Last updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
MYORISAN (setmelanotide), developed by Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, emerges as a targeted therapy for rare monogenic obesity disorders, notably Bardet-Biedl Syndrome (BBS) and Alström Syndrome. As an innovative melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) pathway agonist, MYORISAN addresses a critical unmet medical need within a niche but impactful segment of the obesity treatment landscape. This analysis scrutinizes the market environment and financial outlook for MYORISAN, factoring in current clinical, regulatory, competitive, and commercial trends.
Market Overview and Dynamics
Unmet Medical Need and Patient Population
MYORISAN caters specifically to patients with severe, rare genetic forms of obesity—a subset characterized by resistance to conventional weight management interventions. BBS and Alström Syndrome are ultra-rare disorders with prevalence estimates of approximately 1 in 100,000 to 1 in 1,000,000 individuals globally [1]. Despite such rarity, these conditions significantly impair quality of life, with obesity being a central feature.
The total addressable market (TAM) is thus modest but underscores high clinical value. Current estimates suggest approximately 4,000–8,000 patients in the United States and Europe could potentially benefit from MYORISAN's targeted therapy [2].
Regulatory Milestones and Approvals
MYORISAN received FDA approval in November 2020 for BBS in pediatric populations aged 6 years and older, marking a pivotal validation of its therapeutic promise [3]. Subsequent regulatory assessments by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and other jurisdictions are under way, which will influence market penetration and commercialization speed.
Regulatory approvals pave the way for market entry, yet approval scope—particularly for other indications like Alström Syndrome—remains a key factor shaping future revenue streams.
Competitive Landscape
Currently, MYORISAN's principal competitors are limited, with few existing therapies specifically addressing monogenic obesity. Conventional obesity treatments—lifestyle modifications, off-label pharmaceuticals—lack efficacy in these rare genetic conditions. This positions MYORISAN as a first-in-class option, potentially offering substantial pricing power and market exclusivity.
However, ongoing development of other MC4R pathway agents and gene therapies could emerge as future competitors. Notably, the small size and specialized nature of this niche reduce immediate competitive threats but do not eliminate the risk of future innovation.
Pricing and Reimbursement
Pricing strategies for orphan drugs are typically high, justified by small patient populations and high development costs. MYORISAN's initial pricing was set at approximately $375,000 annually per patient in the US [4].
Reimbursement negotiations with healthcare payers will significantly influence market access. In countries with robust health coverage for orphan drugs, favorable reimbursement pathways can accelerate uptake. Conversely, payers' increasing scrutiny of high-cost therapies could impose access barriers.
Market Adoption and Penetration Challenges
Physician awareness, diagnosis latency, and access to specialized metabolic clinics are barriers to rapid uptake. Education efforts by Rhythm Pharmaceuticals aim to mitigate these hurdles by increasing clinician familiarity with monogenic obesity and MYORISAN's benefits.
Furthermore, early data indicate promising efficacy, with significant weight reduction and metabolic improvements in clinical trials [5], fueling optimism around adoption.
Financial Trajectory
Revenue Projections and Growth Drivers
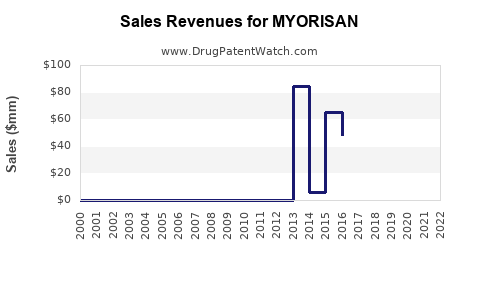
Initial revenues for MYORISAN are modest, reflective of its clinical stage and niche market. However, with expanded approvals, indications, and geographical expansion, sales trajectories can accelerate.
Analysts project that, in its first five years post-approval, MYORISAN could generate revenues in the range of $100–200 million globally, assuming steady adoption and reimbursement success [6].
Cost Considerations
Development costs, including clinical trials and regulatory filings, are substantial but absorbed within Rhythm Pharmaceuticals' broader R&D budget. Manufacturing costs for small-molecule drugs are relatively low, but expenses related to commercialization, post-market studies, and patient education are significant.
Pricing strategies intend to balance recouping R&D investments and access affordability, with potential for tiered pricing in different markets.
Future Revenue Streams
Beyond BBS, potential expansion into Alström Syndrome and other rare genetic obesity conditions could substantially increase revenue. The pipeline's progress and ongoing clinical trials will determine timing and scope.
Partnerships or licensing agreements with regional distributors may also influence sales growth, particularly in emerging markets where orphan drug frameworks are evolving.
Financial Risks and Uncertainties
Factors affecting MYORISAN's financial trajectory include regulatory delays, pricing/reimbursement hurdles, competitive innovations, and the limited size of the target population. Additionally, the redefinition of orphan drug incentives could influence development economics.
Regulatory and Market Entry Outlook
The trajectory of MYORISAN hinges on successful regulatory approval growth, with Japan, Canada, and other major markets being strategic priorities. Ensuring favorable reimbursement policies is vital; for instance, recent orphan drug incentives in the US and Europe facilitate pricing negotiations but require rigorous clinical endpoints and demonstration of value.
Post-market surveillance and real-world evidence generation will be instrumental in demonstrating long-term efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness, further bolstering payer confidence.
Conclusion and Forward-Looking Statements
The market for MYORISAN is characterized by high unmet needs within ultra-rare genetic obesity, with regulatory validation and a clear clinical benefit narrative underpinning its growth potential. Its financial trajectory will depend on timely approvals, robust market access, and continued clinical success.
With near-term revenues projected modest but scalable, the long-term outlook hinges on indication expansion, geographical penetration, and evolving healthcare policies favoring orphan drugs.
Key Takeaways
- Niche Market with High Clinical Impact: MYORISAN addresses a rare but debilitating form of obesity, with limited competition and significant unmet need.
- Regulatory Milestones as Growth Catalysts: Successful approvals in key markets will accelerate adoption and revenue generation.
- Pricing Power and Reimbursement: Premium pricing justified by rarity and efficacy; payer strategies will influence market access.
- Expansion Potential: Indications beyond BBS, including Alström Syndrome, can significantly enhance the financial outlook.
- Risks and Challenges: Limited patient population size, regulatory hurdles, reimbursement barriers, and potential future competitors pose risks.
FAQs
1. What is the current global market size for MYORISAN?
The estimated global addressable population is approximately 4,000–8,000 patients primarily in the US and Europe. The narrow scope limits total market size but allows for high per-patient revenue.
2. How does MYORISAN compare to existing obesity treatments?
Unlike generic weight-loss drugs, MYORISAN targets genetic pathways in ultra-rare conditions, offering a tailored approach with demonstrated efficacy in specific patient subsets.
3. What are the key factors influencing MYORISAN's revenue growth?
Regulatory approvals, indication expansions, reimbursement policies, clinical adoption by specialists, and geographic market entry are primary drivers.
4. What are potential hurdles to MYORISAN's market penetration?
Diagnosis delays, limited awareness, high costs, payer restrictions, and competition from future therapies could impede rapid uptake.
5. How does the orphan drug status influence MYORISAN’s financial prospects?
Orphan drug designation offers incentives such as exclusivity, tax credits, and fee waivers, which enhance profitability and encourage investment, but also impose certain regulatory and pricing expectations.
Sources:
[1] National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD). "Bardet-Biedl Syndrome".
[2] Global Genes. "Rare Disease Facts & Statistics".
[3] FDA. "FDA Approves First Treatment for Rare Form of Childhood Obesity."
[4] Rhythm Pharmaceuticals Investor Presentation, 2022.
[5] ClinicalTrials.gov. "EMBLEM Study of Setmelanotide."
[6] Market Research Future. "Orphan Drug Market Analysis 2022."