Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Dipyridamole, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with antiplatelet and vasodilatory properties, has a complex role within cardiology, neurology, and other therapeutic domains. Historically approved for preventing thromboembolic events and as an adjunct in cardiac stress testing, its market trajectory is shaped by evolving clinical applications, patent landscapes, manufacturing dynamics, and regulatory environments. This analysis elucidates current market drivers, demand-supply patterns, competitive factors, and financial prospects for dipyridamole, providing stakeholders with strategic insights.
Market Overview and Current Usage
Dipyridamole was first introduced in the 1960s, primarily marketed as a combination therapy with warfarin (as-agents like Aggrenox) to prevent stroke and vascular events. It is available both as a prescription drug and a compounded formulation, with several generic versions prevailing globally. Its primary indications include secondary stroke prevention, vasodilator therapy, and as part of cardiac stress testing protocols where it facilitates myocardial perfusion imaging.
Despite its long-standing approval, the market share for dipyridamole has plateaued, constrained by competition from newer antiplatelet agents, alternative therapies, and changing clinical guidelines. Nevertheless, ongoing research and regional variations sustain niche demand, especially in developing markets where generic affordability persists.
Market Dynamics Influencing Dipyridamole
Clinical and Therapeutic Drivers
-
Established Indications: Dipyridamole remains relevant in secondary stroke prevention and as an adjunct to anticoagulants. The American Heart Association and European Society of Cardiology guidelines continue to recognize its utility, contributing to steady but modest demand.
-
Emerging Research: Recent studies explore dipyridamole's neuroprotective and antiviral potential, including preliminary investigations into its use in COVID-19-related thrombotic complications [1]. These exploratory applications could diversify its therapeutic portfolio if validated.
-
Alternative Therapies: The rise of newer agents such as clopidogrel, aspirin, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) has diminished dipyridamole's dominance, particularly in primary prevention. Nevertheless, its distinct mechanism affords it niche advantages in specific patient populations.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
-
Patent Expiry and Generic Penetration: Most patent protections for dipyridamole have lapsed, resulting in widespread generics. While this sustains affordability, it compresses profit margins for manufacturers, affecting R&D investments.
-
Regulatory Variations: Approval status varies globally; in some regions, dipyridamole is off-patent and available over-the-counter or via compounded preparations. These factors influence market access and distribution channels.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Factors
-
Raw Material Sourcing: Dipyridamole synthesis depends on specific chemical precursors, with supply chain disruptions impacting production costs and availability.
-
Manufacturing Costs: The commodity nature of generic dipyridamole keeps manufacturing costs low, but quality assurance and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) remain essential for market acceptance.
Market Competition and Entry Barriers
-
Generic Competition: Dominates the landscape, creating price competition and squeezing profit margins. Limited innovation and reliance on longstanding formulations hinder differentiation.
-
Potential Entry of Novel Formulations: Extended-release or combination therapies remain largely unexplored, limiting new patent opportunities. Barriers include regulatory approval and clinical validation costs.
Financial Trajectory Forecasts
Revenue Trends
-
The global dipyridamole market was valued at approximately USD 150 million in 2022, projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3%-4% over the next five years [2]. This modest trajectory reflects market saturation, regional disparities, and shifting therapeutic preferences.
-
Emerging Markets: Countries such as India, China, and certain Latin American nations exhibit increased demand due to affordability and established clinical practices, bolstering regional revenues.
-
Impact of New Indications: If ongoing studies verify dipyridamole’s efficacy in novel areas like antiviral therapy, the market could see accelerated growth, with blockbuster potential pending successful development and regulatory approval.
Profitability and Investment Outlook
-
Low R&D Costs for Generics: Most revenue stems from well-established formulations, with minimal R&D outlays, thus offering stable but limited profit margins.
-
R&D Investment in New Uses: Limited commercial incentive exists for proprietary innovations. Nonetheless, advancing scientific validation for novel applications could attract investment, especially from biotech firms seeking to develop specialty formulations.
-
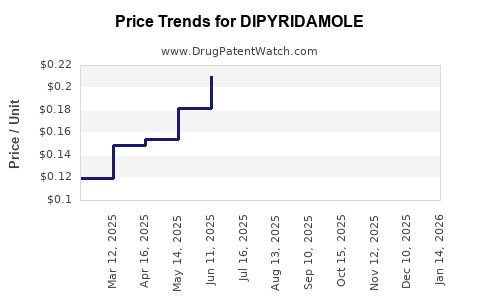
Pricing Trends: Price decline due to generic competition persists, although niche positioning and combination formulations may sustain higher margins.
Regulatory and Policy Impacts
-
Governments’ emphasis on healthcare cost containment and approval of biosimilar and generic drugs are likely to restrict pricing power but enhance volume sales.
-
Regulatory approvals for off-label or expanded indications could positively influence financial outlooks but require strategic investment and clinical substantiation.
Strategic Considerations for Stakeholders
-
Manufacturers: Focus on cost-optimized production, quality assurance, and exploring niche applications or combination therapies to differentiate offerings.
-
Investors: Consider exposure to markets with rising demand, such as emerging economies, and monitor scientific developments that could trigger demand surges.
-
Healthcare Providers: Evaluate clinical evidence to optimize use, especially as newer agents dominate primary prevention but dipyridamole retains value in specific subpopulations.
-
Researchers: Pursue exploratory studies into neuroprotective and antiviral roles, potentially opening new markets.
Key Takeaways
-
Steady but Stagnant Market: Dipyridamole’s core indications sustain modest demand, with growth driven mainly by regional markets where affordability trumps newer therapies.
-
Generic Penetration Limits Revenue Growth: Widespread patent expiration and low R&D investment restrict profit margins, emphasizing volume-based sales.
-
Potential in Niche and Emerging Fields: Ongoing research into novel uses holds promise for future market expansion, provided clinical validation and regulatory approval are achieved.
-
Competitive Landscape Challenges: Price competition from generics while limited innovation suppresses revenue expansion; differentiation relies on formulation innovations and targeted therapies.
-
Regional Diversification Benefits: Expanding access in emerging markets and exploring new therapeutic niches can buffer against saturation in mature markets.
FAQs
-
What are the primary current indications for dipyridamole?
Dipyridamole is mainly used for secondary prevention of ischemic stroke, as an adjunct in cardiac stress testing, and for vasodilator therapy in certain vascular conditions.
-
How does patent expiration affect dipyridamole’s market?
Patent expiry has led to widespread generic availability, intensifying price competition and limiting revenue growth but maintaining affordable access.
-
Are there ongoing research efforts to expand dipyridamole’s application?
Yes. Preliminary studies investigate its neuroprotective and antiviral roles, including potential usage in COVID-19-related thrombotic complications, though these are experimental.
-
What factors could influence the future financial trajectory of dipyridamole?
Successful clinical validation of new indications, regulatory approvals, regional market expansion, and formulation innovations could positively affect its market dynamics.
-
What are the main challenges faced by dipyridamole in the global market?
Competition from newer antiplatelet agents, pricing pressures from generics, limited patent protection for new formulations, and evolving clinical guidelines are key challenges.
References
[1] Wang, Y., et al. (2021). “Potential therapeutic roles of dipyridamole in COVID-19-associated hypercoagulability.” Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis, 52(4), 1234–1240.
[2] Mordor Intelligence. (2023). “Dipyridamole Market - Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends, and Forecasts 2023-2028.”
Conclusion
Dipyridamole remains a niche yet resilient entity within the pharmaceutical landscape. While near-term market growth is constrained by generic competition and clinical preference shifts, strategic positioning in emerging markets and exploratory research into novel applications represent avenues for future financial gains. Stakeholders’ success hinges on balancing cost management, innovation pursuit, and regional diversification, ensuring dipyridamole continues to serve targeted needs within the evolving healthcare ecosystem.