Last updated: July 31, 2025
Introduction
Betapace, the brand name for sotalol, a non-selective beta-adrenergic blocker with antiarrhythmic properties, remains a pivotal treatment in the management of certain cardiac arrhythmias. Since its FDA approval in 1982, Betapace has occupied a niche in arrhythmia therapy, particularly for atrial fibrillation/flutter and ventricular arrhythmias. This analysis explores the current market landscape, evolving drug dynamics, patent status, competitive pressures, regulatory considerations, and projected financial trajectories associated with Betapace.
Market Overview and Key Drivers
The global antiarrhythmic drugs market, valued at approximately USD 2.1 billion in 2022, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% from 2023 to 2030 (Grand View Research). Betapace commands a modest but significant position within this market, primarily in North America and Europe, where demand for arrhythmia management remains strong owing to an aging population and increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).
Prevalence of Cardiac Arrhythmias
The rising burden of atrial fibrillation (AF), which affects over 37 million people worldwide, significantly influences demand for antiarrhythmics like Betapace [1]. Additionally, ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death remain critical health issues, prompting sustained use of sotalol in hospital and outpatient settings.
Therapeutic Role of Betapace
Betapace’s dual mechanism—beta-adrenergic blockade and class III antiarrhythmic activity—makes it effective in maintaining sinus rhythm and reducing arrhythmic events. However, its use is contraindicated in patients with reactive airway diseases and certain electrolyte imbalances, limiting its broader adoption.
Market Dynamics
Patent and Exclusivity Landscape
Betapace’s original patent has long expired, leading to the proliferation of generic formulations. Generic competition has exerted downward pressure on prices, reducing margins for the originator manufacturer and limiting revenue growth potential.
Generic Market Penetration and Pricing Trends
Generic sotalol’s availability has democratized access but also intensified price competition. According to IQVIA data, generic sotalol prices have declined by approximately 35% over the past five years. This price erosion constrains sales revenues for branded Betapace and impacts overall market profitability.
Regulatory Environment
While the basic molecule remains unchanged, regulatory agencies are increasingly scrutinizing formulation labels, indications, and safety profiles—particularly concerning QT prolongation, a known risk of sotalol. Regulatory caution has led to restricted prescribing patterns in certain patient populations.
Emerging Therapies and Competition
Novel antiarrhythmic agents with improved safety profiles and targeted mechanisms, such as dronedarone and amiodarone derivatives, challenge Betapace’s market share. Additionally, catheter ablation procedures have gained favor for rhythm control, potentially reducing the reliance on pharmacotherapy.
Clinical Evidence and Guidelines
Guideline updates, notably by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and American Heart Association (AHA), influence prescribing behaviors. Recent emphasis on personalized therapy and risk stratification impacts Betapace's utilization, favoring high-risk or specialized patients.
Financial Trajectory
Current Revenue Performance
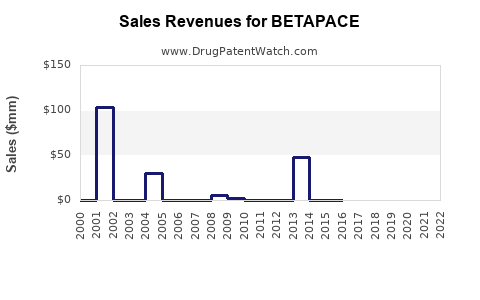
While precise sales data for Betapace are confidential, estimates suggest annual global revenues in the low hundreds of millions USD, predominantly driven by generic sales. The decline of originator sales due to generic competition has historically impacted profitability.
Forecasted Growth and Challenges
Projected growth for Betapace’s revenue remains modest, constrained by patent expiry and competitive dynamics. However, stabilizing factors include:
- Niche indications and specialized use cases: Patients contraindicated for newer therapies depend on Betapace.
- Hospitals and pharmacies with limited generic options.
- Potential for formulation innovations: Extended-release formulations or combinations may rejuvenate interest.
Strategic Opportunities
Pharmaceutical companies might explore lifecycle management strategies such as:
- Developing biosimilars or authorized generics.
- Expanding indications through clinical trials.
- Enhancing safety profiles to reduce adverse events and broaden use.
Market Challenges and Risks
- Safety concerns: QT prolongation and proarrhythmic potential necessitate controlled prescribing, limiting volume growth.
- Pricing pressures: In an environment favoring cost-containment, generic competition suppresses profit margins.
- Therapeutic shifts: The rise of non-pharmacologic treatments like ablation reduces long-term reliance on drugs like Betapace.
- Regulatory restrictions: Approvals and label updates may restrict use or introduce new safety warnings.
Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations
The outlook for Betapace hinges on balancing its niche utility against mounting generic competition and evolving treatment paradigms. For market stakeholders, maintaining differentiated positioning—such as risk management programs or targeted indications—may foster revenue stability.
Advancements in risk stratification tools and monitoring technology could influence Betapace's safety profile management, indirectly enabling broader use within appropriate patient groups. Furthermore, collaborations with healthcare providers emphasizing the drug’s role in specific arrhythmic conditions can foster sustained demand.
Key Takeaways
- Market stability is primarily driven by Betapace's niche indications and safety profile. While generic competition suppresses sales volumes and margins, specialized use cases support ongoing revenue streams.
- Patent expiration and increasing generic availability exert consistent downward pressure on prices, challenging profit margins.
- Emerging therapies and procedural interventions threaten Betapace’s position as a first-line treatment for certain arrhythmias.
- Regulatory caution and safety profile concerns necessitate targeted, judicious prescribing, which may limit market expansion.
- Lifecycle management strategies, including formulation innovations and indication expansion, are vital for preserving financial trajectory.
FAQs
Q1: What is the current patent status of Betapace (sotalol)?
A1: The original patent for Betapace has expired, leading to widespread generic availability, which significantly impacts market pricing and revenue streams.
Q2: How does the safety profile of Betapace influence its market trajectory?
A2: Its risk of QT prolongation and proarrhythmic effects necessitates careful patient selection, limiting widespread use but maintaining demand in certain high-risk groups.
Q3: What competition does Betapace face from newer antiarrhythmic drugs?
A3: Agents like dronedarone and amiodarone offer alternative mechanisms with distinct safety profiles, often preferred for broader patient populations or specific conditions.
Q4: How are procedural advances affecting Betapace’s market?
A4: Increasing adoption of catheter ablation reduces dependence on pharmacotherapy for rhythm control, potentially diminishing Betapace’s role in long-term management.
Q5: What strategic moves can preserve Betapace’s financial viability?
A5: Lifecycle management through formulation improvements, indication expansion, and targeted marketing can sustain revenues amid generic competition and market shifts.
References
- Global Burden of Atrial Fibrillation: Chugh SS, et al. (2014). Worldwide Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation: A Global Burden of Disease Study. Circulation.
- Antiarrhythmic Market Data: Grand View Research. (2022). Antiarrhythmic Drugs Market Size & Trends.
- Regulatory and Safety Considerations: FDA. (2021). Sotalol (Betapace) Drug Label.
- Therapeutic Guidelines: ESC Guidelines for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation, 2020.
- Market Competition and Dynamics: IQVIA Reports, 2022.
Conclusion
Betapace’s market landscape remains shaped by its proven efficacy, safety considerations, patent expiry, and evolving treatment algorithms. Strategic adaptation to market and regulatory changes is essential for sustaining its financial trajectory. Stakeholders must focus on niche positioning, lifecycle innovations, and safety management to navigate future market challenges effectively.