Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
LOMOTIL, branded as a perennial staple in the management of diarrhea, particularly acute and chronic diarrhea, is a pharmaceutical product primarily comprising diphenoxylate and atropine. Approved by the FDA in the 1950s, LOMOTIL has maintained relevance within the gastrointestinal therapeutics market. Despite its longstanding history, evolving market dynamics—driven by regulatory shifts, emerging competition, and changing consumer health preferences—shape its current and future financial trajectory. This analysis traces the key market drivers, competitive landscape, regulatory considerations, and financial prospects of LOMOTIL, providing vital insights for industry stakeholders.
Market Overview and Key Drivers
Historical Market Position
LOMOTIL holds a significant share in the anti-diarrheal pharmaceuticals segment worldwide, especially in regions with constrained healthcare access where OTC and prescription luminal agents remain critical. Traditional reliance on opioids like diphenoxylate has sustained demand despite the advent of newer therapies.
Global Demand and Usage Trends
The global diarrhea management market is projected to grow steadily, driven by factors such as increasing incidences of infectious diseases and travelers’ diarrhea, especially in developing regions. The World Health Organization estimates that diarrhea accounts for approximately 525,000 deaths annually among children under five, underscoring ongoing therapeutic necessity [1].
Impact of Autonomous and Physician-Directed Usage
LOMOTIL's prescription-based model limits its accessibility, but evolving prescribing behaviors—particularly in regions emphasizing managed care—directly influence its sales volume. Notably, concerns over opioid misuse have nudged physicians toward alternative therapies, similarly affecting LOMOTIL’s market share.
Regulatory Environment and Market Constraints
Regulatory Status and Scheduling
LOMOTIL's diphenoxylate component, an opioid, is classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions, including Schedule V in the U.S., affecting its prescribing and distribution framework. Governments tighten regulations in response to misuse potential, impacting availability and sales growth [2].
Reformulation and Abuse-Deterrent Measures
Regulatory agencies and manufacturers are increasingly deploying abuse-deterrent formulations. While such innovations extend the lifecycle of existing drugs, they may entail substantial R&D costs and influence pricing strategies.
Legal and Reimbursement Landscape
Price controls and reimbursement policies further influence the drug’s financial prospects. In countries where government healthcare systems dominate, reimbursements are scrutinized, impacting profitability.
Competitive Landscape and Market Challenges
Emerging Alternatives
Novel anti-diarrheal agents—such as loperamide (Imodium), bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol), and opioid-sparing therapeutics—pose competitive threats. Notably, non-opioid options are preferred in certain markets due to safety concerns.
Patent and Intellectual Property Dynamics
LOMOTIL’s original patent expired decades ago, leaving the market open to generics, which substantially reduce brand-specific revenues. Although some formulations remain under proprietary rights, price competition among generics is fierce.
Changing Consumer Preferences
Increasing consumer awareness regarding opioid misuse prompts shifts toward non-opioid therapies. Furthermore, advancements in probiotic therapy and probiotics’ integration into diarrhea management influence market share distribution.
Financial Trajectory and Future Outlook
Revenue Trends and Market Potential
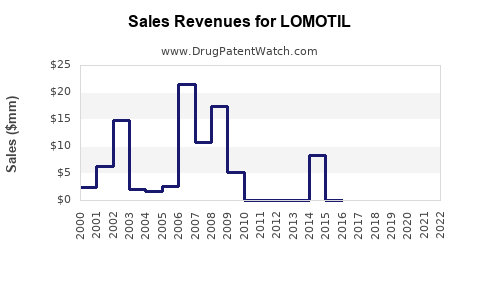
Despite declining dominance in some regions, LOMOTIL maintains a niche market, especially in areas with limited access to newer therapies. The global anti-diarrheal market was valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of nearly 4% through 2030 [3]. LOMOTIL’s segment will likely track this growth, albeit at a tempered pace due to competition and regulatory restrictions.
Growth Opportunities
- Emerging Markets: Increasing unmet needs in Africa, Asia, and Latin America offer growth avenues, especially if regulatory hurdles are eased.
- Formulation Innovations: Development of abuse-deterrent formulations could safeguard its market base.
- Partnerships with Governments: Collaborations for distribution in public health initiatives may bolster sales volumes.
Risks and Limitations
- Regulatory Restrictions: Tightened controls on opioids could constrain supply.
- Market Displacement: The advent of effective, non-opioid therapies may accelerate decline.
- Patent and Legal Challenges: Litigations or patent disputes could impact production or profits.
Conclusion
LOMOTIL’s market dynamics are intricately tied to evolving regulatory landscapes, competitive forces, and shifting consumer health priorities. Its financial trajectory is characterized by gradual decline expectations in developed markets with mature competition but retains growth potential in emerging regions. Strategic adaptations—such as formulation modifications and targeted regional expansion—will be essential to sustain profitability.
Key Takeaways
- The aging global population and persistent gastrointestinal health concerns sustain demand for anti-diarrheal therapies, including LOMOTIL.
- Regulatory constraints on opioids and abuse potential pose significant hurdles, requiring innovative formulation and marketing strategies.
- The presence of generic competitors exerts downward pressure on prices, constraining margins.
- Growth potential exists in emerging markets with expanding healthcare access and less stringent regulations.
- Investment in abuse-deterrent technologies and strategic regional partnerships are crucial to extending product lifespan and financial viability.
FAQs
1. How does regulatory classification impact LOMOTIL’s marketability?
LOMOTIL's classification as a Schedule V controlled substance in the U.S. limits prescribing and distribution, affecting availability. Stricter regulations globally restrict its use, potentially reducing sales but also increasing compliance costs.
2. What competitive alternatives have emerged for diarrhea management?
Non-opioid options like loperamide (OTC in many markets) and Bismuth-based therapies have gained prominence due to better safety profiles, challenging LOMOTIL’s market share.
3. Can formulation innovations improve LOMOTIL’s market position?
Yes. Abuse-deterrent formulations and combination therapies can mitigate misuse concerns and meet regulatory standards, potentially opening new market segments.
4. What regional strategies could enhance LOMOTIL’s revenues?
Expanding into emerging markets with high diarrhea burdens and less stringent regulations, coupled with targeted distribution, offers growth opportunities.
5. What is the long-term financial outlook for LOMOTIL?
While mature markets face decline, strategic adaptations and regional expansion could sustain revenues temporarily. However, long-term prospects depend heavily on regulatory developments and competitive innovations.
References
[1] World Health Organization. (2019). Diarrhoeal disease. WHO Fact Sheet.
[2] U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration. (2022). Schedules of Controlled Substances.
[3] Grand View Research. (2023). Anti-diarrheal pharmaceuticals market size, share & trends analysis.
This comprehensive analysis offers business professionals a detailed understanding of LOMOTIL’s market dynamics and financial prospects, equipping stakeholders to make informed strategic decisions.