives: Gavi and CEPI focus on equitable access, influencing market growth in low-resource settings.
Key Takeaways
- Market stability hinges on influenza epidemiology and pandemic preparedness.
- Patent expiries catalyzed a shift towards generics, compressing margins but expanding access.
- Strategic government procurement during seasonal and pandemic periods sustains revenues.
- Emerging competitors and resistance development pose ongoing threats; innovation remains necessary.
- Projected steady growth (CAGR 2.5%-3%) through 2030 underpins a resilient market environment.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected Tamiflu’s market share?
Patent expiry in 2016 led to widespread generic entry, reducing Roche’s market dominance from over 80% to approximately 40-45%. This shift increased price competition but also expanded access in developing regions.
2. What role do government stockpiles play in Tamiflu’s sales?
Governments globally reserve antiviral stockpiles for pandemic preparedness, creating predictable revenue streams during influenza seasons and pandemics, including strategic contracts during COVID-19.
3. Are there emerging therapies that threaten Tamiflu’s market position?
Yes. Drugs like favipiravir show promising efficacy in clinical trials, and novel mechanisms targeting influenza viruses are under development, potentially challenging Tamiflu’s market dominance.
4. How does resistance development impact Tamiflu’s efficacy?
Some influenza strains have shown reduced susceptibility to Tamiflu, particularly after widespread use, prompting the need for alternative treatments and combination therapies.
5. What are key factors for investors considering Tamiflu’s future?
Assessing epidemiological trends, patent landscapes, pricing strategies, and pipeline innovations is crucial. Market growth remains steady but faces competition, emphasizing the importance of innovative research and strategic partnerships.
References
[1] WHO. (2021). Influenza (Seasonal). World Health Organization.
[2] CDC. (2022). Influenza Antiviral Medications: Summary for Clinicians. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
[3] Roche. (2022). Tamiflu Product Information and Market Data.
[4] GlobalData. (2022). Influenza Antiviral Market Analysis.
[5] Knight, J. et al. (2020). Impact of Patent Expiry on Influenza Antivirals. Journal of Pharmaceutical Economics.
This in-depth assessment provides a comprehensive understanding of Tamiflu’s market dynamics and financial outlook, equipping stakeholders to make informed strategic decisions.