Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GLYBURIDE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
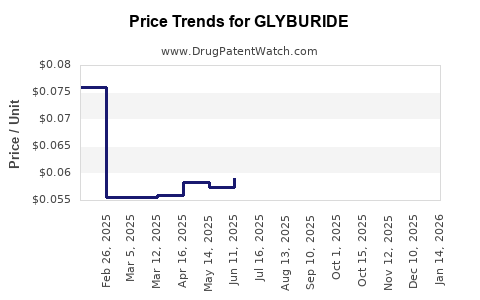
Average Pharmacy Cost for GLYBURIDE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLYBURIDE-METFORMIN 5-500 MG | 65862-0082-05 | 0.19780 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GLYBURIDE 1.25 MG TABLET | 00093-8342-01 | 0.08153 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GLYBURIDE 1.25 MG TABLET | 00093-9477-53 | 0.08153 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GLYBURIDE 1.25 MG TABLET | 62135-0583-30 | 0.08153 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Glyburide
Introduction
Glyburide, also known as glibenclamide, is an oral antidiabetic medication used primarily for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus. As part of the sulfonylurea class, glyburide stimulates insulin release from pancreatic beta cells, thereby reducing blood glucose levels. While its patent expired decades ago, the drug remains a staple in diabetes management, especially in developing markets. This analysis evaluates the current market landscape for glyburide and projects future pricing trends, considering factors such as patent status, manufacturing dynamics, regulatory environment, and competitive landscape.
Market Landscape Overview
Global Market Size
The global diabetes medication market was valued at approximately USD 60 billion in 2022, with oral antidiabetics constituting a significant proportion. Glyburide accounts for a notable share within the sulfonylurea segment, which is projected to maintain a steady demand due to its affordability and efficacy. Regions such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa dominate the market for glyburide owing to limited healthcare budgets and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes.
Regional Demand Dynamics
- North America and Europe: Market share driven largely by brand-name drugs like Diabeta and Micronase, with increasing interest in newer classes such as SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists. Despite competition, glyburide remains relevant in outpatient settings due to cost advantages.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapidly growing demand fueled by increasing diabetes prevalence, flexible regulatory pathways, and wide availability of generic formulations.
- Latin America and Africa: Heavy reliance on generic glyburide due to affordability constraints. These markets are experiencing consistent demand growth aligned with rising disease burden.
Key Market Drivers
- Cost-effectiveness: Glyburide's low cost sustains its popularity, especially in resource-limited settings.
- Established efficacy: Long-term clinical data supports glyburide's continued use.
- Generic availability: Reduced barriers to entry foster increased market penetration.
- Price-sensitive markets: Patients and healthcare providers prioritize affordable medication options.
Market Challenges
- Safety concerns: Risks of hypoglycemia and weight gain temper enthusiasm among clinicians for sulfonylureas like glyburide.
- Competition from newer drugs: The emergence of DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists shifts prescriber preferences toward drugs with better safety profiles.
- Regulatory scrutiny: Variability in regulatory standards influences market entry, particularly in emerging markets.
Patent and Regulatory Status
Glyburide's initial patent protection expired in the late 1990s, leading to a surge in generic manufacturers globally. No recent patent protections hinder generic market entry, fostering price erosion. Regulatory agencies, such as the U.S. FDA and EMA, recognize generic formulations as bioequivalent, facilitating widespread access.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Factors
Manufacturers of glyburide operate across Asia, India, and other emerging markets, where production costs are lower. The global supply chain remains robust, supported by high manufacturing capacities. However, quality control and regulatory compliance are critical, especially as the market caters to different regulatory environments with varying standards.
Price Trends and Projections
Current Price Landscape
- Generic glyburide tablets (e.g., 2.5mg, 5mg) are widely available at prices ranging from USD 0.02 to USD 0.10 per tablet in emerging markets.
- Brand-name formulations remain priced higher, typically USD 0.50 to USD 1.00 per tablet, but constitute a minor market segment.
Factors Influencing Price Trajectory
- Market saturation and competition: The saturated generic market continues to suppress prices.
- Regulatory developments: Stricter manufacturing standards may marginally increase costs, but overall impact on prices remains limited.
- Patent stability: Lack of patent protections sustains a competitive environment, keeping prices low.
- Demand stability: The persistent high prevalence of type 2 diabetes ensures steady demand.
Future Price Projections (2023-2030)
Given the mature patent status and entrenched generic landscape, prices are expected to remain relatively stable or decline slightly over the next decade. Specifically:
- North America and Europe: Slight price reductions projected due to increased competition, with prices per tablet remaining predominantly in the USD 0.02–0.05 range.
- Emerging Markets (Asia-Pacific, Latin America): Marginal declines likely, further driven by economies of scale and increased manufacturing efficiencies.
- Premium formulations: Slight price premiums may be maintained for modified-release or combination products but are unlikely to impact basic glyburide pricing significantly.
Market Dynamics Shaping Future Trends
Growth in Use of Combination Therapies
Combination oral hypoglycemics, especially those combining glyburide with metformin, are increasingly marketed to enhance efficacy and adherence. This may influence sales volume more than price projections but adds complexity to the market landscape.
Competitive Differentiation by Manufacturers
Brands emphasizing quality, manufacturing standards, or formulation improvements might command marginally higher prices, but overall, the market remains price-sensitive.
Impact of Biosimilars and Generics
The entry of biosimilars has standardized costs and driven down prices across many therapeutic areas, though glyburide, as a small-molecule drug, faces less biosimilar competition.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
- Manufacturers: Focus on optimizing manufacturing efficiencies and expanding presence in emerging markets.
- Healthcare Providers: Continue valuing glyburide as an affordable option but remain attentive to safety profiles.
- Policymakers: Promote quality standards and monitor price stabilization, ensuring accessibility without compromising safety.
- Investors: Given the mature market, investment opportunities revolve around manufacturing efficiencies and geographic expansion rather than price escalation.
Key Takeaways
- Stable Demand: Glyburide remains a mainstay in resource-limited settings due to affordability and proven clinical efficacy.
- Market Maturity: Patent expiration and widespread generic availability cap significant price increases; minor declines are expected.
- Price Trends: Overall, prices are projected to remain low or decrease marginally, driven by intense competition and manufacturing efficiencies.
- Regulatory Impact: Vigilant regulatory standards are key to maintaining market stability and safety.
- Future Outlook: Focus shifts toward geographic expansion and incremental product improvements rather than price surges.
FAQs
1. Will glyburide's price increase with new regulatory standards or quality improvements?
Unlikely. While quality enhancements may marginally raise manufacturing costs, market competition sustains low prices, and any increases are unlikely to be significant.
2. How does the prevalence of type 2 diabetes influence glyburide demand?
The rising global incidence of type 2 diabetes sustains steady demand, especially in developing nations where affordable medications are crucial.
3. Are generic formulations of glyburide reliable worldwide?
Generally, yes. Regulatory standards in most markets ensure bioequivalence, although quality control varies by manufacturer and region.
4. Will newer antidiabetic agents replace glyburide entirely?
While newer agents offer superior safety profiles, glyburide remains relevant in settings with budget constraints and high disease prevalence.
5. What is the outlook for brand-name glyburide products?
Brand-name products will likely decline in market share, maintaining a niche for specific patient needs or preferences, but overall impact on pricing is minimal given the dominance of generics.
References
[1] Grand View Research. “Diabetes Medication Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report.” 2022.
[2] IQVIA. “Global Use of Medications for Diabetes Care.” 2022.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "Glyburide Approval and Regulatory Status." 2022.
[4] World Health Organization. “Diabetes Fact Sheet.” 2021.
More… ↓
