Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Quinine sulfate, a naturally derived alkaloid primarily used for treating malaria and other protozoal infections, holds a unique position within the global pharmaceutical landscape. As resistance to synthetic antimalarials persists and global health priorities shift, understanding the market dynamics and financial trajectory of quinine sulfate is crucial for stakeholders. This analysis offers a comprehensive overview of the key factors influencing the quinine sulfate market, including supply-demand trends, regulatory challenges, manufacturing shifts, and emerging competitive pressures.
Historical Context and Market Overview
Historically, quinine sulfate has played an essential role in malaria therapy since its discovery in the 17th century. Derived from the bark of the Cinchona tree varieties, the compound's demand fluctuated with the prevalence of malaria and the advent of synthetic alternatives. In the early 20th century, quinine remained a frontline treatment; however, the advent of chloroquine and other synthetic antimalarials in the mid-20th century led to a decline in its use, relegating it primarily to cases resistant to or intolerant of newer drugs.
Despite this decline, quinine sulfate maintains niche applications in countries where resistance to synthetic drugs remains prevalent, notably in parts of Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. The pharmaceutical industry, however, faces significant complexities in maintaining and scaling production due to supply chain, regulatory, and environmental factors.
Market Dynamics
1. Supply Chain and Raw Material Constraints
The supply of quinine sulfate hinges heavily on Cinchona tree cultivation, predominantly in regions like Peru, India, and Indonesia. Environmental challenges such as deforestation, climate change, and pests threaten Cinchona plantations, leading to supply restrictions [1]. Moreover, the reliance on natural extraction introduces variability in the purity, yield, and cost.
Synthetic alternatives are notably absent for quinine sulfate, preserving its importance where natural extraction remains feasible. Nonetheless, shifting ecological and geopolitical risks impact availability and pricing. For example, disruptions in Cinchona harvesting can lead to price surges, affecting global supply stability.
2. Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Quinine sulfate is classified as an older, off-patent compound. This status diminishes exclusivity and reduces incentives for innovation, thereby constraining R&D investments. It also complicates market exclusivity and licensing negotiations.
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA require rigorous manufacturing standard compliance. Recent reviews focusing on the purity, contamination risks (e.g., quinine-related hypersensitivity), and environmental concerns modulate market entry and expansion strategies. Although non-proprietary, ensuring quality standards incurs costs that influence profit margins.
3. Disease Epidemiology and Demand Shifts
The global malaria burden fluctuates annually, with WHO estimating approximately 241 million cases in 2020, predominantly in sub-Saharan Africa [2]. While some regions have transitioned to synthetic drugs, quinine sulfate remains essential for resistant cases and specific clinical scenarios.
Demand is also influenced by the awareness of drug resistance. Emergence of quinine-resistant Plasmodium strains diminishes its utility, pushing clinicians towards newer therapies like artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs). Nonetheless, in contexts where ACTs are inaccessible due to cost or logistics, quinine sulfate maintains relevance.
4. Competition from Synthetic and Alternative Therapies
Over the decades, synthetic antimalarials have overshadowed quinine sulfate, leading to a dwindling market share. However, regional preferences and treatment protocols still favor quinine in certain circumstances, especially for severe malaria and pregnant women.
Emerging therapeutic innovations, such as drugs targeting drug-resistant strains, impact market demand. Also, the development of new formulations (e.g., long-acting injectables) could redefine competitive dynamics.
5. Emerging Markets and Niche Applications
Beyond antimalarial therapy, quinine sulfate finds applications in thrombosis prevention, cardiac arrhythmia management, and even as a flavoring agent in tonic waters, although these are economically minor segments. The growing awareness of its use in traditional medicine in certain regions can intermittently influence demand.
Financial Trajectory
1. Revenue Trends and Market Size
The global quinine sulfate market is modest, with estimates suggesting a size of approximately USD 50-70 million annually, driven primarily by endemic regions. The market experienced decline through the late 20th and early 21st centuries, compounded by competition from synthetic drugs [3].
However, recent periods show stabilization, predicated on supply constraints and regional treatment policies. The niche markets and limited competition help sustain revenue levels within a narrow band.
2. Pricing Dynamics
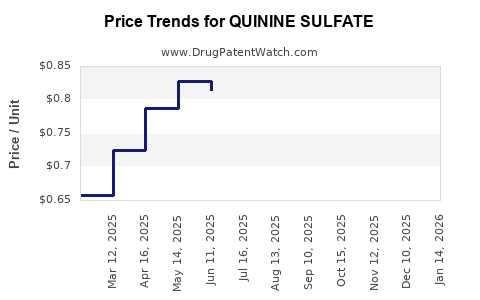
The price of quinine sulfate has exhibited volatility, oscillating with raw material costs, regulatory compliance expenses, and geopolitical risks. Prices range from USD 10 to USD 20 per gram on wholesale levels, with variability based on quality standards and regional factors.
Price elasticity remains low due to the specialized application scope; however, increased environmental or extraction costs could exert upward pressure.
3. Profitability and Cost Structures
Profit margins are constrained by the low value of raw materials and intense regulatory compliance costs. Additionally, the limited scope for innovation and end-market competition restricts pricing power.
Manufacturers employing low-cost extraction and bulk manufacturing operations can maintain margins, but environmental sustainability investments and quality assurance increase operational expenditures.
4. Investment and R&D Outlook
Given its status as an off-patent drug with limited new applications, direct R&D investments into quinine sulfate are infrequent. Nonetheless, efforts in sustainable cultivation, environmentally friendly extraction methods, and quality enhancement are ongoing.
Novel formulations (e.g., extended-release tablets) or combination therapies could present future revenue streams but face regulatory and efficacy hurdles.
Future Market Drivers and Constraints
-
Environmental and Supply Chain Stability: Enhanced sustainable Cinchona cultivation practices and alternative sourcing methods are critical for ensuring consistent supply.
-
Regional Health Policies: Governments' malaria control strategies and funding levels influence demand. Prioritization of synthetic alternatives or newer therapies could further diminish quinine sulfate's role.
-
Emerging Resistance: Growing quinine resistance could undermine its clinical use, prompting a decline in demand unless alternative formulations or combination therapies prove efficacy.
-
Environmental Regulations: Increasing environmental scrutiny on natural extraction processes may inflate production costs, impacting profitability.
-
Innovation and Niche Applications: Expanding into new therapeutic areas or improving formulations could stabilize or grow market revenues but require strategic investments.
Key Takeaways
-
Niche Market Position: Quinine sulfate remains vital in regions with resistant malaria strains and where synthetic options are limited, ensuring continued—but modest—market activity.
-
Supply and Environmental Challenges: Raw material constraints, environmental concerns, and ecological impacts heavily influence production stability and costs.
-
Pricing and Margins: Limited pricing flexibility and regulatory compliance elevate costs, constraining profit margins for manufacturers.
-
Market Decline and Resistance: Trends favoring synthetic drugs and emerging resistance patterns threaten the long-term viability of quinine sulfate as a first-line treatment.
-
Opportunity for Sustainable Practices: Adoption of sustainable cultivation and extraction techniques, along with research into new formulations, could prolong its market relevance.
FAQs
1. What are the primary factors affecting quinine sulfate's market growth?
Supply chain constraints owing to ecological and geopolitical factors, regulatory compliance costs, shifting treatment guidelines favoring synthetic drugs, and emerging drug resistance limit growth prospects.
2. How does environmental sustainability impact quinine sulfate production?
Environmental concerns regarding Cinchona cultivation and extraction raise regulatory scrutiny and operational costs, potentially constraining supply and affecting pricing.
3. Are there any new therapeutic applications for quinine sulfate?
While traditionally used for malaria, limited research suggests potential in other areas, but significant breakthroughs or novel formulations remain scarce, keeping its primary use as antimalarial.
4. How is the market for quinine sulfate expected to evolve over the next decade?
Market size may decline further as synthetic alternatives dominate and resistance issues intensify, but sustainable sourcing and niche uses may stabilize demand.
5. What strategic moves can manufacturers adopt to sustain their quinine sulfate business?
Investing in sustainable cultivation, quality improvement, exploring alternative formulations, and expanding into niche therapeutic or non-therapeutic markets might bolster long-term prospects.
Sources
[1] World Health Organization. (2021). Malaria Report 2021.
[2] World Health Organization. (2020). World Malaria Report 2020.
[3] MarketsandMarkets. (2022). Global Infectious Disease Market Reports.
Disclaimer: The data and projections outlined are based on current industry trends, publicly available reports, and expert analyses, and are subject to change with evolving market conditions.