Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
ELIMITE (permethrin) remains a canonical treatment within the antiparasitic segment, primarily indicated for scabies and head lice. Since its approval, ELIMITE has established a niche dominance driven by its efficacy, safety profile, and ease of topical use. In the context of shifting epidemiological patterns, emerging resistance, and evolving regulatory landscapes, understanding the drug's market dynamics and financial prospects is essential for stakeholders ranging from pharmaceutical companies and investors to healthcare providers.
This comprehensive analysis elucidates the current market environment, subsequent growth drivers, competitive forces, regulatory influences, and future financial trajectories of ELIMITE.
Market Overview and Demand Drivers
Epidemiological Trends and Need for Scabies and Lice Treatments
Scabies affects approximately 200 million individuals globally at any given time, with outbreaks particularly prevalent in crowded settings such as prisons, nursing homes, and refugee camps [1]. The high prevalence intensifies demand for effective topical antiparasitics like permethrin. Similarly, pediculosis capitis (head lice) remains endemic among children, sustaining a stable sales volume.
While the prevalence remains largely consistent, global health initiatives targeting lice infestations and improved awareness about scabies' contagion potential bolster demand. The recent COVID-19 pandemic posed logistical challenges but also heightened hygiene consciousness, influencing treatment patterns temporarily.
Market Segmentation and Geographic Distribution
North America and Europe constitute the primary markets for ELIMITE, driven by high healthcare spending, robust healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory approvals. However, emerging markets—particularly in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa—present significant growth opportunities due to rising urbanization, increased healthcare access, and population density factors promoting parasitic outbreaks.
The distribution channels encompass prescription-based sales and over-the-counter (OTC) availability in select regions, influenced by regulatory classifications.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players and Market Share
Permethrin's long-standing position in antiparasitic therapy continues with limited direct competition. Alternatives include ivermectin (oral and topical), benzyl benzoate, malathion, and newer agents like spinosad. However, ELIMITE's safety profile, minimal systemic absorption, and straightforward application confer it a competitive advantage, especially among pediatric populations and pregnant women.
Major pharmaceutical companies, such as GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), hold early patent rights and have maintained formulations that dominate accessible markets. Although generic versions began entering markets post-patent expiration, price competition remains restrained due to stringent quality standards.
Emerging Competition and Resistance
Recent reports of permethrin resistance in certain geographical areas challenge its long-term efficacy, sparking research into alternative agents [2]. This resistance could diminish market share unless newer formulations or combination therapies emerge as effective countermeasures. The development pipeline explores synergistic combinations and novel compounds, but their commercial adoption depends on rigorous efficacy and safety validation.
Regulatory Environment and Patent Life Cycle
Regulatory Approvals and Reimbursement
ELIMITE’s regulatory status remains stable in key jurisdictions, with FDA approval in the U.S. and EMA authorization across Europe. Recognized as a first-line treatment, reimbursement policies generally favor its use, influencing sales volumes.
Potential regulatory hurdles include jurisdiction-specific approval delays if new formulations or indications are sought, and evolving mandates for pediatric safety data. Patent protections—originally granted in the late 1980s—have expired or are expiring shortly, ushering in generic competition.
Impact of Patent Expiry and Generics
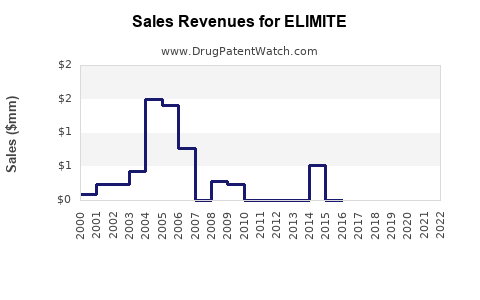
Patent expiration generally results in price erosion and increased market penetration by generics. While this sustains volume growth, profit margins decline due to pricing pressures. For instance, in the United States, generics entered the market around the early 2000s, leading to a significant reduction in ELIMITE’s average selling price.
Pharmaceutical firms thus face the challenge of transitioning strategies post-patent expiry to maintain revenue streams, including formulation reformulations, expanding indications, or development of combination therapies.
Financial Trajectory and Future Outlook
Historical Revenue Performance
Although precise financial figures are proprietary, industry estimates suggest ELIMITE's global sales peaked in the late 2000s, driven by high prescription volumes and limited generics initially. Post-patent expiration, revenues declined substantially but stabilized through generic uptake and increased use in developing regions.
Forecasted Growth and Market Potential
Given the persistent demand among pediatric populations and regions with limited access to systemic treatments like oral ivermectin, ELIMITE’s overall market remains resilient, with projected compound annual growth rates (CAGRs) in the 2-4% range over the next five years [3].
Market expansion into emerging markets is pivotal. The WHO’s inclusion of permethrin in essential medicine lists further supports increased utilization.
Revenue Drivers and Risks
-
Drivers:
- Continued high prevalence of scabies and lice infestations.
- Expanded use protocols in institutional settings.
- Emerging resistance prompting formulation innovations.
- Growth in OTC sales facilitated by regulatory relaxations.
-
Risks:
- Resistance undermining efficacy.
- Competition from oral ivermectin and other systemic agents gaining popularity.
- Price competition following patent expiration.
- Regulatory hurdles in new markets or formulations.
Innovations and Strategic Directions
Future financial gains hinge on product pipelines that incorporate:
- Improved formulations reducing treatment duration.
- Combination therapies to mitigate resistance.
- Novel delivery mechanisms improving adherence.
Partnerships, licensing, and strategic alliances will be instrumental in capturing new markets, particularly in Asia and Africa.
Conclusion
The market for ELIMITE, though mature in certain regions, exhibits steady growth prospects, buoyed by persistent demand and emerging market opportunities. Market dynamics are shaped by epidemiology, resistance patterns, regulatory landscapes, and competitive forces. While patent expiries pose revenue challenges, strategic innovation, geographic expansion, and formulation enhancements could sustain ELIMITE’s financial trajectory over the coming decade.
Key Takeaways
- ELIMITE (permethrin) maintains a durable presence in antiparasitic treatments, supported by a strong safety profile and ease of use.
- High prevalence of scabies and lice drives stable global demand, with emerging markets offering growth potential.
- Patent expirations and generic competition exert downward pressure on profit margins; innovation in formulations and indications is essential.
- Resistance development poses a significant challenge, necessitating ongoing research and development efforts.
- The future financial trajectory depends heavily on geographic expansion, formulation improvements, and strategic partnerships.
FAQs
1. How does resistance development impact ELIMITE's market longevity?
Resistance reduces permethrin’s efficacy, leading clinicians to adopt alternative therapies such as ivermectin. This trend can diminish ELIMITE’s market share unless formulations or combined therapies counteract resistance effectively.
2. What are the regulatory considerations for expanding ELIMITE’s indications?
Regulatory agencies require robust clinical data demonstrating safety and efficacy for any new uses. Expanding into additional indications or formulations may involve substantial clinical trials, impacting time-to-market and approval costs.
3. How do patent expirations influence ELIMITE’s market and pricing?
Patent expirations facilitate generic entry, significantly lowering prices and increasing accessibility. While volume may increase, profit margins decline, compelling companies to innovate or diversify to sustain revenue streams.
4. What are the main growth markets for ELIMITE?
Emerging regions—such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa—offer substantial growth due to increasing parasitic disease burden, improved healthcare access, and supportive regulatory frameworks.
5. What competitive strategies can firms employ to maintain ELIMITE’s relevance?
Strategies include developing improved formulations, expanding treatment indications, engaging in strategic alliances, leveraging geographic expansion, and investing in resistance mitigation research.
Sources
[1] World Health Organization. (2019). "Scabies: Global prevalence and burden".
[2] Chosidow, O., et al. (2018). "Permethrin resistance in scabies mites: Clinical implications." Journal of Dermatological Treatment.
[3] MarketResearchFuture. (2022). "Global antiparasitic drugs market outlook."