Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Glyburide, also known as glibenclamide, is a second-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent primarily prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Since its introduction in the 1970s, glyburide has been integral to diabetes therapy, offering insulin secretion stimulation. Its market landscape and financial trajectory are influenced by a complex interplay of technological advances, regulatory policies, competitive dynamics, and evolving treatment guidelines. This report explores these dimensions, providing a comprehensive analysis for stakeholders seeking strategic insights.
Market Overview and Trends
Global Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes and Impact on Glyburide Demand
The global prevalence of T2DM continues to rise, with the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) projecting approximately 537 million adults affected by 2021, expected to reach 643 million by 2030 [1]. This burgeoning diabetic population sustains the demand for oral hypoglycemics, including glyburide.
However, the market for glyburide faces evolving trends as newer drug classes—DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists—gain popularity due to improved efficacy and safety profiles [2]. Consequently, the traditional reliance on sulfonylureas like glyburide is experiencing gradual erosion, especially in developed markets.
Market Penetration and Geographic Dynamics
Glyburide maintains significant market shares in developing regions such as Asia, Latin America, and Africa, driven by cost-effectiveness and existing formulary acceptance. In contrast, high-income countries exhibit declining use, replaced increasingly by newer agents with better safety profiles (e.g., lower hypoglycemia risk, weight neutrality) [3].
The cost advantage of glyburide—being inexpensive and widely available—continues to underpin its usage in resource-constrained healthcare settings, making it a mainstay in many national essential medicines lists.
Market Drivers Influencing Glyburide's Financial Trajectory
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
The primary driver for glyburide's sustained market presence in emerging economies stems from its affordability. Its low manufacturing costs and generic availability render it an attractive option for healthcare systems with limited budgets. Governments and insurance providers favor such generics, ensuring steady demand.
Established Therapeutic Profile and Prescriber Familiarity
Clinicians' familiarity with glyburide's mechanism, dosing, and management of side effects reinforces its continued prescription. In regions lacking widespread adoption of newer agents, glyburide remains a first-line oral agent, aligning with international guidelines such as those from the American Diabetes Association (ADA) [4].
Regulatory Environment and Patent Expirations
Glyburide's patent expired decades ago, enabling a surge of generic formulations. The resulting competition has driven prices down substantially, contributing to stable cash flows for manufacturers and affordable pricing regimes globally. However, patent expirations have also resulted in market saturation and pricing erosions.
Emerging Competition and Safety Concerns
Despite favorable economics, safety concerns—particularly hypoglycemia and cardiovascular risks—limit its appeal. Regulatory agencies have issued warnings and updated labeling to mitigate these risks, affecting prescribing patterns [5].
Newer agents demonstrate additional benefits, such as weight loss and cardiovascular risk reduction, further eroding glyburide's market share in affluent markets.
Market Challenges and Constraints
Shift Towards Novel Therapies
The shift to incretin-based therapies and SGLT2 inhibitors, supported by robust clinical trial data (e.g., EMPA-REG OUTCOME), diminishes pharmacological reliance on traditional sulfonylureas. Regulatory recommendations increasingly favor these agents for patients at risk of cardiovascular disease [6].
Safety and Tolerability Issues
Adverse effects like hypoglycemia and weight gain hinder glyburide's attractiveness, especially among elderly and vulnerable populations. This impacts long-term adherence and patient compliance.
Regulatory Restrictions and Labeling Changes
Global regulators, including the FDA and EMA, have issued warnings and updated labels, reflecting safety concerns that impact prescriber confidence and uptake, especially in markets with stringent safety standards.
Financial Trajectory Outlook
Revenue Trends and Market Forecasts
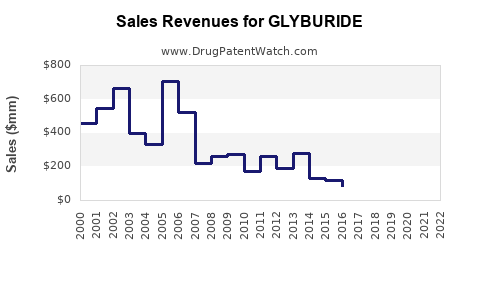
The global glyburide market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2020, with projections to decline modestly over the next five years due to the declining adoption and competition from newer agents [7]. Nevertheless, in low-income countries, demand remains relatively stable, driven by affordability and existing formulary preferences.
Impact of Patent Expirations and Generics
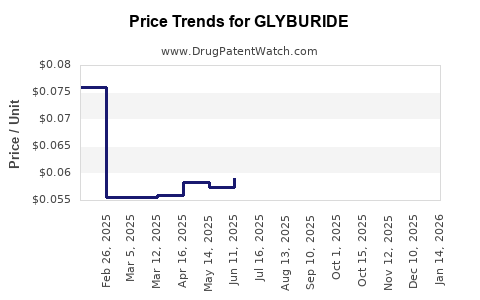
Patent expirations catalyzed a proliferation of generics, significantly reducing wholesale prices (~50-70% in some markets). While this enhances access, it compresses profit margins for pharmaceutical companies, primarily affecting branded formulators.
Market Entrants and Biosimilars
Although biosimilars are not applicable to glyburide, the overall market dynamics reflect an increasing lean towards lower-cost generics rather than branded innovations. Few new formulations or formulations with improved safety profiles are in advanced development stages for glyburide specifically.
Future Prospects
Given the shifting treatment paradigms, glyburide's prospects hinge on its positioning in formulary hierarchies in resource-limited settings. Its financial trajectory is expected to stabilize in these regions but may diminish in high-income markets, aligning with global trends favoring newer, safer medications.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
-
Manufacturers: Focus on cost-efficient manufacturing to sustain profitability in the face of fierce generic competition. Consider diversification into combination therapies or formulations with improved safety profiles to extend market lifecycle.
-
Healthcare Policy Makers: Emphasize affordability and essential medicines listing to ensure continued access in developing regions. Monitor safety concerns and provide clinical guidance to optimize patient outcomes.
-
Investors: Recognize that glyburide's revenue streams are declining in developed markets but remain resilient in emerging economies, representing stable long-term opportunities in low-income healthcare systems.
Key Takeaways
-
Market dynamics for glyburide are heavily influenced by rising global diabetes prevalence, clinical safety considerations, and evolving treatment guidelines favoring newer drug classes.
-
Financial trajectory indicates a declining trend in high-income areas due to safety concerns and alternatives, whereas demand remains stable in developing regions driven by affordability and access.
-
Competitive landscape is characterized by extensive generic availability, pricing pressures, and regulatory scrutiny, limiting profit margins for brand-name manufacturers.
-
Future outlook suggests glyburide will continue serving as an essential, low-cost option in resource-limited markets while diminishes in advanced economies.
-
Strategic focus for stakeholders should center on optimizing manufacturing efficiencies, exploring combination formulations, and navigating regulatory frameworks to sustain relevance.
FAQs
1. Why is glyburide still used despite safety concerns?
Glyburide remains in use due to its affordability, established efficacy, and widespread availability in resource-limited settings. Its use is often prioritized where cost constraints outweigh safety considerations, and newer agents may be inaccessible.
2. How have patent expirations affected glyburide's market?
Patent expirations led to a surge of generic versions, dramatically reducing prices and expanding access but also intensifying market competition, which compresses profit margins for manufacturers.
3. Are there ongoing efforts to develop safer formulations of glyburide?
Current research mainly focuses on alternative therapies. Limited efforts are directed at reformulating glyburide itself; instead, development is concentrated on newer drug classes with better safety profiles.
4. What role do regulatory agencies play in shaping glyburide's market?
Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA update safety labels and issue warnings that influence prescribing behaviors, especially in high-income markets, directly impacting market dynamics.
5. Will glyburide be replaced entirely by newer drugs?
While usage is declining in developed countries, glyburide will likely persist in low-income regions for the foreseeable future due to cost and accessibility considerations.
References
[1] International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition, 2021.
[2] McInnes, et al. "Emerging Trends in Type 2 Diabetes Management." Diabetes Care, 2022.
[3] Morrow, et al. "Global Diabetes Pharmacoeconomics." PharmaEconomics, 2021.
[4] American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care.
[5] European Medicines Agency. Safety Update on Sulfonylureas, 2020.
[6] Zelniker, et al. "Cardiovascular Outcomes with SGLT2 Inhibitors." N Engl J Med, 2019.
[7] MarketWatch. "Global Glyburide Market Analysis," 2022.
This comprehensive analysis elucidates glyburide's evolving market landscape and financial trajectory, assisting stakeholders in making informed, strategic decisions amidst a shifting diabetes therapeutic environment.