QINLOCK Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Which patents cover Qinlock, and what generic alternatives are available?
Qinlock is a drug marketed by Deciphera Pharms and is included in one NDA. There are forty-one patents protecting this drug.
This drug has one hundred and fifteen patent family members in twenty-five countries.
The generic ingredient in QINLOCK is ripretinib. One supplier is listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the ripretinib profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Generic Entry Outlook for Qinlock
Qinlock was eligible for patent challenges on May 15, 2024.
By analyzing the patents and regulatory protections it appears that the earliest date
for generic entry will be December 30, 2040. This may change due to patent challenges or generic licensing.
There have been three patent litigation cases involving the patents protecting this drug, indicating strong interest in generic launch. Recent data indicate that 63% of patent challenges are decided in favor of the generic patent challenger and that 54% of successful patent challengers promptly launch generic drugs.
Indicators of Generic Entry
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for QINLOCK?
- What are the global sales for QINLOCK?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for QINLOCK?
Summary for QINLOCK
| International Patents: | 115 |
| US Patents: | 41 |
| Applicants: | 1 |
| NDAs: | 1 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 1 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 33 |
| Clinical Trials: | 1 |
| Patent Applications: | 366 |
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for QINLOCK |
| Patent Litigation and PTAB cases: | See patent lawsuits and PTAB cases for QINLOCK |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in QINLOCK? | QINLOCK excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | QINLOCK at DailyMed |
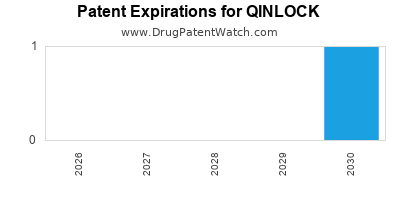

DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Loss of Exclusivity (LOE) Date for QINLOCK
Generic Entry Date for QINLOCK*:
Constraining patent/regulatory exclusivity:
NDA:
Dosage:
TABLET;ORAL |
*The generic entry opportunity date is the latter of the last compound-claiming patent and the last regulatory exclusivity protection. Many factors can influence early or later generic entry. This date is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source.
Recent Clinical Trials for QINLOCK
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| Deciphera Pharmaceuticals LLC | Phase 1 |
Pharmacology for QINLOCK
US Patents and Regulatory Information for QINLOCK
QINLOCK is protected by forty-one US patents and two FDA Regulatory Exclusivities.
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the earliest date for a generic version of QINLOCK is ⤷ Get Started Free.
This potential generic entry date is based on patent ⤷ Get Started Free.
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deciphera Pharms | QINLOCK | ripretinib | TABLET;ORAL | 213973-001 | May 15, 2020 | RX | Yes | Yes | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Deciphera Pharms | QINLOCK | ripretinib | TABLET;ORAL | 213973-001 | May 15, 2020 | RX | Yes | Yes | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||
| Deciphera Pharms | QINLOCK | ripretinib | TABLET;ORAL | 213973-001 | May 15, 2020 | RX | Yes | Yes | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
EU/EMA Drug Approvals for QINLOCK
| Company | Drugname | Inn | Product Number / Indication | Status | Generic | Biosimilar | Orphan | Marketing Authorisation | Marketing Refusal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deciphera Pharmaceuticals (Netherlands) B.V. | Qinlock | ripretinib | EMEA/H/C/005614Qinlock is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) who have received prior treatment with three or more kinase inhibitors, including imatinib. | Authorised | no | no | yes | 2021-11-18 | |
| >Company | >Drugname | >Inn | >Product Number / Indication | >Status | >Generic | >Biosimilar | >Orphan | >Marketing Authorisation | >Marketing Refusal |
International Patents for QINLOCK
When does loss-of-exclusivity occur for QINLOCK?
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the following patents block generic entry in the countries listed below:
Argentina
Patent: 2354
Patent: FORMULACIONES DE INHIBIDORES DE LA CINASA AMORFA Y MÉTODOS DE ESTAS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2355
Patent: COMPOSICIONES DE 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETIL-7-(METILAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2- DIHIDRO-1,6-NAFTIRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROFENIL)-3-FENILUREA
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Australia
Patent: 20417282
Patent: Compositions of 1-(4-bromo-5-(1-ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-1,6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenylurea
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 20419197
Patent: Amorphous kinase inhibitor formulations and methods of use thereof
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 23241368
Patent: Compositions of 1-(4-bromo-5-(1-ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-1,6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenylurea
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 23248048
Patent: Amorphous kinase inhibitor formulations and methods of use thereof
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 24227597
Patent: Amorphous kinase inhibitor formulations and methods of use thereof
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 24259742
Patent: Compositions of 1-(4-bromo-5-(1-ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-1,6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenylurea
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Brazil
Patent: 2022013109
Patent: FORMULAÇÕES DE INIBIDOR DE QUINASE AMORFO E MÉTODOS DE USO DAS MESMAS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2022013169
Patent: COMPOSIÇÕES DE 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETIL-7-(METILAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIIDRO-1,6-NAFTIRIDIN-3-IL)-2-FLUOROFEIL)-3-FENILUREA
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Canada
Patent: 63051
Patent: COMPOSITIONS DE 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETHYL-7-(METHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIHYDRO -1,6-NAPHTHYRIDINE-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHENYL)-3-PHENYLUREE (COMPOSITIONS OF 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETHYL-7-(METHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIHYDRO-1,6-NAPHTHYRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHENYL)-3-PHENYLUREA)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 63053
Patent: FORMULATIONS D'INHIBITEUR DE KINASE AMORPHE ET LEURS PROCEDES D'UTILISATION (AMORPHOUS KINASE INHIBITOR FORMULATIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
China
Patent: 5135308
Patent: 非晶型激酶抑制剂制剂及其使用方法 (Amorphous kinase inhibitor formulations and methods of use thereof)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 5243681
Patent: 1-(4-溴-5-(1-乙基-7-(甲氨基)-2-侧氧基-1,2-二氢-1,6-萘啶-3-基)-2-氟苯基)-3-苯基脲的组合物 (Compositions of 1-(4-bromo-5-(1-ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-pendant oxy-1, 2-dihydro-1, 6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenylurea)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 8948772
Patent: 1-(4溴-5-(1乙基-7-(甲氨基)-2侧氧基-1,2-二氢-1,6-萘啶-3基)-2氟苯基)-3-苯基脲的组合物 (Compositions of 1-(4 bromo-5-(1 ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-pendant oxy-1, 2-dihydro-1, 6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2 fluorophenyl)-3-phenylurea)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 8948773
Patent: 1-(4溴-5-(1乙基-7-(甲氨基)-2侧氧基-1,2-二氢-1,6-萘啶-3基)-2氟苯基)-3-苯基脲的组合物 (Compositions of 1-(4 bromo-5-(1 ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-pendant oxy-1, 2-dihydro-1, 6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2 fluorophenyl)-3-phenylurea)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 8948774
Patent: 1-(4溴-5-(1乙基-7-(甲氨基)-2侧氧基-1,2-二氢-1,6-萘啶-3基)-2氟苯基)-3-苯基脲的组合物 (Compositions of 1-(4 bromo-5-(1 ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-pendant oxy-1, 2-dihydro-1, 6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2 fluorophenyl)-3-phenylurea)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 9950433
Patent: 非晶型激酶抑制剂制剂及其使用方法 (Amorphous kinase inhibitor formulations and methods of use thereof)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 9970649
Patent: 非晶型激酶抑制剂制剂及其使用方法 (Amorphous kinase inhibitor formulations and methods of use thereof)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 0827525
Patent: 非晶型激酶抑制剂制剂及其使用方法
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Croatia
Patent: 0231699
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 0241699
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Denmark
Patent: 84778
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84779
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
European Patent Office
Patent: 84778
Patent: FORMULATIONS D'INHIBITEUR DE KINASE AMORPHE ET LEURS PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION (AMORPHOUS KINASE INHIBITOR FORMULATIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84779
Patent: COMPOSITIONS DE 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ÉTHYL-7-(MÉTHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIHYDRO -1,6-NAPHTHYRIDINE-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHÉNYL)-3-PHÉNYLUREE (COMPOSITIONS OF 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETHYL-7-(METHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIHYDRO-1,6-NAPHTHYRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHENYL)-3-PHENYLUREA)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 27827
Patent: FORMULATIONS D'INHIBITEURS DE KINASE AMORPHE ET LEURS PROCÉDÉS D'UTILISATION (AMORPHOUS KINASE INHIBITOR FORMULATIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 01931
Patent: COMPOSITIONS DE 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETHYL-7-(METHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIHYDRO-1,6-NAPHTHYRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHEYL)-3-PHENYLUREE (COMPOSITIONS OF 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETHYL-7-(METHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIHYDRO-1,6-NAPHTHYRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHEYL)-3-PHENYLUREA)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Finland
Patent: 84778
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84779
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Hungary
Patent: 65493
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 70151
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Israel
Patent: 3864
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 3866
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Japan
Patent: 34416
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 95672
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 23509628
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 23509629
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 24097009
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 25028954
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Lithuania
Patent: 84778
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84779
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Mexico
Patent: 22008097
Patent: COMPOSICIONES DE 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETIL-7-(METILAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIH IDRO-1,6-NAFTIRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROFEIL)-3-FENILUREA. (COMPOSITIONS OF 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETHYL-7-(METHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-D IHYDRO-1,6-NAPHTHYRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHENYL)-3-PHENYLUREA.)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 22008103
Patent: FORMULACIONES DE INHIBIDORES DE LA CINASA AMORFA Y METODOS DE ESTAS. (AMORPHOUS KINASE INHIBITOR FORMULATIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF.)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
New Zealand
Patent: 9199
Patent: Compositions of 1-(4-bromo-5-(1-ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-1,6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2-fluorophenyl)-3-phenylurea
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Poland
Patent: 84778
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84779
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Portugal
Patent: 84778
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84779
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
San Marino
Patent: 02300467
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 02400484
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Serbia
Patent: 058
Patent: FORMULACIJE INHIBITORA AMORFNE KINAZE I POSTUPCI NJIHOVE PRIMENE (AMORPHOUS KINASE INHIBITOR FORMULATIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 335
Patent: KOMPOZICIJE 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETIL-7-(METILAMINO)-2-OKSO-1,2-DIHIDRO-1,6-NAFTIRIDIN-3-IL)-2-FLUOROFENIL)-3-FENILUREA (COMPOSITIONS OF 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETHYL-7-(METHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIHYDRO-1,6-NAPHTHYRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHENYL)-3-PHENYLUREA)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Slovenia
Patent: 84778
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84779
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Korea
Patent: 2800493
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 220123057
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 220123058
Patent: 1--3-페닐우레아의 조성물
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 250057151
Patent: 1--3-페닐우레아의조성물 (1-4--5-1--7--2--12--16--3--2--3- COMPOSITIONS OF 1-4-BROMO-5-1-ETHYL-7-METHYLAMINO-2-OXO-12-DIHYDRO-16-NAPHTHYRIDIN-3-YL-2-FLUOROPHENYL-3-PHENYLUREA)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 250060322
Patent: 비정질 키나아제 억제제 제형 및 이의 사용 방법 (AMORPHOUS KINASE INHIBITOR FORMULATIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Spain
Patent: 66336
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 91414
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Taiwan
Patent: 2136257
Patent: Amorphous kinase inhibitor formulations and methods of use thereof
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2136258
Patent: Compositions of 1-(4-bromo-5-(1-ethyl-7-(methylamino)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-1,6-naphthyridin-3-yl)-2-fluoropheyl)-3-phenylurea
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
See the table below for additional patents covering QINLOCK around the world.
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slovenia | 4084778 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Japan | 2024097009 | 1-(4-ブロモ-5-(1-エチル-7-(メチルアミノ)-2-オキソ-1,2-ジヒドロ-1,6-ナフチリジン-3-イル)-2-フルオロフェニル)-3-フェニル尿素の組成物 (COMPOSITIONS OF 1-(4-BROMO-5-(1-ETHYL-7-(METHYLAMINO)-2-OXO-1,2-DIHYDRO-1,6-NAPHTHYRIDIN-3-YL)-2-FLUOROPHENYL)-3-PHENYLUREA) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Japan | 5265550 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for the Pharmaceutical Drug: QINLOCK
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
