Last updated: August 4, 2025
Introduction
Glucophage (generic name: metformin) remains one of the most widely prescribed antidiabetic medications worldwide. Since its approval in the 1950s and subsequent global adoption, its market dynamics and financial trajectory have been shaped by evolving therapeutic landscapes, regulatory policies, manufacturing innovations, and demographic shifts. This detailed analysis delineates the current market factors influencing Glucophage’s position and prospects within the pharmaceutical industry.
Historical Context and Market Penetration
Glucophage was first introduced in France in the late 1950s and gained approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1995. Its emergence as a first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) stemmed from its efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness, distinguishing it from older drugs like sulfonylureas and insulin. Globally, metformin has been prescribed to over 120 million patients annually, underscoring its entrenched market presence [1].
The drug’s affordability and recognition as an effective, low-risk medication have sustained its high prescription volume, especially in emerging markets where economic factors heavily influence pharmaceutical choices. Data indicates that the global metformin market was valued at approximately USD 2.3 billion in 2020, with projections reaching USD 3.5 billion by 2027, driven by increasing diabetes prevalence and expanding healthcare access [2].
Market Dynamics
1. Increasing Global Diabetes Prevalence
The central driver in the demand for Glucophage is the rising incidence of T2DM. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), approximately 463 million adults lived with diabetes in 2019, with projections exceeding 700 million by 2045. Developing economies, such as India and China, report the largest absolute growth, fueled by urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and dietary shifts. This demographic trend directly propels the demand for metformin, considering its position as the first-line treatment choice recommended by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) [3].
2. Therapeutic Market Expansion
Beyond its traditional role, research has expanded metformin’s potential applications. Clinical trials explore its efficacy in weight management, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and as an adjunct in cancer therapy. These emerging indications could diversify revenue streams, stimulate off-label use, and influence future patent strategies, especially considering some formulations are now under patent expiration.
3. Patent Expirations and Generic Competition
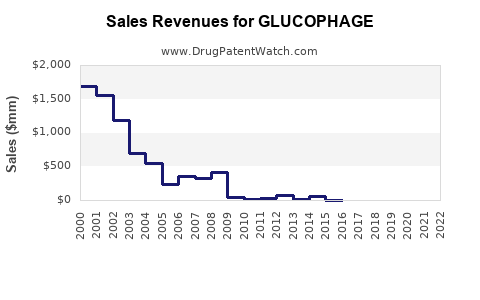
Major patent for Glucophage has long expired, facilitating widespread generic manufacturing. Generics account for over 90% of prescriptions in most markets, significantly reducing prices and profit margins for brand holders. For example, in the U.S., the first generic versions appeared post-2003, intensifying price competition (see figure 1). This commoditization pressures brand revenues but also boosts volume sales through affordability and broad accessibility.
4. Regulatory and Quality Control Factors
Regulatory agencies monitor manufacturing standards to prevent issues like the 2019 FDA recall of certain metformin products due to N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) impurities, a potential carcinogen. Such events influence supply chains, costs, and consumer confidence, impacting sales volumes temporarily but driving manufacturers to tighten quality controls, possibly raising production costs.
5. Competitive Landscape and Alternative Therapies
Newer classes of antidiabetic drugs, including SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists, have gained popularity due to additional cardiovascular and renal benefits. While these drugs command higher margins, they also pose threat to metformin’s market share, especially among patients with comorbidities. Nonetheless, metformin’s low-cost profile sustains its market dominance, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Financial Trajectory Analysis
1. Revenue Trends
The stable and predictable prescription patterns make Glucophage a reliable revenue contributor for manufacturers. While overall revenue growth hinges on volume rather than price increases—given the extensive generic competition—incremental growth is driven by rising disease prevalence and expanding indications.
Major pharmaceutical companies like Teva, Mylan, and pharmaceutical giants such as Merck and Novo Nordisk generate substantial sales from metformin formulations, including oral tablets and combination products.
2. Pricing Strategies
The commoditized nature of generics constrains pricing flexibility. Nonetheless, companies focus on differentiated formulations—extended-release versions, fixed-dose combinations—to command premium pricing in certain markets. In the U.S., the average retail price for metformin 500 mg extended-release tablets can reach USD 20-30 per month, compared to USD 5-10 in low-income countries.
3. Market Penetration and Access
Expanding healthcare coverage and generic availability in developing nations bolster sales volume. The Affordable Care Act in the U.S. and initiatives by the WHO support increased access, translating to steady revenue streams. Additionally, patent lapses facilitate market entry of biosimilars and generics, further intensifying competition but also expanding market size.
4. Future Revenue Projection
Given the global diabetes epidemic, projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the metformin market is estimated at 4-6% through 2027. The high prevalence of prediabetes, where metformin is used for prevention, can further contribute to revenue streams. However, pricing pressures remain a significant constraint on profit margins.
Emerging Trends Impacting Market and Finance
- Personalized Medicine: Innovations in pharmacogenomics may influence patient stratification, affecting prescribing patterns.
- Combination Drugs: Co-formulations of metformin with SGLT2 inhibitors or DPP-4 inhibitors are gaining approval, creating new patent opportunities and revenue streams.
- Regulatory Environment: Strict impurity standards for NDMA lead to higher manufacturing costs, influencing profit margins.
- Sustainability Pressures: Manufacturers are investing in environmentally sustainable production processes, which may marginally affect costs but could enhance market goodwill.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
While the original patent for Glucophage has expired in most markets, some derivatives and formulations remain under patent protection, offering exclusivity advantages. Patent landscapes are complex, with recent litigations focusing on formulation patents and manufacturing processes. Biosimilars and generics dominate the landscape, pressuring prices but expanding access.
Conclusion
The market for Glucophage exemplifies a mature therapeutic segment characterized by high demand driven by global diabetes prevalence, cost-effective manufacturing, and extensive generic competition. Financially, the trajectory remains stable and moderately growing, constrained mainly by pricing pressures and emerging therapies. Strategic diversification into combination formulations, expanding indications, and quality assurance processes will be pivotal for sustained profitability.
Key Takeaways
- Demand persists: The rising prevalence of T2DM worldwide maintains robust demand for Glucophage, supporting ongoing revenue streams.
- Pricing constraints: Extensive generic competition limits price increases, emphasizing volume-driven growth.
- Patent dynamics: Expiration of key patents opened markets for generics and biosimilars, intensifying competition but expanding access.
- Market diversification: New formulations, combinations, and indications can mitigate revenue stagnation.
- Regulatory vigilance: Quality control for impurities like NDMA remains critical, affecting production costs and brand reputation.
FAQs
1. How does patent expiration impact the financial outlook for Glucophage?
Patent expiration has led to a surge in generic manufacturing, drastically reducing the drug’s price and margins for branded versions. While this pressures revenues, overall sales volume increases due to broader access, ensuring continued profitability for manufacturers focused on volume sales and new formulations.
2. What are the key factors influencing the growth of Glucophage in emerging markets?
Factors include the expanding prevalence of diabetes, increasing healthcare infrastructure, preferential pricing of generics, and governmental initiatives aimed at non-communicable disease control. These elements collectively drive sales expansion in regions like Asia and Africa.
3. What emerging therapies threaten Glucophage’s market share?
Newer drug classes like SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists offer additional benefits such as cardioprotective effects, positioning them as alternatives for patients with specific comorbidities, potentially diminishing the reliance on metformin in certain segments.
4. How do regulatory standards affect the manufacturing and financial viability of Glucophage?
Strict standards for purity (e.g., limits on NDMA impurities) increase manufacturing costs and compliance expenses. Non-compliance can result in recalls, reputational damage, and financial penalties, influencing profit margins and supply stability.
5. What is the future outlook for Glucophage’s market and profitability?
The outlook remains positive, driven by demographic trends and expanding indications. Innovations like fixed-dose combinations and ongoing research into new therapeutic roles bolster its financial trajectory. However, pricing pressures and regulatory challenges necessitate strategic adaptation.
References
[1] International Diabetes Federation. (2019). IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition.
[2] MarketWatch. (2021). Global Metformin Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis, 2020-2027.
[3] American Diabetes Association. (2023). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2023.