Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
MacroDantin (nitrofurantoin) is a broad-spectrum antibiotic primarily prescribed for uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs). Historically, it has maintained steady market presence owing to its efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness. This analysis delves into the evolving market dynamics and financial trajectory of MacroDantin, considering recent regulatory, clinical, and competitive developments shaping its future.
Market Overview and Historical Context
Nitrofurantoin, under the brand MacroDantin, is a staple in the antimicrobial arsenal against UTIs. Its popularity stems from:
- Efficacy against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- Low resistance rates compared to other antibiotics.
- Favorable safety profile when used appropriately.
- The global prevalence of UTIs, which impacts demand.
According to IQVIA data, the U.S. antibiotic market for urinary indications has experienced consistent growth, with Nitrofurantoin accounting for a significant portion of oral UTI treatments[1].
Regulatory and Clinical Developments Impacting Market Dynamics
In recent years, regulatory agencies, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have issued updated guidance on Nitrofurantoin’s safety, particularly concerning its use in elderly populations and renal impairment. The 2019 FDA communication reaffirmed its safe use in appropriate populations but underscored cautious prescribing in cases of decline in renal function[2].
Clinical trials and observational studies continue to support Nitrofurantoin as a first-line agent for uncomplicated UTIs, reinforcing its quasi-monopoly status. Moreover, the drug’s non-resistance-prone profile remains a key differentiator, bolstering its utility in antimicrobial stewardship programs.
Competitive Landscape
The macro-level competition includes other oral antibiotics such as fosfomycin, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, and ciprofloxacin, some of which have faced rising resistance or safety issues:
- Fosfomycin: Emerging as a promising alternative due to its broad spectrum and low resistance, but limited availability and higher costs constrain its market share[3].
- Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim: Resistance rates have increased, diminishing its attractiveness.
- Fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin): Safety concerns over adverse effects have led to tightening prescribing guidelines and reduced usage.
The reliance on Nitrofurantoin remains strong, particularly in regions with high resistance rates to other antibiotics, due to its affordability, safety, and efficacy profile.
Market Drivers and Challenges
Drivers:
- Rising antibiotic resistance against traditional agents. Nitrofurantoin’s low resistance makes it a preferred option.
- Guideline endorsements from CDC, European Society of Clinical Microbiology, and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), favoring Nitrofurantoin as first-line treatment[4].
- Increased global prevalence of UTIs, attributed to aging populations and lifestyle factors.
- Enhanced awareness of antimicrobial stewardship, promoting use of narrow-spectrum agents like MacroDantin.
Challenges:
- Regulatory limitations: FDA warnings regarding use in specific patient groups may restrict prescribing.
- Generic competition: Market share is primarily held by generic manufacturers, capping revenue growth.
- Supply chain risks: Monopolies on raw materials or manufacturing disruptions could impact availability.
- Emerging alternatives: Development of novel agents, such as gepotidacin, could threaten market share.
Financial Trajectory and Revenue Projections
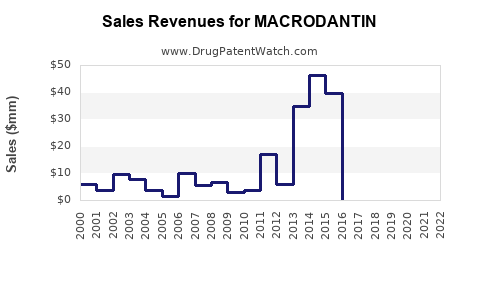
Given MacroDantin’s current status as a generic drug with stable demand, revenue trajectories are characterized by plateauing sales with potential modest growth attributable to increased UTI prevalence and resistant infection rates.
Short-term outlook (1-3 years):
- Revenue stability driven by existing contracts and consistent prescribing patterns.
- Margins maintained through cost efficiencies in generic manufacturing.
Medium- and long-term outlook (4-10 years):
Emerging molecular diagnostics may increase prescriptions in appropriate populations, further stabilizing revenues. Conversely, if new antimicrobial agents gain approval and favorable positioning, MacroDantin’s market share could decline.
Emerging Trends and Innovation Opportunities
The pharmaceutical landscape is witnessing shifts toward:
- Extended-release formulations for improved compliance.
- Combination therapies integrating Nitrofurantoin with other agents.
- Prophylactic applications for recurrent UTIs.
- Global market expansion in developing regions with limited access to advanced antibiotics.
Investments in these areas could influence MacroDantin's financial trajectory, either positively through market expansion or negatively via substitution.
Impact of Patent and Regulatory Outlook
While macroDantin, being a generic, is post-patent, future regulatory measures might influence manufacturing and approval pathways. Notably, the potential reclassification or stricter guidelines could impact prescribing patterns, expected to modestly impact revenue streams.
Conclusion
MacroDantin’s market remains relatively stable, driven by its enduring efficacy, safety, and low resistance profile. Regulatory trends and emerging competition pose threats, but current clinical and regulatory endorsements support its continued relevance. Overall, the drug's financial trajectory is characterized by moderate, steady revenues with potential for incremental growth dependent on global healthcare trends, resistance patterns, and innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Steady Demand: MacroDantin's role in UTI management ensures consistent prescription volumes, especially in resistant infection landscapes.
- Resistance Advantage: Its low resistance profile grants it a sustained competitive edge over alternative antibiotics.
- Regulatory Factors: Evolving safety guidelines could restrict use, influencing revenues; ongoing monitoring is essential.
- Market Competition: Emergence of agents like fosfomycin challenges the dominance, although cost and availability remain barriers.
- Growth Potential: Adoption of new formulations and global expansion can provide avenues for modest revenue growth.
FAQs
-
What is the primary clinical benefit of MacroDantin over other antibiotics?
Its broad-spectrum activity against common UTI pathogens, low resistance development, and favorable safety profile make MacroDantin a first-line therapy in uncomplicated UTIs.
-
How might regulatory changes affect MacroDantin’s market?
New safety warnings, especially regarding use in vulnerable populations, could restrict prescriptions, potentially reducing market size. However, current guidelines favor its continued use within established safety parameters.
-
What are the main competitors to MacroDantin?
Fosfomycin, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, and fluoroquinolones are primary competitors, with varying degrees of resistance and safety concerns impacting their market share.
-
Can global market expansion influence MacroDantin’s revenue?
Yes, increasing UTI prevalence and healthcare infrastructure improvements in emerging markets provide growth opportunities, contingent on regulatory approvals and local prescribing practices.
-
What innovations could help sustain MacroDantin’s market position?
Development of extended-release formulations, combination therapies, and use in prophylaxis could extend its market relevance and revenue stability.
References
- IQVIA. Pharmaceutical Market Insights, 2022.
- FDA. Nitrofurantoin Safety Communication, 2019.
- European Medicines Agency. Fosfomycin Overview, 2021.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Antimicrobial Guidelines for UTI, 2020.