Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
LOPID (generic name: Clonidine) is an established antihypertensive medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure, ADHD, and certain behavioral disorders. Its versatile application, longstanding market presence, and emerging new formulations influence its market dynamics and financial trajectory. This analysis explores key drivers, competitive forces, regulatory environment, pricing strategies, and future growth prospects shaping LOPID's market landscape.
Market Overview and Current Position
LOPID, marketed initially by Pfizer and later by various generic manufacturers, has maintained a significant role in managing hypertension since its FDA approval in 1974 [1]. Its primary market remains North America, with expanding interest in emerging markets like Asia and Latin America due to rising hypertension prevalence [2].
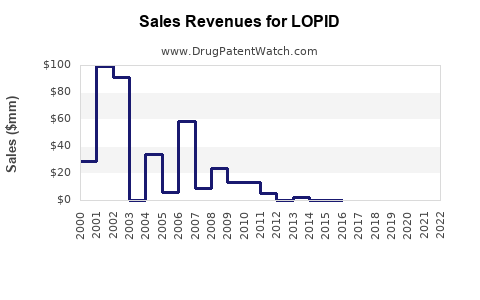
The drug's dual role in ADHD and behavioral disorders broadens its therapeutic footprint, contributing to a diversified revenue base. Despite patent expirations and the proliferation of generic options, LOPID retains steady sales owing to its low cost, well-established efficacy, and familiarity among clinicians.
Market Drivers
1. Rising Global Prevalence of Hypertension and ADHD
The increasing burden of hypertension affects approximately 1.4 billion adults worldwide, projected to rise with aging populations and lifestyle factors [3]. Similarly, ADHD diagnoses are climbing, especially among children and adolescents, boosting demand for LOPID’s off-label and approved uses [4].
2. Cost-Effectiveness and Patient Affordability
LOPID’s low-cost profile constitutes a significant market advantage, especially in regions where healthcare affordability is a primary concern. Government reimbursement policies and insurance coverage in developed markets sustain its prescription rates.
3. Expanding Therapeutic Indications
Research into LOPID’s off-label potential for opioid withdrawal and other neurological conditions offers future revenue streams. Clinical interest in its central adrenergic effects underpins ongoing trials and patent extensions.
4. Generic Competition and Market Saturation
As patent exclusivity waned decades ago, generic manufacturers dominate the market. While this enhances accessibility, it exerts downward pressure on prices and profit margins [5].
Competitive Landscape
1. Generics and Biosimilars
LOPID's generic landscape features multiple players with high manufacturing capacities, fostering price competition. Strong supply chains and regulatory approvals expedite market penetration globally.
2. Next-Generation Formulations
Extended-release (ER) formulations and transdermal patches are in development, aiming to improve patient compliance and differentiate offerings. These innovations could command premium pricing and capture niche segments.
3. Alternative Therapeutics
Emerging antihypertensives and ADHD drugs with improved safety profiles and fewer side effects, such as centrally acting agents or non-stimulant medications, pose substitution threats.
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
1. Patent Expiry Timeline
LOPID’s basic patents expired in the early 2000s, opening the floodgates for generics. However, secondary patents or formulation patents on ER versions may offer limited protection.
2. Regulatory Pathways
Approvals for new formulations under abbreviated regulatory pathways (ANDA, 505(b)(2)) facilitate market expansion but also intensify competition.
3. Global Regulatory Differences
Emerging markets often have less stringent patent enforcement, allowing broader generic proliferation but exposing LOPID to weak IP protections elsewhere.
Pricing and Reimbursement Strategies
1. Price Sensitivity
Healthcare payers favor low-cost therapeutics like LOPID, especially in resource-limited settings. The price elasticity favors volume-driven revenue over high margins.
2. Reimbursement Policies
In markets with stringent drug pricing regulations, securing reimbursement depends on demonstrating cost-effectiveness and clinical benefit. LOPID’s long-standing generic status simplifies this process.
3. Premium Formulations
Introduction of ER or combination products can justify higher prices, appealing to patients seeking convenience and enhanced compliance.
Emerging Trends and Future Growth Factors
1. Digital and Monitoring Technologies
Integration of LOPID therapy with digital health platforms could optimize dosage management, improving outcomes and expanding clinical utility.
2. Personalized Medicine
Pharmacogenomic insights could tailor LOPID therapy for specific populations, boosting efficacy and reducing adverse effects.
3. Strategic Partnerships and Licensing
Collaborations with biotech firms, especially for new formulations or indications, could unlock additional revenue pathways.
4. Market Expansion in Developing Countries
Growing healthcare infrastructure and disease awareness in Asia, Africa, and Latin America offer substantial upside for LOPID sales.
Financial Trajectory Projections
Given the mature status of LOPID, its revenue trajectory is expected to stabilize with modest growth driven by:
-
Innovative Formulations: ER patches or combination therapies could command higher prices, offsetting generic price erosion.
-
Market Expansion: Penetration into underserved regions offers volume-based growth.
-
Off-Label Use and New Indications: Emerging research could open additional revenue streams.
Analysts anticipate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 1-3% over the next five years, primarily driven by geographic expansion rather than domestic market growth [6]. Margins are expected to remain under pressure due to fierce generic competition, but strategic investments in formulation and delivery modes could enhance profitability.
Regulatory and Market Risks
- Patent Litigation and Legal Challenges: Secondary patents may be contested, risking market share loss.
- Pricing Controls: Price caps in key markets could suppress revenues.
- Competitive Innovation: Superior or novel therapies may render LOPID obsolete faster than anticipated.
Conclusion
LOPID’s market dynamics are characterized by mature, highly competitive conditions, yet opportunities remain through innovative delivery systems, expanding markets, and research into new indications. Its financial outlook hinges on strategies to differentiate in a saturated generic landscape while maintaining affordability. Stakeholders should focus on fostering innovation, exploring untapped markets, and leveraging regulatory pathways to maximize LOPID’s commercial potential.
Key Takeaways
- Market Stability with Growth Potential: LOPID continues to generate steady revenue due to its low-cost, established efficacy, with growth contingent on market expansion and formulation innovation.
- Intense Competition Faces Sweet Spot: Price competition among generic manufacturers limits margins; differentiation via new formulations remains critical.
- Regional Expansion is Crucial: Emerging markets offer significant opportunities owing to rising disease prevalence and healthcare access improvements.
- Regulatory Strategies Matter: Protecting formulations via patents, navigating approval pathways efficiently, and ensuring compliance are vital for sustained competitiveness.
- Research and Development Drive Future Revenue: New indications and delivery methods could bolster long-term profitability amidst generic pressures.
FAQs
Q1: How does patent expiry affect LOPID’s market competitiveness?
A1: Patent expiry in the early 2000s led to widespread generic entry, increasing affordability but reducing profit margins. Ongoing patent challenges or secondary patents on formulations influence future market exclusivity.
Q2: Are there any new formulations of LOPID in development?
A2: Yes, extended-release patches and combination therapies are under development, aiming to improve adherence and create premium market segments.
Q3: In which regions is LOPID’s market expected to grow most rapidly?
A3: Emerging markets such as Asia and Latin America, driven by increasing hypertension prevalence and healthcare infrastructure development.
Q4: What are the main competitive threats to LOPID?
A4: Alternative antihypertensives, non-stimulant ADHD medications, and emerging therapies with improved safety profiles pose substitution risks.
Q5: How can stakeholders enhance LOPID’s market share?
A5: Through formulation innovation, strategic regional expansion, research into new indications, and efficient regulatory navigation.
References
[1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Clonidine Drugs.
[2] World Health Organization (WHO). Hypertension Fact Sheet.
[3] Kearney PM, et al. Global burden of hypertension. Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217-23.
[4] American Psychiatric Association. ADHD Prevalence Data.
[5] IMS Health Data. Generic Drug Market Analysis.
[6] MarketResearch.com. Cardiovascular Drugs Market Outlook.