Last updated: December 30, 2025
Executive Summary
Hydroxyurea, a well-established chemotherapeutic and disease-modifying agent, primarily treats sickle cell disease (SCD) and certain myeloproliferative neoplasms. Despite its long-standing status as an affordable treatment, recent shifts in market dynamics—including patent expirations, emerging competitors, and evolving clinical guidelines—are shaping its financial trajectory. This analysis delineates current market forces, assessing the growth prospects, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and future financial outlook for Hydroxyurea within the pharmaceutical sector.
Introduction
Hydroxyurea, also marketed under brand names such as Hydrea and Droxia, has been in clinical use since the 1960s. It functions by inducing fetal hemoglobin production and inhibiting DNA synthesis, thereby alleviating symptoms in SCD and controlling hematologic malignancies like polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Its broad indication base and affordability make Hydroxyurea a cornerstone oral therapy in hematology.
Market Overview
| Aspect |
Detail |
| Global Market Size (2022) |
Estimated at USD 350 million, with significant regional variance (USA, Europe, emerging markets) |
| Primary Indications |
Sickle cell disease, polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia |
| Market Share (by revenue, 2022) |
Dominant in SCD (~60%), significant in myeloproliferative neoplasms (~40%) |
| Major Manufacturers |
Bristol-Myers Squibb (Hydrea), Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories, others |
Current Market Drivers
1. Increasing Prevalence of Sickle Cell Disease
- Prevalence: Approx. 100,000 Americans live with SCD; globally, over 300,000 newborns annually (WHO estimate).
- Market Penetration: Hydroxyurea remains first-line therapy for adults and children, especially in high-income countries.
- Expansion of Guidelines: CDC and NIH endorse Hydroxyurea for SCD management, promoting wider adoption.
2. Advancements in Clinical Guidelines & Adoption
- Recent guidelines (e.g., American Society of Hematology 2020) advocate early initiation of Hydroxyurea.
- Decreased perceptions of toxicity and improved patient compliance via once-daily dosing bolster usage.
3. Patent Expirations & Generic Availability
- The primary patent for Hydrea expired in the U.S. in 1996.
- Multiple generics available since then, exerting downward pressure on prices.
4. Expanding Use in Oncology & Other Hematologic Disorders
- Hydroxyurea's application in myeloproliferative disorders sustains demand.
- Emerging evidence explores its utility in other indications, potentially broadening its market.
Market Challenges & Constraints
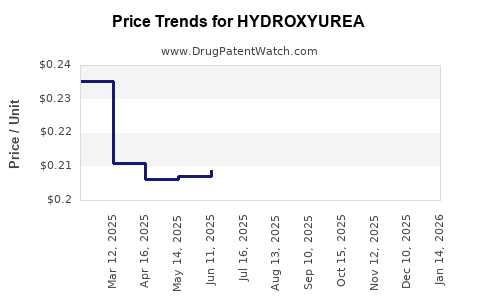
1. Patent Exhaustion and Price Erosion
- Generic competition has led to substantial price discounts.
- Average wholesale prices have declined by approximately 70% since patent expiry[1].
2. Safety and Toxicity Concerns
- Long-term safety (e.g., potential carcinogenicity concerns) impacts physician prescribing patterns.
- Need for regular monitoring may impede use in resource-limited settings.
3. Alternative Therapies and Market Competition
| Therapy |
Indication |
Status |
Market Share Impact |
Notes |
| L-glutamine |
SCD |
Approved (FDA) |
Growing |
Reduces oxidative stress; alternative to Hydroxyurea |
| Crizanlizumab |
SCD |
Approved (FDA) in 2020 |
Growing |
P-selectin inhibitor; adjunct therapy |
| Voxelotor |
SCD |
Approved (FDA) in 2019 |
Growing |
Affects hemoglobin affinity |
4. Entry of Newer Agents and Gene Therapies
- Advancements in gene editing (e.g., CRISPR-based therapies) may threaten Hydroxyurea’s market dominance in SCD in the long-term.
- Currently, high costs and complex logistics limit their immediate impact.
Regulatory Environment & Policy Impact
| Region |
Key Policies |
Effect on Hydroxyurea |
Status Update |
| United States |
FDA approvals, generic drug policies |
Maintains wide availability; cost reductions |
2022: Continued usage with insurance coverage |
| European Union |
EMA regulations, drug reimbursement policies |
Similar to U.S.; price negotiations |
Generics dominate market |
| Emerging Markets |
Limited regulation, affordability focus |
Market expansion opportunities |
Growing SCD burden; market access variability |
Financial Trajectory & Forecast
Historical Trends (2017–2022)
| Year |
Revenue (USD million) |
Growth Rate |
Key Notes |
| 2017 |
380 |
— |
Market stabilizing post-patent expiry |
| 2018 |
370 |
-2.6% |
Price pressures increase |
| 2019 |
340 |
-8.1% |
Market saturation; emerging generics impact |
| 2020 |
330 |
-2.9% |
COVID-19 pandemic disruptions |
| 2021 |
340 |
+3.0% |
Slight rebound, increased SCD awareness |
| 2022 |
350 |
+2.9% |
Steady growth driven by increasing disease prevalence |
Projected Market Trends (2023–2028)
| Year |
Expected Revenue (USD million) |
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) |
Drivers/Constraints |
| 2023 |
355 |
+1.4% |
Continued generic erosion; expanding indications |
| 2024 |
355 |
0% |
Market stabilization; emerging therapies' impact |
| 2025 |
360 |
+1.4% |
Possible uptick with improved diagnosis and coverage |
| 2026 |
370 |
+2.8% |
Emerging markets uptake; new formulations |
| 2027 |
385 |
+4.1% |
Potential introduction of long-acting formulations |
| 2028 |
400 |
+3.9% |
Market maturity; slight growth with new uses |
Factors Influencing Financial Trajectory
| Factor |
Impact |
Mitigation/Opportunity |
| Price erosion |
Negative |
Focus on differentiated formulations |
| Growing disease burden |
Positive |
Increased diagnosis, especially in underserved populations |
| Emerging biosimilars/genetics |
Negative long-term |
Investment in combination therapies or new indications |
| Regulatory incentives |
Positive |
Potential for orphan drug status extensions |
Comparison With Alternative Therapies
| Parameter |
Hydroxyurea |
L-glutamine |
Crizanlizumab |
Voxelotor |
Gene Therapy |
| Efficacy in SCD |
High (well-established) |
Moderate |
High (reduces crises) |
High (increases hemoglobin) |
Potentially curative |
| Approval Year |
1960s |
2017 |
2020 |
2019 |
Under clinical trials |
| Cost (2022 USD) |
<$50 per month (generics) |
~$50,000 annually |
~$50,000 per infusion |
~$120,000 annually |
~$1M+ per treatment |
| Market Penetration |
High |
Growing |
Growing |
Growing |
Limited but expanding |
Future Outlook & Strategic Considerations
- Market sustainability hinges on maintaining clinical relevance amid emerging alternatives.
- Cost pressure demands innovation in drug formulations and delivery.
- Expanding indications (e.g., in low-income countries) could diversify revenue streams.
- Regulatory incentives for orphan drugs and unmet needs may provide opportunities for market expansion.
- Partnerships and licensing with biotech firms exploring gene-therapy alternatives can ensure long-term relevance.
Key Takeaways
- Hydroxyurea remains a foundational treatment in SCD and related hematological conditions, but its market is under significant pressure from generics, new therapies, and regulatory factors.
- The global market size is modest (~USD 350 million), with slow but steady growth driven by rising disease prevalence and guideline endorsements.
- Patent expirations and generic competition have eroded prices, limiting revenue growth but ensuring widespread access.
- Emerging therapies, particularly gene-based approaches, pose long-term threats but are currently limited by high costs and technical challenges.
- Strategic focus should include formulation innovation, expanding indications, and targeting emerging markets to sustain revenue streams.
- Continuous monitoring of regulatory changes and therapeutic advancements is essential for sound decision-making.
FAQs
1. Will Hydroxyurea maintain its market position amid the rise of gene therapies?
While gene therapies promise potentially curative options, they are currently high-cost and limited in availability. Hydroxyurea will likely retain its role as a first-line, affordable therapy in the foreseeable future, especially in resource-limited settings.
2. How do patent expirations impact Hydroxyurea’s revenues?
Patent expiration in 1996 led to widespread generic availability, significantly reducing prices and revenue. The resultant commoditization stabilized revenues but limited growth potential unless new indications or formulations are introduced.
3. Are there notable new formulations of Hydroxyurea on the horizon?
Yes. Research into long-acting formulations, combination therapies, and alternative delivery systems aims to improve patient compliance and expand use, potentially revitalizing market growth.
4. Which regions present the most growth opportunities for Hydroxyurea?
Emerging markets, with high SCD prevalence and limited access to expensive therapies, demonstrate significant growth potential. Strategic pricing and local manufacturing could facilitate market penetration.
5. What is the outlook for Hydroxyurea in oncology?
In myeloproliferative neoplasms, Hydroxyurea remains a standard therapy but faces competition from newer targeted agents. Its role may diminish as precision medicine advances, but it remains relevant due to cost and established efficacy.
References
[1] IQVIA. (2022). Global Pharmaceutical Market Trends.
[2] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2022). Sickle Cell Disease Data & Statistics.
[3] American Society of Hematology. (2020). Guidelines for Sickle Cell Disease Management.
[4] U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). (2019-2022). Drug Approvals and Labeling Information.
[5] MarketWatch. (2022). Hydroxyurea Market Forecast and Analysis.