ILEVRO Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Which patents cover Ilevro, and what generic alternatives are available?
Ilevro is a drug marketed by Harrow Eye and is included in one NDA. There are two patents protecting this drug and one Paragraph IV challenge.
This drug has fifty-five patent family members in twenty-seven countries.
The generic ingredient in ILEVRO is nepafenac. There are eight drug master file entries for this compound. One supplier is listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the nepafenac profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Generic Entry Outlook for Ilevro
By analyzing the patents and regulatory protections it appears that the earliest date
for generic entry will be December 1, 2030. This may change due to patent challenges or generic licensing.
There have been two patent litigation cases involving the patents protecting this drug, indicating strong interest in generic launch. Recent data indicate that 63% of patent challenges are decided in favor of the generic patent challenger and that 54% of successful patent challengers promptly launch generic drugs.
Indicators of Generic Entry
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for ILEVRO?
- What are the global sales for ILEVRO?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for ILEVRO?
Summary for ILEVRO
| International Patents: | 55 |
| US Patents: | 2 |
| Applicants: | 1 |
| NDAs: | 1 |
| Finished Product Suppliers / Packagers: | 1 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 93 |
| Clinical Trials: | 6 |
| Patent Applications: | 3,059 |
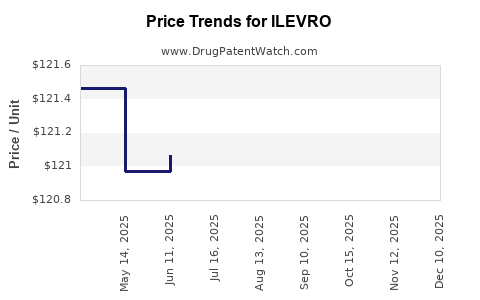
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for ILEVRO |
| Patent Litigation and PTAB cases: | See patent lawsuits and PTAB cases for ILEVRO |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in ILEVRO? | ILEVRO excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | ILEVRO at DailyMed |
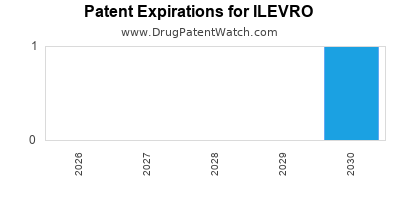
DrugPatentWatch® Estimated Loss of Exclusivity (LOE) Date for ILEVRO
Generic Entry Date for ILEVRO*:
Constraining patent/regulatory exclusivity:
NDA:
Dosage:
SUSPENSION/DROPS;OPHTHALMIC |
*The generic entry opportunity date is the latter of the last compound-claiming patent and the last regulatory exclusivity protection. Many factors can influence early or later generic entry. This date is provided as a rough estimate of generic entry potential and should not be used as an independent source.
Recent Clinical Trials for ILEVRO
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| Research Insight LLC | PHASE4 |
| Vance Thompson Vision - MT | Phase 4 |
| MDbackline, LLC | N/A |
Pharmacology for ILEVRO
| Drug Class | Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug |
| Mechanism of Action | Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors |
US Patents and Regulatory Information for ILEVRO
ILEVRO is protected by two US patents.
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the earliest date for a generic version of ILEVRO is ⤷ Get Started Free.
This potential generic entry date is based on patent ⤷ Get Started Free.
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harrow Eye | ILEVRO | nepafenac | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OPHTHALMIC | 203491-001 | Oct 16, 2012 | RX | Yes | Yes | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| Harrow Eye | ILEVRO | nepafenac | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OPHTHALMIC | 203491-001 | Oct 16, 2012 | RX | Yes | Yes | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | Y | ⤷ Get Started Free | |||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
Expired US Patents for ILEVRO
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | Patent No. | Patent Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harrow Eye | ILEVRO | nepafenac | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OPHTHALMIC | 203491-001 | Oct 16, 2012 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Harrow Eye | ILEVRO | nepafenac | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OPHTHALMIC | 203491-001 | Oct 16, 2012 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Harrow Eye | ILEVRO | nepafenac | SUSPENSION/DROPS;OPHTHALMIC | 203491-001 | Oct 16, 2012 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration |
EU/EMA Drug Approvals for ILEVRO
| Company | Drugname | Inn | Product Number / Indication | Status | Generic | Biosimilar | Orphan | Marketing Authorisation | Marketing Refusal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Novartis Europharm Limited | Nevanac | nepafenac | EMEA/H/C/000818Nevanac is indicated for:, , , prevention and treatment of postoperative pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery;, reduction in the risk of postoperative macular oedema associated with cataract surgery in diabetic patients., , | Authorised | no | no | no | 2007-12-11 | |
| >Company | >Drugname | >Inn | >Product Number / Indication | >Status | >Generic | >Biosimilar | >Orphan | >Marketing Authorisation | >Marketing Refusal |
International Patents for ILEVRO
When does loss-of-exclusivity occur for ILEVRO?
Based on analysis by DrugPatentWatch, the following patents block generic entry in the countries listed below:
Argentina
Patent: 0572
Patent: SUSPENSIONES DE NANOPARTICULAS QUE CONTIENEN POLIMERO DE CARBOXIVINILO
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 2463
Patent: SUSPENSIONES DE NANOPARTÍCULAS QUE CONTIENEN POLÍMERO DE CARBOXIVINILO
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Australia
Patent: 10326099
Patent: Carboxyvinyl polymer-containing nanoparticle suspension
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Brazil
Patent: 2012013503
Patent: suspensões de nanopartícula contendo polímero de carboxivinila
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Canada
Patent: 81254
Patent: SUSPENSION DE NANOPARTICULES CONTENANT UN POLYMERE DE TYPE CARBOXYVINYLE (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSION)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Chile
Patent: 12001402
Patent: Composicion farmaceutica en suspension oftalmica acuosa de administracion topica que comprende polimero de carboxivinilo, galactomanana, borato, compuesto en nanoparticulas escasamente soluble, agentes para ajustar ph y tonicidad, conservante y quelante; metodo para tratar trastornos oftalmicos, metodo para mantener viscosidad.
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
China
Patent: 2724965
Patent: Carboxyvinyl polymer-containing nanoparticle suspensions
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Croatia
Patent: 0140016
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 0181337
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Cyprus
Patent: 14871
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 20585
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Denmark
Patent: 06831
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 86426
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 65749
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
European Patent Office
Patent: 06831
Patent: SUSPENSION DE NANOPARTICULES CONTENANT UN POLYMÈRE DE TYPE CARBOXYVINYLE (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 86426
Patent: Suspension de nanoparticules contenant un polymère de type carboxyvinyle (Carboxyvinyl polymer-containing nanoparticle suspensions)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 65749
Patent: SUSPENSIONS DE NANOPARTICULES CONTENANT UN POLYMÈRE CARBOXYVINYLIQUE (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Hong Kong
Patent: 70164
Patent: CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 78802
Patent: 含毫微顆粒懸浮體的羧基乙烯聚合物 (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 17091
Patent: 含羧乙烯基聚合物的納米顆粒混懸液 (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Hungary
Patent: 25838
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 38821
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Japan
Patent: 64433
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 55849
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 13512912
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 15061886
Patent: カルボキシビニルポリマー含有ナノ粒子懸濁物 (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSION)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 16106155
Patent: カルボキシビニルポリマー含有ナノ粒子懸濁物 (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Lithuania
Patent: 65749
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Mexico
Patent: 12006231
Patent: SUSPENSION DE NANOPARTICULAS QUE CONTIENEN POLIMERO DE CARBOXIVINILO. (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSION.)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Poland
Patent: 06831
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 86426
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 65749
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Portugal
Patent: 06831
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 86426
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 65749
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Russian Federation
Patent: 71078
Patent: СУСПЕНЗИИ НАНОЧАСТИЦ, СОДЕРЖАЩИЕ КАРБОКСИВИНИЛОВЫЙ ПОЛИМЕР (SUSPENSIONS OF NANOPARTICLES, CONTAINING CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 12127675
Patent: СУСПЕНЗИИ НАНОЧАСТИЦ, СОДЕРЖАЩИЕ КАРБОКСИВИНИЛОВЫЙ ПОЛИМЕР
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Serbia
Patent: 085
Patent: SUSPENZIJE NANOČESTICA KOJE SADRŽE KARBOKSIVINILNI POLIMER (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSION)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 465
Patent: NANOČESTIČNE SUSPENZIJE KOJE SADRŽE KARBOKSIVINIL POLIMER (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Slovenia
Patent: 06831
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 86426
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 65749
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Africa
Patent: 1203770
Patent: CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
South Korea
Patent: 1543613
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1809484
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 120099269
Patent: CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER- CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSION
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 150063587
Patent: 카복시비닐 폴리머를 포함하는 나노입자 현탁액 (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS)
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Spain
Patent: 41420
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 50942
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 84752
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Taiwan
Patent: 86178
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Patent: 1129395
Patent: Carboxyvinyl polymer-containing nanoparticle suspensions
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Uruguay
Patent: 081
Patent: SUSPENSIONES DE NANOPARTÍCULAS QUE CONTIENEN POLÍMEROS DE CARBOXIVINILO
Estimated Expiration: ⤷ Get Started Free
Generics may enter earlier, or later, based on new patent filings, patent extensions, patent invalidation, early generic licensing, generic entry preferences, and other factors.
See the table below for additional patents covering ILEVRO around the world.
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mexico | 2012006231 | SUSPENSION DE NANOPARTICULAS QUE CONTIENEN POLIMERO DE CARBOXIVINILO. (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSION.) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Argentina | 013272 | COMPOSICIONES OFTALMICAS TOPICAS EN LA FORMA DE UN LíQUIDO QUE CONTIENEN POLíMEROS DE GUAR Y BORATO Y USO DE DICHAS COMPOSICIONES PARA PREPARAR UN MEDICAMENTO | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Serbia | 57465 | NANOČESTIČNE SUSPENZIJE KOJE SADRŽE KARBOKSIVINIL POLIMER (CARBOXYVINYL POLYMER-CONTAINING NANOPARTICLE SUSPENSIONS) | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Supplementary Protection Certificates for ILEVRO
| Patent Number | Supplementary Protection Certificate | SPC Country | SPC Expiration | SPC Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0716600 | C00716600/01 | Switzerland | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: NEPAFENAC; REGISTRATION NUMBER/DATE: SWISSMEDIC 58745 24.09.2008 |
| 0999825 | C300622 | Netherlands | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: NEPAFENAC; REGISTRATION NO/DATE: EU/1/07/433/002 20130503 |
| 0999825 | 122013000085 | Germany | ⤷ Get Started Free | PRODUCT NAME: NEPAFENAC (OPHTHALMISCHE SUSPENSION); REGISTRATION NO/DATE: EU 1/07/433/002 20130503 |
| >Patent Number | >Supplementary Protection Certificate | >SPC Country | >SPC Expiration | >SPC Description |
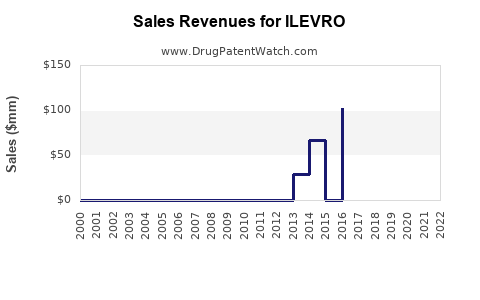
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for ILEVRO (Nepafenac)
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
