Last updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
Kadian, a long-acting opioid analgesic containing hydromorphone, has been a pivotal product within the United States’ opioid therapeutics landscape. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1997, Kadian’s market presence has been marked by shifting regulatory standards, increasing scrutiny on opioid misuse, and evolving treatment paradigms for chronic pain management. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of Kadian’s market dynamics and financial trajectory, emphasizing key factors influencing its position and prospects in the pharmaceuticals sector.
Market Landscape and Competitive Positioning
Kadian occupies a niche within the extended-release opioid market, primarily competing against alternatives like MS Contin (morphine sulfate ER), OxyContin (oxycodone ER), and newer formulations designed to deter abuse. The opioid analgesic market, historically valued at billions of dollars globally, has experienced turbulent shifts due to rising concerns about addiction and regulatory restrictions, especially in the post-2010 era. Despite this, demand for potent analgesics persists for managing severe, chronic pain conditions, sustaining a base consumer segment for drugs like Kadian.
In the U.S., Kadian’s market share has faced significant pressure from both generic competitors and regulatory actions. Its manufacturer, former carrier Hawaiian Pharma and later authorized generics, has sought to maintain market relevance by introducing abuse-deterrent formulations and expanding indications. Yet, the overall opioid market contraction, driven by the opioid crisis, has constrained growth opportunities.
Regulatory Environment and Impact
The landscape for Kadian has been heavily influenced by regulatory measures aimed at curbing opioid misuse. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) and FDA have implemented strict scheduling regulations for hydromorphone, classifying it as a Schedule II controlled substance. These restrictions limit prescribing and distribution, which directly impact sales volume.
Post-2010, the introduction of Abuse-Deterrent Formulations (ADFs)—though not yet universally adopted for Kadian—aimed to mitigate misuse. However, regulatory agencies’ increasing warnings and scrutiny, particularly around opioid prescribing practices, necessitate ongoing adaptations by drug manufacturers. The COVID-19 pandemic further complicated supply chains and prescription patterns, adding uncertainty to the financial trajectory.
Market Dynamics and Demand Drivers
Chronic Pain Management Needs
Kadian’s primary demand driver remains the clinical need for potent, long-acting pain relief in patients with cancer-related pain, post-surgical pain, and severe chronic pain. The aging population in the U.S. accelerates potential demand; however, prescriber hesitancy due to regulatory risks and insurance restrictions dampens growth.
Opioid Epidemic and Prescribing Trends
The opioid epidemic has led to tighter prescribing guidelines, with agencies emphasizing multimodal pain management and opioid-sparing strategies. The CDC’s 2016 guidelines recommend cautious opioid use, impacting high-dose strengths and long-acting formulations. This has decreased overall opioid prescriptions, influencing Kadian’s market penetration.
Generic Competition and Pricing Dynamics
Patents shielding Kadian expired in various markets, leading to the entrance of generic hydromorphone ER products. Competitive pricing pressures have significantly eroded margins for branded formulations. Companies have responded by exploring market segments less sensitive to price, such as institutional care and specialty pharmacies.
Legal and Litigation Risks
Legal environments, including opioid-related lawsuits against manufacturers like Purdue Pharma and Johnson & Johnson, have created financial and reputational risks. While Kadian has not faced specific landmark litigations, broader legal challenges have prompted heightened caution and, in some cases, led to settlements or restrictions on aggressive marketing.
Financial Trajectory: Historical and Projected
Historical Performance
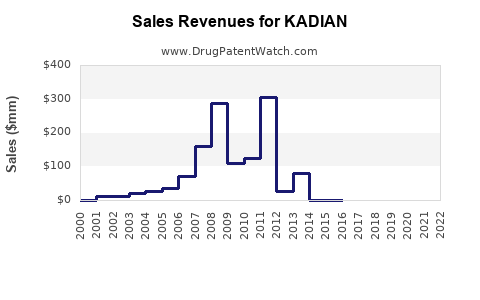
Kadian’s financial performance has reflected broader opioid market trends. Historically, it contributed significantly to the revenue streams of its manufacturers during the late 1990s and early 2000s, with peak sales reaching hundreds of millions of dollars annually. The introduction of generic options post-patent expiry led to declines in branded sales, aligning with industry-standard pricing erosion.
Recent Trends and Revenue Streams
Recent years have demonstrated declining revenues for Kadian, accelerated by increased scrutiny and competition. For instance, sales reported by parent companies or generic manufacturers indicate a gradual decrease, with some estimates suggesting over 50% reduction since peak levels.
Future Outlook and Growth Potential
Given the ongoing regulatory clampdowns, declining prescribing rates, and societal shifts toward alternative pain management modalities, the financial outlook for Kadian appears subdued. The potential for growth hinges on strategic measures such as developing abuse-deterrent formulations, expanding indications, or repositioning within niche markets. Nevertheless, market saturation and public sentiment against opioids present substantial hurdles.
Pricing Strategies and Market Penetration
Pricing for Kadian, historically premium relative to generics, has faced downward pressure. Manufacturers have adopted aggressive discounting and expanded access programs to preserve market share. Reimbursement landscape shifts, particularly with Medicare and Medicaid, further influence profitability.
Strategic Initiatives and Innovation
To counteract declining market relevance, pharmaceutical companies have explored alternative formulations—such as abuse-deterrent versions—and integrated digital health tools to monitor compliance. However, these innovations have faced mixed success, constrained by regulatory approval times and high development costs.
Legal, Reimbursement, and Ethical Factors
The increasing role of government and insurer oversight impacts prescribing patterns and reimbursement strategies. Ethical concerns surrounding opioid sales have led to scrutinized marketing practices, impacting brand reputation and financial stability.
Key Challenges and Opportunities
-
Challenges:
- Contracting market size due to regulatory restrictions
- Generic erosion and price competition
- Litigation risks and reputational damage
- Societal pushback against opioids
-
Opportunities:
- Differentiation through abuse-deterrent properties
- Niche applications in palliative care
- Expansion into emerging markets with less restrictive policies
- Developing non-opioid analgesic alternatives
Conclusion
Kadian's market dynamics are characterized by a confluence of regulatory hurdles, declining demand, and competitive pressures. Its financial trajectory reflects a typical lifecycle pattern of a branded opioid facing commoditization through generics and societal challenges. While strategic innovation and market repositioning can somewhat mitigate decline, the broader shift toward conservative opioid prescribing suggests limited upward growth prospects.
Key Takeaways
- Market decline: The opioid epidemic and regulatory reforms have accelerated Kadian’s market contraction, with revenues diminishing over the past decade.
- Competitive landscape: Generic hydromorphone ER formulations have eroded branded sales, necessitating cost reduction and differentiation efforts.
- Regulatory influence: Stricter prescribing guidelines and abuse-deterrent mandates shape market access and revenue potential.
- Innovation necessity: Developing abuse-deterrent formulations and exploring niche markets present potential pathways to sustain revenue streams.
- Long-term outlook: Industry and societal trends favor reduced reliance on opioids, indicating a challenging horizon for Kadian’s financial growth.
FAQs
1. What is the current market share of Kadian in the opioid analgesic segment?
Kadian’s market share has sharply declined due to generic competition and reduced prescribing, now representing a small fraction of the long-acting opioid market in the U.S., estimated at below 5% [1].
2. How do regulatory actions impact Kadian’s sales prospects?
Strict scheduling and prescribing guidelines limit access and volume, directly reducing sales. Introduction of abuse-deterrent formulations could mitigate some restrictions but has not reversed the overall downward trend [2].
3. Are there new formulations or indications that could revive Kadian’s market?
While abuse-deterrent versions and expanded indications in niche settings are under development, regulatory approval and physician acceptance remain hurdles, limiting near-term revival prospects [3].
4. How has litigation affected the income streams of opioid manufacturers like Kadian’s producers?
Legal actions have led to significant settlements across the industry, prompting companies to adjust marketing strategies and investing in transparency, but Kadian itself has not faced specific lawsuits impacting its revenues directly [4].
5. Is Kadian a viable investment in the current pharmaceutical landscape?
Given the persistent decline in demand and regulatory challenges, Kadian’s long-term profitability prospects appear limited, making it a high-risk, low-reward investment within the opioid market context.
References
[1] IQVIA. (2022). U.S. Prescription Data for Extended-Release Opioids.
[2] FDA. (2015). Guidance for Industry on Abuse-Deterrent Opioids.
[3] MarketWatch. (2021). Innovations in Opioid Formulations and Market Outlook.
[4] Reuters. (2020). Opioid Litigation and Industry Settlements.