Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Misoprostol, a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analogue, plays a vital role in both obstetric and gastrointestinal therapeutic contexts. Originally developed for gastric ulcer prevention, it has gained prominence due to its efficacy in inducing labor, terminating pregnancies, and managing postpartum hemorrhage in resource-limited settings. Its multifaceted applications and regulatory landscape critically influence the drug’s market dynamics and financial prospects.
Market Overview
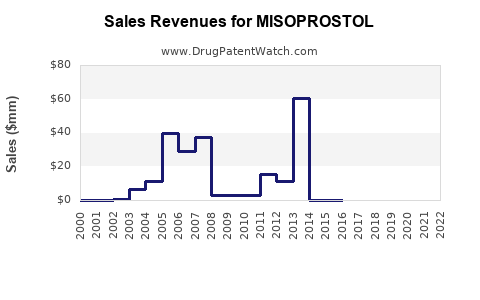
The global misoprostol market has experienced significant growth driven by expanding reproductive health initiatives, increasing awareness of safe abortion practices, and government support for maternal health programs. The increasing incidence of unsafe abortions, especially in developing countries, has amplified demand for affordable and effective termination options like misoprostol. According to industry reports, the global obstetrics and gynecology drug segment is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8% over the next five years[1].
In parallel, the gastrointestinal (GI) segment, primarily for gastric ulcers and management of side effects from NSAIDs, continues to be a consistent revenue driver. However, the growth here is tempered by alternative therapies and changing prescribing practices. The market’s future hinges upon regulatory approvals, patent landscapes, and regional healthcare policies, especially as misoprostol faces regulatory scrutiny in some markets due to misuse and off-label applications.
Regulatory and Legal Framework
Regulatory status significantly impacts market trajectory. Misoprostol is approved in many countries; however, its categorization under strict abortion laws in some jurisdictions hampers widespread utilization. In the United States, misoprostol is approved solely for gastric ulcer prevention, with its use in obstetrics and gynecology considered off-label, complicating commercial strategies for pharmaceutical companies[2].
In contrast, countries such as India, Mexico, and several African nations have embraced misoprostol in maternal health programs, often with government subsidies or inclusion in essential medicines lists. Recent regulatory advancements in Latin America and Africa have facilitated easier access, leading to bolstered sales and distribution channels.
Supply Chain and Patent Landscape
Multiple manufacturers, including pharmaceutical giants and generic producers, contribute to the supply of misoprostol. Patent expiration in several key markets has facilitated a surge in generic manufacturing, lowering costs and increasing access. This has, however, introduced price competition, impacting profit margins for branded formulations.
Major markets have seen a shift towards local manufacturing to circumvent import restrictions and reduce logistics costs, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and quality assurance remains pivotal, as counterfeit or substandard products can undermine credibility and lead to regulatory actions with significant financial repercussions.
Market Drivers
-
Reproductive Health Initiatives: Governments and NGOs prioritize maternal mortality reduction, fueling demand through programs that promote safe abortion and postpartum hemorrhage management, both of which leverage misoprostol’s efficacy.
-
Affordable Access in LMICs: The availability of low-cost generics and inclusion in national essential medicine lists facilitate widespread adoption, especially in African and South Asian healthcare settings.
-
Regulatory Endorsements: WHO’s recommendation for misoprostol in medical abortions and postpartum hemorrhage management has propelled acceptance and procurement, influencing procurement budgets and healthcare policies[3].
-
Demographic Trends: Population growth in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure underscores the need for accessible, stable, and easy-to-administer medications like misoprostol.
Market Challenges
-
Regulatory Hurdles and Misuse: In some regions, misoprostol’s potential for misuse (e.g., incorrect self-administration resulting in complications) prompts restrictive policies, limiting market penetration.
-
Off-Label Use and Litigation Risks: Off-label employment, while expanding markets, raises legal and safety concerns, affecting pharmaceutical firms’ willingness to invest in promotion.
-
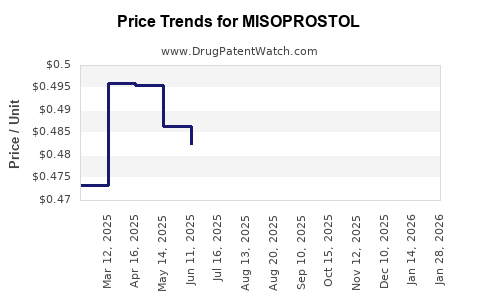
Pricing Pressures: Intense competition among generic manufacturers exerts downward pressure on prices, impacting revenue and profit margins.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Political instability, import restrictions, and manufacturing disruptions pose risks to consistent supply, impacting market growth.
Financial Trajectory and Future Outlook
The financial prospects for misoprostol are buoyed by its low-cost manufacturing and high demand in underserved markets. Industry analysts forecast a CAGR of 7-10% over the next five years, driven largely by expanding usage in maternal health programs and the global push for achieving Sustainable Development Goals related to maternal mortality reduction.
Key drivers impacting revenue include:
-
Increased Government and NGO Procurement: Investments in maternal health initiatives amplify demand, with procurement budgets expanding annually.
-
Market Expansion via New Indications: Research exploring off-label uses and potential new indications could further enhance revenue streams, provided regulatory approvals are secured.
-
Manufacturing Cost Optimization: Generics producers leverage economies of scale, reducing production costs and offering competitive pricing, thus accessing broader markets.
Conversely, patent landscapes are increasingly open, with many formulations facing generic competition, constraining pricing power. Companies heavily invested in branded formulations must navigate this environment by differentiating through formulation improvements or value-added services.
Strategic Opportunities
-
Regional Market Penetration: Strengthening presence in emerging markets through regulatory filings and partnerships with local manufacturers.
-
Education and Training Programs: Collaborations with healthcare providers and NGOs to improve awareness, prevent misuse, and expand safe administration practices.
-
New Formulation Development: Innovative delivery systems, such as fixed-dose combinations or sustained-release formulations, could command premium pricing and enhance market share.
-
Policy Advocacy: Engaging with policymakers to streamline regulatory pathways and include misoprostol in essential medicines programs.
Risks and Uncertainties
-
Changing Regulatory Landscapes: Stringent laws on abortion and medication access threaten to restrict markets.
-
Emergence of Alternative Therapies: Advances in other pharmaceuticals or non-pharmacological interventions could diminish misoprostol's relevance.
-
Socio-political Factors: Political resistance and cultural beliefs about abortion influence market acceptance and funding.
Concluding Analysis
The market strength of misoprostol remains robust, especially in LMICs, owing to its proven efficacy, low cost, and alignment with global maternal health goals. Its financial trajectory is favorable, provided pharmaceutical firms adapt to regulatory changes, leverage strategic partnerships, and innovate product offerings. As global health policies evolve and demand for accessible reproductive health solutions escalates, misoprostol stands to benefit, albeit amid regulatory and competitive challenges.
Key Takeaways
- The global misoprostol market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 8%, driven predominantly by reproductive health applications.
- Expansion in LMICs, supported by WHO recommendations and government programs, enhances market potential.
- Patent expirations and generic manufacturing stimulate price competition but also facilitate broader access.
- Regulatory challenges and misuse concerns necessitate strategic engagement with policymakers and healthcare providers.
- Innovation in formulations and regional market penetration are vital for sustaining growth and profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the primary therapeutic applications of misoprostol driving market growth?
Misoprostol is primarily used for medical abortion, postpartum hemorrhage management, and gastric ulcer prophylaxis. Its role in reproductive health significantly influences market expansion, especially in countries prioritizing maternal mortality reduction.
2. How does regulatory environment influence the global market for misoprostol?
Regulatory restrictions, especially around abortion laws, impact access and sales in certain regions. Conversely, supportive policies and inclusion in essential medicines lists promote increased procurement and distribution.
3. What are the main challenges faced by pharmaceutical companies dealing with misoprostol?
Challenges include regulatory restrictions, competition from low-cost generics, counterfeit medications, supply chain disruptions, and societal concerns about misuse.
4. How does the patent landscape affect the financial potential of misoprostol?
Patent expirations have led to a surge in generic production, lowering prices but intensifying competition, which compresses margins for branded formulations.
5. What strategic moves can companies adopt to capitalize on misoprostol’s market potential?
Key strategies include regional market expansion, forming partnerships with local manufacturers, investing in product innovation, and advocating for supportive policies in target markets.
Sources:
[1] Market Research Future. “Global Misoprostol Market Analysis & Trends.” 2022.
[2] FDA. “Misoprostol (Cytotec) Overview.” 2021.
[3] WHO. “Medical Management of Abortion and Postpartum Hemorrhage.” 2020.