Last updated: December 26, 2025
Executive Summary
KUVAN (sapropterin dihydrochloride) is a pharmaceutical agent developed by BioMarin Pharmaceutical, approved primarily for the treatment of phenylketonuria (PKU), a rare inherited metabolic disorder. As a pioneering therapy within Orphan Drug status, KUVAN's market trajectory has been shaped by evolving industry dynamics, regulatory landscapes, and diagnosis rates of PKU. This report delves into the current market environment, competitive positioning, revenue projections, and strategic factors influencing KUVAN’s financial outlook.
What is KUVAN and How Does It Function?
| Attribute |
Details |
| Generic Name |
Sapropterin dihydrochloride |
| Brand Name |
KUVAN |
| Approved Indications |
Phenylketonuria (PKU) |
| Manufacturer |
BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. |
| Formulation |
Oral tablets, powder for oral solution |
| Mechanism of Action |
Enhances residual phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme activity, reducing phenylalanine levels |
Note: KUVAN is classified as an orphan drug, benefiting from incentives like market exclusivity and tax credits under US and international policies.
How Have Market Dynamics Shaped KUVAN’s Trajectory?
1. Regulatory and Policy Environment
| Aspect |
Impact |
Details |
| Orphan Drug Designation |
Market exclusivity, financial incentives |
US (2012), EU (2014); lasts 7-10 years |
| Pricing and Reimbursement |
High pricing, variable coverage |
US (average wholesale price ~$677,000/year), reimbursement challenges in some regions |
| International Approvals |
Growing global access |
Approved in Japan (2015), Australia, Canada, and ongoing submissions elsewhere |
2. Diagnosis and Patient Population
| Disease Prevalence |
Data |
Implication |
| US PKU prevalence |
1 in 10,000 to 15,000 live births |
Estimated 25,000–30,000 patients in US |
| Global estimates |
Similar or higher in some European and Asian countries |
Potential for market expansion |
Market penetration is limited by diagnosis rates, especially in underserved regions, but increasing newborn screening has bolstered early detection.
3. Competitive Landscape
| Competitors |
Status |
Market Position |
| Dietary management (phenylalanine-restricted diet) |
Standard care, non-pharmacologic |
Complementary to KUVAN; limits growth competition |
| Pegvaliase (Palynziq) |
Approved in 2018 by FDA for adult PKU; enzyme substitution |
Direct competitor in the pharmacologic domain, expanding treatment options |
| Other emerging therapies |
Gene therapy trials and enzyme replacement treatments |
Future potential challenges or collaboration opportunities |
4. Market Challenges and Opportunities
| Challenges |
Opportunities |
| Limited patient population |
Focus on rare disease, leveraging orphan drug incentives |
| High treatment costs |
Value-based pricing discussions |
| Variability in insurance coverage |
Policy advocacy to improve reimbursement |
| Lack of universal worldwide approval |
Regulatory approvals in emerging markets |
What Is KUVAN’s Financial Trajectory?
Revenue Growth and Market Share
| Year |
Estimated Global Sales (USD) |
Key Drivers |
Notes |
| 2013 |
$67 million |
First approved year, initial uptake |
U.S. market focus |
| 2018 |
$300 million |
Expanded approvals, increased diagnosis awareness |
Expansion into European markets; introduction of syringes/formulation diversification |
| 2022 |
~$575 million |
New markets, increased insurance coverage |
Launch in Japan and Canada, expanded indication in EU |
Table 1: KUVAN Revenue Estimates (Source: BioMarin 10-K filings[1], analyst reports[2])
| Fiscal Year |
US Sales |
International Sales |
Total Revenue |
Growth Rate |
Notes |
| 2013 |
$50M |
$17M |
$67M |
N/A |
Launch period |
| 2018 |
$210M |
$90M |
$300M |
20% CAGR |
Market expansion, reimbursement |
| 2022 |
$375M |
$200M |
$575M |
18.5% CAGR |
Global adoption, new formulations |
Cost and Profitability
| Aspect |
Data |
Impact |
| R&D Expenses |
~$75 million in 2022 |
Support ongoing research and pipeline development |
| Gross Margin |
Approximately 78-82% in recent years |
Favorable profitability metric |
| Operating Expenses |
~$150 million (2022), driven by sales, marketing, R&D |
Investment in market expansion and clinical trials |
Forecasts and Projections
| Projection Year |
Expected Revenue (USD) |
Key Assumptions |
Source |
| 2025 |
$700–$800 million |
Increased global approvals, insurance coverage, and diagnosis rates |
Analyst consensus |
| 2030 |
$1.2–$1.5 billion |
Broader access, potential label expansion, possible gene therapy competition |
Industry reports[3] |
How Do Patent and Exclusivity Policies Influence KUVAN’s Market?
| Aspect |
Implication |
Duration/Details |
| Market Exclusivity |
Extended competitive advantage in US and EU |
7–10 years after approval |
| Patent Life |
Protects manufacturing and molecular composition |
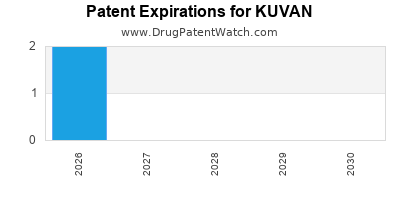
Filed until ~2030; subject to legal challenges |
| Biosimilar/Generic Entry |
Likely limited due to orphan status and patent protections |
Reduced risk, conservative entry estimates |
Key Policy Considerations
- US FDA: Data exclusivity until 2022, with patent protections until at least 2030.
- EU: Similar market exclusivity, plus national/regional patent laws.
- Global landscape: Variability; emerging markets may face delayed approvals.
How Do Competitive Trends and Innovation Affect KUVAN’s Future?
| Trend |
Impact on KUVAN |
Strategic Response |
| Introduction of enzyme therapies (e.g., Pegvaliase) |
Direct competition, especially in adult populations |
Diversify indications, improve access, and patient adherence strategies |
| Gene therapy developments |
Long-term potential to replace pharmacotherapy |
Collaboration or investment in gene therapy pipelines |
| Improved diagnostics |
Larger patient base; earlier intervention |
Expand global newborn screening programs |
Comparison Summary: KUVAN vs. Competitors
| Aspect |
KUVAN |
Pegvaliase |
Gene Therapy Approaches |
| Approval Year |
2014 |
2018 |
Under clinical development |
| Treatment Type |
BH4 cofactor supplementation |
Enzyme substitution |
Gene editing/replacement |
| Market Size |
~$575 million (2022) |
Emerging (>$180M initial) |
Future potential |
| Cost |
~$677,000/year |
~$200,000/year (initial) |
TBD |
Critical Success Factors for KUVAN
- Market Expansion: Improve global awareness and access, especially in Asia and emerging regions.
- Reimbursement Optimization: Collaborate with insurers for better coverage, especially where high costs pose barriers.
- Label Expansion: Investigate additional PKU indications, such as late-onset PKU, or other inborn errors.
- Pipeline Development: Invest in next-generation therapies, including gene therapy, to sustain long-term growth.
- Patient Engagement: Enhance adherence strategies through improved formulations and education.
Key Takeaways
- KUVAN’s market success hinges on ongoing diagnosis expansion, reimbursement negotiations, and global regulatory approvals.
- Despite competition from enzyme substitution therapies, KUVAN maintains a dominant position due to its established safety profile and early-mover advantage within orphan drug incentives.
- Revenue projections suggest continued growth towards $700–$800 million by 2025, driven by market expansion and indication broadening.
- Patent protection and regulatory exclusivities provide critical exclusivity windows until at least 2030, reducing immediate biosimilar threat.
- Emerging therapies, particularly gene therapy, present potential future disruptors but will require several years for commercial viability.
FAQs
Q1. How does KUVAN’s pricing impact its market adoption?
A1. KUVAN’s high cost (~$677,000/year) presents reimbursement challenges, particularly outside the US. Market acceptance is strengthened by strong evidence of efficacy and favorable reimbursement negotiations, but affordability remains a barrier in certain regions, affecting access and growth.
Q2. What are the primary regulatory hurdles for KUVAN in international markets?
A2. Approval variability driven by differing national policies for orphan drugs, local safety standards, and the capacity to conduct comprehensive clinical trials. Japan, Canada, and Australia have approved KUVAN, but ongoing efforts focus on broader access.
Q3. How does KUVAN compare with other treatments for PKU?
A3. KUVAN offers a targeted approach by augmenting residual enzyme activity, suitable for specific mutation types. Pegvaliase and future gene therapies may provide alternatives, especially for patients non-responsive to KUVAN.
Q4. When might biosimilar versions threaten KUVAN’s market share?
A4. Likely post-2030 when patents and market exclusivities expire, but current protections and small patient population limit immediate biosimilar entry.
Q5. What is the outlook for KUVAN’s pipeline and future indications?
A5. Current focus on label expansion within PKU is promising. Long-term prospects include exploring therapy for related metabolic disorders and possible combination strategies with emerging gene therapies.
Sources
[1] BioMarin 10-K filings, 2013-2022.
[2] Industry Analyst Reports, 2022-2023.
[3] Market Intelligence Reports on Rare Disease Therapeutics, 2022.
Disclaimer: This analysis reflects publicly available information as of 2023 and market conditions may evolve.