INREBIC Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Which patents cover Inrebic, and what generic alternatives are available?
Inrebic is a drug marketed by Bristol-myers and is included in one NDA. There are five patents protecting this drug and one Paragraph IV challenge.
This drug has one hundred and nineteen patent family members in forty-two countries.
The generic ingredient in INREBIC is fedratinib hydrochloride. One supplier is listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the fedratinib hydrochloride profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Generic Entry Outlook for Inrebic
Inrebic was eligible for patent challenges on August 16, 2023.
By analyzing the patents and regulatory protections it appears that the earliest date
for generic entry will be June 4, 2032. This may change due to patent challenges or generic licensing.
There has been one patent litigation case involving the patents protecting this drug, indicating strong interest in generic launch. Recent data indicate that 63% of patent challenges are decided in favor of the generic patent challenger and that 54% of successful patent challengers promptly launch generic drugs.
Indicators of Generic Entry
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for INREBIC?
- What are the global sales for INREBIC?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for INREBIC?
Summary for INREBIC
| International Patents: | 119 |
| US Patents: | 5 |
| Applicants: | 1 |
| NDAs: | 1 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 1 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 134 |
| Clinical Trials: | 4 |
| Patent Applications: | 117 |
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for INREBIC |
| Patent Litigation and PTAB cases: | See patent lawsuits and PTAB cases for INREBIC |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in INREBIC? | INREBIC excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | INREBIC at DailyMed |
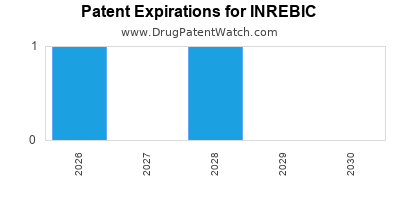

DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Loss of Exclusivity (LOE) Date for INREBIC
Generic Entry Date for INREBIC*:
Constraining patent/regulatory exclusivity:
NDA:
Dosage:
CAPSULE;ORAL |
*The generic entry opportunity date is the latter of the last compound-claiming patent and the last regulatory exclusivity protection. Many factors can influence early or later generic entry. This date is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source.
Recent Clinical Trials for INREBIC
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| Joseph Jurcic | Phase 1 |
| Bristol-Myers Squibb | Phase 1 |
| H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute | Phase 2 |
Paragraph IV (Patent) Challenges for INREBIC
| Tradename | Dosage | Ingredient | Strength | NDA | ANDAs Submitted | Submissiondate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INREBIC | Capsules | fedratinib hydrochloride | 100 mg | 212327 | 1 | 2023-08-16 |
US Patents and Regulatory Information for INREBIC
INREBIC is protected by five US patents and one FDA Regulatory Exclusivity.
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the earliest date for a generic version of INREBIC is ⤷ Get Started Free.
This potential generic entry date is based on patent ⤷ Get Started Free.
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
International Patents for INREBIC
When does loss-of-exclusivity occur for INREBIC?
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the following patents block generic entry in the countries listed below:
Australia
Patent: 10363329
Patent: Compositions and methods for treating myelofibrosis
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 11323108
Patent: Compositions and methods for treating myelofibrosis
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Brazil
Patent: 2013011184
Patent: composições e métodos para tratamento de mielofibrose
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Canada
Patent: 16710
Patent: COMPOSITIONS ET METHODES DE TRAITEMENT DE LA MYELOFIBROSE (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 16957
Patent: COMPOSITIONS ET PROCEDES DE TRAITEMENT DE LA MYELOFIBROSE (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Chile
Patent: 13001252
Patent: Capsula para administracion oral que comprende n-terc-butil-3-[(5-metil-2-{[4-(2-pirrolidin-1-iletoxi)fenil]amino}pirimidin-4-il)amino]bencenosulfonamida, una celulosa microcristalina y estearil fumarato de sodio; forma de dosificacion unitaria; metodo para tratar mielofibrosis; metodo de preparacion; y articulo de preparacion.
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
China
Patent: 3282036
Patent: Compositions and methods for treating myelofibrosis
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 8125923
Patent: 用于治疗骨髓纤维化的组合物和方法 (Compositions and methods for treating myelofibrosis)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Colombia
Patent: 01724
Patent: Composiciones y métodos para el tratamiento de la mielofibrosis
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Croatia
Patent: 0221269
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Denmark
Patent: 35282
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Dominican Republic
Patent: 013000097
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y MÉTODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE LA MIELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Ecuador
Patent: 13012658
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y MÉTODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE LA MIELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
European Patent Office
Patent: 35282
Patent: COMPOSITIONS ET MÉTHODES DE TRAITEMENT DE LA MYÉLOFIBROSE (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 59216
Patent: COMPOSITIONS DE TRAITEMENT DE LA MYÉLOFIBROSE (COMPOSITIONS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Hungary
Patent: 60254
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Israel
Patent: 6101
Patent: פורמולציות קפסולה של n-טרט-בוטיל-3-[(5 -מתיל-2-{[4-(2 -פירולידין-1-אילאתוקסי(פניל[אמינו{פירימידין-4-איל)אמינו]בנזינסולפונאמיד ושימוש בהן להכנת תרופות לטיפול במיאלופיברוזיס (Capsule formulations of n-tert-butyl-3-[(5-methyl-2-{[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]amino}pyrimidin-4-yl)amino]benzenesulfonamide and use thereof in the preparation of medicaments for treating myelofibrosis)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Japan
Patent: 33211
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 13541595
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Lithuania
Patent: 35282
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Malaysia
Patent: 1164
Patent: COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Mexico
Patent: 0246
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y METODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE LA MIELOFIBROSIS. (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS.)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1913
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y METODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE LA MIELOFIBROSIS. (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 13005020
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y METODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE LA MIELOFIBROSIS. (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS.)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Morocco
Patent: 723
Patent: COMPOSITIONS ET MÉTHODES DE TRAITEMENT DE LA MYÉLOFIBROSE
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
New Zealand
Patent: 1363
Patent: Compositions and methods for treating myelofibrosis
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Nicaragua
Patent: 1300038
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y MÉTODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE LA MIELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Peru
Patent: 140389
Patent: COMPOSICIONES Y METODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE LA MIELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Philippines
Patent: 013500924
Patent: COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Poland
Patent: 35282
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Portugal
Patent: 35282
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Russian Federation
Patent: 16262
Patent: КОМПОЗИЦИИ И СПОСОБЫ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ МИЕЛОФИБРОЗА (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR MYELOFIBROSIS TREATMENT)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 13126121
Patent: КОМПОЗИЦИИ И СПОСОБЫ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ МИЕЛОФИБРОЗА
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
San Marino
Patent: 02200453
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Serbia
Patent: 996
Patent: KOMPOZICIJE ZA LEČENJE MIJELOFIBROZE (COMPOSITIONS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Singapore
Patent: 0134
Patent: COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Slovenia
Patent: 35282
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Africa
Patent: 1303423
Patent: COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Korea
Patent: 1940979
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2131241
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 130137647
Patent: COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 180122029
Patent: 골수 섬유증을 치료하기 위한 조성물 및 방법 (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 200083676
Patent: 골수 섬유증을 치료하기 위한 조성물 및 방법 (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 240029118
Patent: 골수 섬유증을 치료하기 위한 조성물 및 방법 (COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Spain
Patent: 30650
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Taiwan
Patent: 31389
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1306882
Patent: Compositions and methods for treating myelofibrosis
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Tunisia
Patent: 13000195
Patent: COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS FOR TREATING MYELOFIBROSIS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Ukraine
Patent: 4076
Patent: КОМПОЗИЦІЯ І СПОСІБ ЛІКУВАННЯ МІЄЛОФІБРОЗУ
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
See the table below for additional patents covering INREBIC around the world.
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hungary | E060254 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Croatia | P20221269 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Russian Federation | 2013126121 | КОМПОЗИЦИИ И СПОСОБЫ ЛЕЧЕНИЯ МИЕЛОФИБРОЗА | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| European Patent Office | 1951684 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Spain | 2930650 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Russian Federation | 2012103851 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Peru | 20140389 | COMPOSICIONES Y METODOS PARA EL TRATAMIENTO DE LA MIELOFIBROSIS | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Supplementary Protection Certificates for INREBIC
| Patent Number | Supplementary Protection Certificate | SPC Country | SPC Expiration | SPC Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1951684 | 767 | Finland | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| 1951684 | CR 2021 00011 | Denmark | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: FEDRATINIB ELLER ET FARMACEUTISK ACCEPTABELT SALT DERAF ELLER ET FARMACEUTISK ACCEPTABELT HYDRAT DERAF, ISAER FEDRATINIB-DIHYDROCHLORIDMONOHYDRAT; REG. NO/DATE: EU/1/20/1514 20210209 |
| 1951684 | C202130029 | Spain | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: FEDRATINIB, O UNA SAL FARMACEUTICAMENTE ACEPTABLE DEL MISMO, O UN HIDRATO FARMACEUTICAMENTE ACEPTABLE DEL MISMO, EN PARTICULAR MONOHIDRATO DE DIHIDROCLORURO DE FEDRATINIB; NATIONAL AUTHORISATION NUMBER: EU/1/20/1514; DATE OF AUTHORISATION: 20210208; NUMBER OF FIRST AUTHORISATION IN EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AREA (EEA): EU/1/20/1514; DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION IN EEA: 20210208 |
| 1951684 | PA2021509 | Lithuania | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: FEDRATINIBAS ARBA FARMACINIU POZIURIU PRIIMTINA JO DRUSKA, ARBA FARMACINIU POZIURIU PRIIMTINAS JO HIDRATAS, YPAC FEDRATINIBO DIHIDROCHLORIDO MONOHIDRATAS; REGISTRATION NO/DATE: EU/1/20/1514 20210208 |
| 1951684 | 132021000000053 | Italy | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: FEDRATINIB, O UN SUO SALE FARMACEUTICAMENTE ACCETTABILE, O UN SUO IDRATO FARMACEUTICAMENTE ACCETTABILE, IN PARTICOLARE FEDRATINIB DICLORIDRATO MONOIDRATO(INREBIC); AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S) AND DATE(S): EU/1/20/1514, 20210209 |
| 1951684 | 301104 | Netherlands | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: FEDRATINIB, OF EEN FARMACEUTISCH AANVAARDBAAR ZOUT DAARVAN, OF EEN FARMACEUTISCH AANVAARDBAAR HYDRAAT DAARVAN, IN HET BIJZONDER FEDRATINIBDIHYDROCHLORIDEMONOHYDRAAT; REGISTRATION NO/DATE: EU/1/20/1514 20210209 |
| 1951684 | PA2021509,C1951684 | Lithuania | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: FEDRATINIBAS ARBA FARMACINIU POZIURIU PRIIMTINA JO DRUSKA, ARBA FARMACINIU POZIURIU PRIIMTINAS JO HIDRATAS, YPAC FEDRATINIBO DIHIDROCHLORIDO MONOHIDRATAS; REGISTRATION NO/DATE: EU/1/20/1514 20210208 |
| >Patent Number | >Supplementary Protection Certificate | >SPC Country | >SPC Expiration | >SPC Description |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for Inrebic (Fedratinib)
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
