ATROVENT Drug Patent Profile
✉ Email this page to a colleague
When do Atrovent patents expire, and when can generic versions of Atrovent launch?
Atrovent is a drug marketed by Boehringer Ingelheim and is included in five NDAs. There is one patent protecting this drug.
The generic ingredient in ATROVENT is ipratropium bromide. There are eight drug master file entries for this compound. Twenty-one suppliers are listed for this compound. Additional details are available on the ipratropium bromide profile page.
DrugPatentWatch® Litigation and Generic Entry Outlook for Atrovent
A generic version of ATROVENT was approved as ipratropium bromide by RITEDOSE CORP on January 26th, 2001.
AI Deep Research
Questions you can ask:
- What is the 5 year forecast for ATROVENT?
- What are the global sales for ATROVENT?
- What is Average Wholesale Price for ATROVENT?
Summary for ATROVENT
| US Patents: | 0 |
| Applicants: | 1 |
| NDAs: | 5 |
| Raw Ingredient (Bulk) Api Vendors: | 64 |
| Clinical Trials: | 47 |
| Patent Applications: | 7,886 |
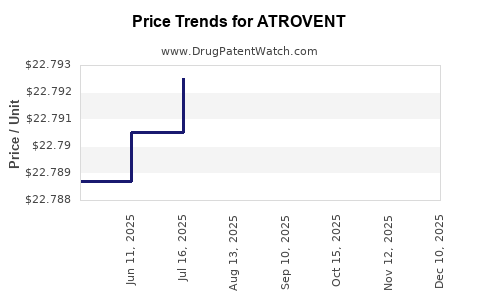
| Drug Prices: | Drug price information for ATROVENT |
| What excipients (inactive ingredients) are in ATROVENT? | ATROVENT excipients list |
| DailyMed Link: | ATROVENT at DailyMed |
Recent Clinical Trials for ATROVENT
Identify potential brand extensions & 505(b)(2) entrants
| Sponsor | Phase |
|---|---|
| Hat Yai Medical Education Center | Phase 3 |
| University of Nevada, Las Vegas | Phase 4 |
| Ohio State University | Phase 4 |
US Patents and Regulatory Information for ATROVENT
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | TE | Type | RLD | RS | Patent No. | Patent Expiration | Product | Substance | Delist Req. | Exclusivity Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim | ATROVENT | ipratropium bromide | AEROSOL, METERED;INHALATION | 019085-001 | Dec 29, 1986 | DISCN | No | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| Boehringer Ingelheim | ATROVENT | ipratropium bromide | SPRAY, METERED;NASAL | 020394-001 | Oct 20, 1995 | DISCN | Yes | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| Boehringer Ingelheim | ATROVENT | ipratropium bromide | SOLUTION;INHALATION | 020228-001 | Sep 29, 1993 | DISCN | Yes | No | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | ||||
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >TE | >Type | >RLD | >RS | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration | >Product | >Substance | >Delist Req. | >Exclusivity Expiration |
Expired US Patents for ATROVENT
| Applicant | Tradename | Generic Name | Dosage | NDA | Approval Date | Patent No. | Patent Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim | ATROVENT | ipratropium bromide | AEROSOL, METERED;INHALATION | 019085-001 | Dec 29, 1986 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Boehringer Ingelheim | ATROVENT | ipratropium bromide | SPRAY, METERED;NASAL | 020393-001 | Oct 20, 1995 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| Boehringer Ingelheim | ATROVENT | ipratropium bromide | SPRAY, METERED;NASAL | 020394-001 | Oct 20, 1995 | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free |
| >Applicant | >Tradename | >Generic Name | >Dosage | >NDA | >Approval Date | >Patent No. | >Patent Expiration |
International Patents for ATROVENT
See the table below for patents covering ATROVENT around the world.
| Country | Patent Number | Title | Estimated Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | 2903957 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Italy | 7949417 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| Belgium | 760251 | ⤷ Get Started Free | |
| >Country | >Patent Number | >Title | >Estimated Expiration |
Market Dynamics and Financial Trajectory for Atrovent (Ipratropium Bromide)
More… ↓
Make Better Decisions: Try a trial or see plans & pricing
Drugs may be covered by multiple patents or regulatory protections. All trademarks and applicant names are the property of their respective owners or licensors. Although great care is taken in the proper and correct provision of this service, thinkBiotech LLC does not accept any responsibility for possible consequences of errors or omissions in the provided data. The data presented herein is for information purposes only. There is no warranty that the data contained herein is error free. We do not provide individual investment advice. This service is not registered with any financial regulatory agency. The information we publish is educational only and based on our opinions plus our models. By using DrugPatentWatch you acknowledge that we do not provide personalized recommendations or advice. thinkBiotech performs no independent verification of facts as provided by public sources nor are attempts made to provide legal or investing advice. Any reliance on data provided herein is done solely at the discretion of the user. Users of this service are advised to seek professional advice and independent confirmation before considering acting on any of the provided information. thinkBiotech LLC reserves the right to amend, extend or withdraw any part or all of the offered service without notice.
