Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
REGLAN, generically known as metoclopramide, is a longstanding pharmaceutical agent primarily utilized to treat gastrointestinal motility disorders, including nausea, vomiting, and gastroparesis. Its market presence spans decades, characterized by evolving regulatory landscapes, competitive pressures, and shifting clinical guidelines. Understanding REGLAN’s current market dynamics and forecasting its financial trajectory necessitates a comprehensive analysis of regulatory statuses, patent lifecycle, clinical utility, and emerging therapies.
Pharmacological Profile and Clinical Utility
Metoclopramide functions as a dopamine antagonist, promoting gastric motility and reducing nausea. Its versatility has sustained demand across hospital inpatient settings, outpatient clinics, and pharmaceutical compendiums. The drug’s indications include diabetic gastroparesis, antiemetic applications, and, historically, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
However, its usage is tempered by concerns over adverse effects such as tardive dyskinesia, particularly with long-term use, prompting reassessment of safety profiles. Consequently, clinical guidelines have emphasized limited durations and caution in prescribing, influencing market exposure.
Regulatory Landscape and Patent Status
REGLAN’s original patent protections have long expired, with the drug falling into the generic classification. The absence of patent exclusivity has led to intense price reductions and market saturation by multiple generic manufacturers. Regulatory agencies, notably the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have maintained approval status but imposed restrictions to mitigate risks associated with long-term use [1].
Recent regulatory updates include boxed warnings and dosage limitations, further impacting the drug's appeal and prescribing volume. These measures, combined with increased awareness of adverse effects, have subdued growth opportunities compared to newer therapeutic options.
Market Dynamics
Competitive Environment
The market for gastrointestinal prokinetics and antiemetics has become increasingly fragmented. Besides generic REGLAN, alternatives such as domperidone (not FDA-approved in the U.S.), erythromycin, and newer agents like serotonergic 5-HT4 receptor agonists (e.g., prucalopride) now compete for market share.
Furthermore, the advent of novel drug delivery systems and formulations aims to improve safety profiles, challenging REGLAN’s dominance. For instance, prokinetic agents with enhanced safety have eroded the clinical reliance on metoclopramide, especially after regulatory advisories.
Regulatory and Safety Constraints
The significant adverse effects associated with prolonged use have led to strict prescribing guidelines and boxed warnings, notably the risk of tardive dyskinesia. These constraints have induced a decline in prescription volumes, especially in outpatient settings where long-term management is considered risky.
Physicians now prefer alternative therapies with better safety profiles, even if less established or with limited indications, which further diminishes occupancy of REGLAN in treatment algorithms.
Pharmacoeconomic Considerations
Pricing pressure among generic manufacturers has resulted in exceedingly low prices for REGLAN formulations. Margins for producers have compressed, constraining incentives for innovation or new formulation development. The low-cost advantage benefits healthcare payers but reduces profitability for manufacturers.
Financial Trajectory Forecast
Historical Performance
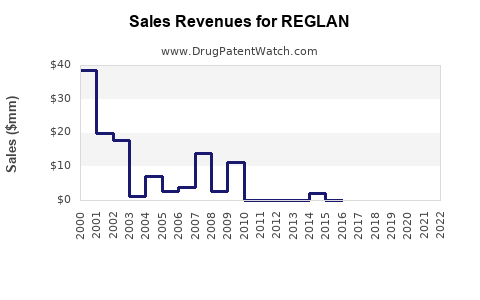
REGLAN’s revenue trajectory over the past decade reveals a marked decline, driven by safety concerns and regulatory restrictions. In the U.S., prescriptions peaked during the late 2000s, with subsequent declines following FDA advisories and the implementation of boxed warnings in 2009 [2].
Current Market Outlook
Forecasting suggests that REGLAN’s market share will continue to erode due to:
- Increased use of alternative agents with better safety profiles.
- Stringent regulatory restrictions limiting prescribing.
- The prevalence of safer, innovative therapies entering clinical practice.
The drug is expected to stabilize at a low-volume, low-margin niche within hospital settings or specific niche indications, with only marginal revenues for generic manufacturers.
Future Revenue Potential
Given the structural challenges, REGLAN’s future revenue potential in the U.S. is minimal without new indications or formulations. Globally, markets where regulatory barriers are lower might sustain slightly higher sales volumes, but overall, the drug’s financial trajectory remains in decline.
Impact of Emerging Therapies
Emerging therapies targeting gastroparesis and nausea, such as 5-HT4 receptor agonists, NK1 antagonists, and novel prokinetics, threaten to further diminish REGLAN’s market share. The healthcare shift towards personalized medicine and safety-first approaches will likely continue to favor newer agents.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
Manufacturers of REGLAN need to assess cost structures against diminishing revenue streams. Potential strategies include:
- Emphasizing niche indications with ongoing clinical support.
- Developing safer formulations or delivery systems.
- Focusing on markets with less regulatory strictness.
Healthcare providers should recognize the limited future utility of REGLAN, favoring safer alternatives when available.
Key Regulatory and Market Trends
- Regulatory Restrictions: The FDA’s boxed warning (2009) and dosage limitations have substantially impacted prescribing and sales.
- Generic Competition: An oversaturated market with numerous low-cost generics limits profitability.
- Safety Profile Concerns: Widespread adverse effects restrict clinical use, particularly in outpatient and long-term settings.
- Emerging Alternatives: Newer therapies with improved safety and efficacy profiles are reducing reliance on REGLAN.
Conclusion
REGLAN’s market dynamics are predominantly characterized by decline due to safety issues and regulatory restrictions. Its financial trajectory continues downward, with marginal opportunities largely confined to specific institutional settings. The pharmaceutical landscape’s evolution, favoring safer, targeted therapies, indicates limited growth prospects for metoclopramide in the medium to long term.
Key Takeaways
- Declining Market Share: Regulatory restrictions and safety concerns have significantly diminished REGLAN’s clinical use and market share.
- Patent and Pricing Realities: The drug's generic status leads to price erosion and low margins for manufacturers.
- Emerging Alternatives: Safer, more effective drugs threaten REGLAN’s relevance, especially beyond niche indications.
- Future Outlook: The drug’s revenues are projected to decline further, with limited upside absent new indications or formulations.
- Strategic Implications: Stakeholders should focus on alternatives and optimize use within specific, safe clinical contexts.
FAQs
1. Why has REGLAN’s prescribing decreased over the years?
Safety concerns, especially the risk of tardive dyskinesia, coupled with FDA-imposed boxed warnings and dosage restrictions, have led clinicians to reduce or avoid prescribing REGLAN.
2. Are there any new formulations or indications that could revive REGLAN’s market?
Currently, no significant new formulations or indications are under development. Regulatory limitations and safety issues hinder potential revival efforts.
3. How do safety concerns impact the global market for metoclopramide?
While some countries may have less stringent regulations, safety concerns generally limit global growth. Markets with different regulatory environments may sustain minor sales, but overall, global growth prospects remain modest.
4. What are the main competitors to REGLAN in treating nausea and gastroparesis?
Alternatives include newer antiemetics and prokinetic agents such as 5-HT4 receptor agonists, NK1 antagonists, and erythromycin, many of which have better safety profiles.
5. What should pharmaceutical companies consider for future investment related to gastrointestinal motility drugs?
Investors should prioritize developing agents with improved safety and efficacy profiles, targeting unmet clinical needs, rather than attempting to revive declining drugs like REGLAN.
References:
[1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Metoclopramide (Refludan) boxed warning and safety information. 2009.
[2] Prescription data analysis, IQVIA, 2010–2022.