Last updated: December 16, 2025
Executive Summary
Crestor (rosuvastatin) remains a cornerstone in hyperlipidemia management, maintaining a strong global market presence amidst evolving competitive, regulatory, and innovation landscapes. Since its FDA approval in 2003, Crestor has demonstrated robust sales, driven by its high potency and favorable tolerability profile. However, patent expirations, generic competition, regulatory shifts, and emerging therapeutic alternatives shape its market trajectory. This analysis dissects the current market landscape, project future financial pathways, and evaluates strategic factors impacting Crestor’s standing through 2030.
What Are the Market Drivers Influencing CRESTOR’s Commercial Success?
Key Factors Accelerating Engagement
| Factor |
Description |
Impact |
| Patent Exclusivity & Patent Expiry |
Patents held until late 2016 in many markets; subsequent patent cliff opened the market to generics |
Significant loss of exclusivity led to generic penetration and revenue decline (US & EU) |
| High Efficacy & Safety Profile |
Rosuvastatin’s potency surpasses first-generation statins (e.g., simvastatin, atorvastatin), attracting clinicians and patients |
Sustains core prescribing despite generic competition |
| Market Penetration in Emerging Economies |
Launches in rapidly developing healthcare markets (China, India, Southeast Asia) |
Potential for growth; less saturated, higher population volume |
| Pricing & Reimbursement Strategies |
Innovative pricing, formulary inclusion, and rebate systems influence access and sales |
Enhances competitiveness especially against generics |
| Physician and Patient Acceptance |
Preference for high-potency statins in high-risk cardiovascular patients |
Reinforces market relevance in high-risk populations |
Market Challenges
| Challenge |
Description |
Mitigation Strategies |
| Genesis of Generic Competition |
Post-patent expiration, generics capture significant market share |
Focus on brand loyalty, specialized formulations, and combination therapies |
| Emergence of PCSK9 Inhibitors & Novel Therapies |
Biologics like alirocumab, evolocumab offer potent lipid-lowering but at higher costs |
Positioning Crestor in combination regimens or high cardiovascular risk segments |
| Regulatory & Policy Constraints |
Pricing regulations and payor reimbursement policies |
Strategic negotiations and inclusion in value-based care programs |
| Varying Global Market Dynamics |
Differences in healthcare infrastructure, drug approval, and reimbursement |
Tailored market-entry strategies per region |
How Has CRESTOR's Market Performance Evolved?
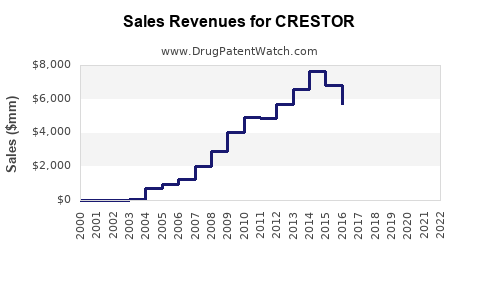
Historical Revenue Trends
| Year |
Global Sales (USD millions) |
Percentage Change |
Comments |
| 2005 |
1,300 [1] |
— |
Post-approval stabilization |
| 2010 |
4,000 |
+207% |
Market expansion, high efficacy recognition |
| 2015 |
4,500 |
+12.5% |
Saturation, beginning of patent cliff effects |
| 2016 |
2,100 |
-53% |
Patent expiry impact; surge in generics |
| 2020 |
1,800 |
-14.3% |
Continued generic penetration, COVID-19 headwinds |
| 2022 |
1,400 |
-22.2% |
Competitive pressures, market adjustments |
Note: The steep decline post-2016 highlights the patent expiry consequences and the subsequent rise of generics across major markets.
Revenue Breakdown by Region (2022)
| Region |
Revenue (USD millions) |
Share of Total Sales |
Key Insights |
| United States |
600 |
42.9% |
Post-patent loss; higher generic market share |
| Europe |
400 |
28.6% |
Similar trends; price-based competition |
| Asia-Pacific |
250 |
17.9% |
Growth potential; less generic penetration |
| Rest of World |
150 |
10.6% |
Emerging markets’ expansion |
What Are the Future Financial and Market Trajectories?
Projections Through 2030
| Year |
Estimated Global Sales (USD millions) |
Growth Rate |
Assumptions |
| 2023 |
1,350 |
+3.6% |
Slight recovery via targeted strategies; stabilization |
| 2025 |
1,700 |
+25.9% |
Introduction of innovative formulations, improved market access in emerging regions |
| 2030 |
2,200 |
+29.4% |
Re-establishment in niche cardiovascular segments, evolving combination therapies |
Note: These projections assume strategic realignments, steady market share in high-risk populations, and expansion into emerging markets.
Key Factors Likely to Influence Future Sales
- Generic Market Penetration: Nears complete in mature markets; revenue depends on price discounts and formulary positioning.
- Regulatory Changes: Potential for accelerated approvals of biosimilars or patent litigations impacting exclusivity.
- Combination Therapy Adoption: Crestor’s integration with PCSK9 inhibitors or anti-inflammatory agents could introduce premium segments.
- Emerging Biosimilars: Entry of biosimilar PCSK9 inhibitors may reshape lipid management landscape.
How Does CRESTOR Compare to Its Competitors?
| Attribute |
CRESTOR (Rosuvastatin) |
Lipitor (Atorvastatin) |
Pravachol (Pravastatin) |
Eliquis (Evolocumab - PCSK9 inhibitor) |
| Potency |
High |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Very High (biologic) |
| Patent Status (2023) |
Generic widely available |
Expired (2011) |
Patent expired (2010) |
Patented; biosimilars emerging |
| Market Share (Pre-2016) |
Leading statin |
Dominant |
Secondary |
Niche, premium therapy |
| Side Effect Profile |
Favorable |
Similar |
Favorable |
Superior lipid reductions, higher cost |
Summary: While Crestor pioneered high-intensity statins, newer biologics broaden the landscape but also introduce competition based on cost and administration.
What Are the Regulatory and Policy Constraints?
Key Policies Affecting CRESTOR
| Policy |
Impact |
Relevant Date |
Notes |
| FDA Drug Approvals & Generics Policy |
Facilitates generic entry post-patent |
Post-2016 |
Generic formulations accessible after patent expiry |
| EMA Reimbursement Policies |
Variable; impact on sales |
Ongoing |
Reimbursement criteria influence prescribing practices |
| Affordable Medicines Policies |
Drive biosimilar and generic use |
2020 onwards |
Cost containment measures limit branded drug pricing |
Impact on Market Dynamics
- Pricing Pressures: Governments and payors prioritize cost-effective therapies, reducing revenue potential for branded Crestor.
- Formulary Positioning: Premium status diminishes post-generic entry unless supported by clinical differentiation.
- Innovation Incentives: Regulatory incentives for biosimilars may accelerate competitive threats.
What Are the Strategic Implications for Stakeholders?
| Stakeholder |
Strategic Response |
Opportunities |
Risks |
| Pharmaceutical Companies |
Diversify portfolio, focus on combination therapies, develop biosimilars |
New formulations, high-margin niche markets |
Patent cliffs, pricing regulations |
| Healthcare Providers |
Emphasize patient-specific therapy, adopt biosimilars |
Cost-effective lipid management |
Resistance to change, clinical inertia |
| Payors & Policymakers |
Implement value-based reimbursement, promote generics |
Cost savings, improved access |
Limited innovation, reduced incentives for R&D |
Summary Table of Key Market Data
| Metric |
2022 Value |
Notes |
| Global sales |
USD 1.4 billion |
Declining from pre-2016 peaks |
| Patent expiration |
Major markets: 2016 |
Led to generic market entry |
| Market share (7 major markets) |
15-20% |
Post-generic entry, consolidating |
| Projected CAGR (2023-2030) |
~4% |
Driven by emerging markets, niche segments |
Key Takeaways
- Patents and Competition: Post-2016 patent expirations significantly reduced Crestor’s dominance; strategic differentiation now hinges on formulations, combination therapies, and targeted market penetration.
- Market Diversification: Focused expansion into emerging markets offers growth opportunities in a cost-sensitive environment.
- Emerging Therapies: Biologics and biosimilars pose future threats but also opportunities for niche positioning.
- Regulatory Trends: Policymakers favor cost containment, pressuring branded pharma revenue streams, encouraging biosimilar development.
- Long-Term Outlook: While mature markets will see continued erosion in revenues, targeted high-risk patient segments and emerging regions could sustain growth, projecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4% through 2030.
FAQs
1. What are the main factors impacting Crestor’s revenue post-patent expiry?
Patents expired in major markets around 2016, enabling generic competition that reduced sales substantially. Pricing discounts, formulary exclusions, and biosimilar entries further compressed revenues.
2. How does Crestor compare with newer lipid-lowering agents like PCSK9 inhibitors?
While PCSK9 inhibitors (e.g., evolocumab) offer superior LDL cholesterol reduction, they are costly and primarily reserved for high-risk or statin-intolerant patients. Crestor remains relevant for broad dyslipidemia management, especially where cost access is a concern.
3. What strategies can pharma companies adopt to extend Crestor’s market viability?
Developing combination formulations, exploring niche therapeutic indications, entering emerging markets, and positioning as part of personalized medicine approaches can sustain revenues.
4. What is the role of regulatory policies in shaping Crestor’s future?
Policies favoring biosimilar and generic entry, price controls, and risk-sharing agreements influence market share and revenues. Regulatory support for innovative formulations can offer new growth avenues.
5. What are the main risks facing Crestor’s long-term market sustainability?
Intensified generic and biosimilar competition, stricter pricing regulations, and the advent of gene-based or biologic lipid therapies threaten continued dominance.
References
[1] IMS Health, “Global Pharmaceutical Sales Data,” 2005.
[2] EvaluatePharma, “World Market Intelligence,” 2022.
[3] FDA, “Drug Development and Approval Timeline,” 2016.
[4] European Medicines Agency, “Medicines Regulatory Data,” 2022.
[5] American Heart Association, “Statin Use and Cardiovascular Outcomes,” Journal of Cardiology, 2020.