Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for QUININE SULFATE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
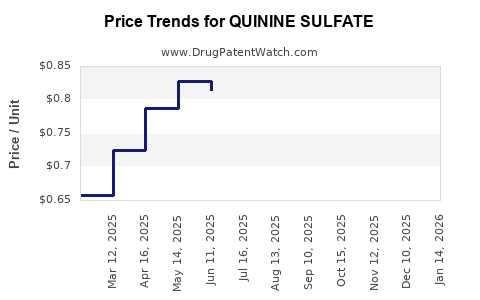
Average Pharmacy Cost for QUININE SULFATE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUININE SULFATE 324 MG CAPSULE | 68180-0560-06 | 0.77735 | EACH | 2026-01-21 |
| QUININE SULFATE 324 MG CAPSULE | 00093-3002-56 | 0.77735 | EACH | 2026-01-21 |
| QUININE SULFATE 324 MG CAPSULE | 50742-0238-30 | 0.77735 | EACH | 2026-01-21 |
| QUININE SULFATE 324 MG CAPSULE | 68180-0560-06 | 0.76373 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| QUININE SULFATE 324 MG CAPSULE | 00093-3002-56 | 0.76373 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| QUININE SULFATE 324 MG CAPSULE | 50742-0238-30 | 0.76373 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Quinine Sulfate: A Strategic Overview
Introduction
Quinine sulfate, historically renowned for its antimalarial properties, remains a critical phytochemical in global healthcare, especially amidst emerging resistance to conventional therapies. Its market dynamics are influenced by factors spanning regulatory landscapes, manufacturing complexities, therapeutic demand, and alternative treatment options. This analysis synthesizes current market data, evaluates trend drivers, and proposes future price trajectories, providing business leaders and investors with comprehensive intelligence.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Usage
Quinine sulfate is derived from the cinchona bark, with a storied history as the first effective treatment for malaria [1]. Despite the advent of synthetic antimalarials, quinine retains niche indications, including severe malaria cases and certain idiopathic conditions like nocturnal leg cramps.
Global Market Size
The global quinine sulfate market has experienced modest growth, estimated at approximately USD 150 million in 2022, with key contributions from endemic regions such as Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America [2]. The demand in these regions is primarily driven by public health initiatives and prescription adherence to WHO guidelines.
Regulatory and Industry Landscape
Regulatory oversight varies globally; in the United States, quinine is classified as a prescription drug with specific labeling regulations due to safety concerns. Additionally, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) restricts quinine's use primarily to severe malaria indications [3]. Manufacturing is concentrated among few suppliers, often in countries with abundant cinchona resources, contributing to supply chain tightness.
Market Drivers
- Malaria Prevalence: Ongoing endemicity sustains demand, especially in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Drug Resistance: Increasing resistance to artemisinin-based therapies prompts reliance on older drugs like quinine in certain contexts.
- Regulatory Constraints: Stringent controls may limit oversupply, influencing price stability.
- Alternative Therapies: The emergence of ACTs (artemisinin-based combination therapies) has curtailed quinine's market share but sustains a niche segment.
Challenges
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Dependence on natural sources subjects supply to climate, geopolitical, and environmental risks.
- Safety and Side Effects: Known adverse reactions, such as cinchonism, limit widespread use.
- Market Competition: Synthetic alternatives and formulations with improved safety profiles reduce demand.
Price Dynamics and Projections
Current Price Level
As of early 2023, the average wholesale price for quinine sulfate (per gram) hovers around USD 0.30–0.50, with bulk quantities commanding lower unit costs. Retail procurement costs are higher, reflecting distribution margins. Price stabilization is observed due to limited manufacturing capacity and steady demand in endemic regions.
Factors Influencing Price Trends
- Raw Material Costs: The price of cinchona bark and its derivatives directly impact quinine sulfate costs. Fluctuations stem from agricultural yields and environmental conditions.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Technological advances in extraction and synthesis can reduce costs, but investments are limited due to declining demand.
- Regulatory Policies: Stricter controls and certification standards may increase compliance costs, impacting prices.
- Market Demand Fluctuations: Variability in malaria incidence influences volume demand, affecting supply-demand equilibrium.
Price Projection (2023–2028)
Considering current trends:
-
Short-term (2023–2025): Prices are expected to remain relatively stable, supported by steady demand in endemic markets. Supply chain disruptions (e.g., due to climate effects on cinchona harvests) may cause occasional price increases of 5–8%.
-
Mid-term (2025–2028): Price pressures may emerge from increasing regulatory scrutiny, potential supply shortages, and competition from synthetic analogs. Prices could see a moderate rise of 10–15%, driven by supply scarcity and rising extraction costs.
-
Long-term (Beyond 2028): Given the declining global reliance on quinine for malaria and preference for newer therapies, demand is expected to decline further, exerting downward pressure on prices, potentially stabilizing at USD 0.25–0.40 per gram.
Emerging Trends and Strategic Considerations
- Synthetic Alternatives and Derivatives: Research into synthetic quinine and analogs might fragment the market, impacting traditional supply and pricing.
- Biotech Innovations: Advances in bioengineering could enable alternative production methods, potentially reducing costs or limiting supply chain reliance.
- Regulatory Evolution: Stricter safety regulations could restrict usage, further diminishing demand.
Concluding Remarks
The quinine sulfate market remains characterized by supply constraints, regional demand stability, and an overarching decline in global clinical use. Price projections suggest stability in the near term, with potential upward shifts driven by supply challenges and regulatory factors, followed by eventual decline as the drug’s role diminishes in modern malaria treatment paradigms.
Key Takeaways
- Quinine sulfate's global market remains niche, primarily driven by endemic disease management and specific medical indications.
- Supply chain vulnerabilities linked to natural resource dependence influence market stability and pricing.
- Short-term price stability is expected, with moderate increases possible due to environmental and regulatory factors.
- Long-term outlook indicates potential price decreases, aligned with declining clinical demand and technological advances.
- Companies engaging in quinine sulfate commercialization should monitor regulatory developments and supply chain dynamics closely to optimize procurement and pricing strategies.
FAQs
1. What factors are most likely to influence quinine sulfate prices in the coming years?
Supply chain stability, raw material costs, regulatory restrictions, and demand fluctuations due to malaria prevalence are primary drivers affecting prices.
2. How does environmental variability impact cinchona bark harvesting and consequently quinine sulfate supply?
Climate conditions, pests, and habitat loss can reduce cinchona cultivation yields, constraining raw material availability and increasing prices.
3. Are synthetic alternatives likely to replace natural quinine in the near future?
While research into synthetic analogs exists, natural quinine dominates niche applications. However, advances in synthetic production could impact future market shares.
4. What are the main regulatory challenges facing quinine sulfate manufacturers?
Regulatory agencies impose safety labeling, usage restrictions, and quality standards, which can increase compliance costs and limit market entry or expansion.
5. How should investors approach the quinine sulfate market given its current trajectory?
Investors should assess regional demand, supply chain risks, and regulatory landscapes. Focusing on supply security and technological innovations may mitigate risks associated with declining demand.
References
[1] World Health Organization. "Malaria Treatment Guidelines," 2021.
[2] Grand View Research. "Global Quinine Market Analysis & Forecasts," 2022.
[3] European Medicines Agency. "Quinine Sulfate Summary," 2021.
More… ↓
