Last updated: July 30, 2025
Introduction
Darifenacin, marketed as Enablex and sometimes as a generic entity, is a selective M3 muscarinic receptor antagonist used primarily to treat overactive bladder (OAB). Since its approval by the FDA in 2004, the drug has navigated a complex market landscape defined by evolving healthcare trends, competitive pressures, and regulatory shifts. This article explores the current market dynamics and examines the financial trajectory of darifenacin within the global pharmaceutical sector.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Market Context
Overactive bladder afflicts approximately 16-17% of the adult population worldwide, primarily impacting individuals aged 40 and above [1]. The condition’s prevalence, coupled with the societal and quality-of-life implications, drives steady demand for effective treatments like darifenacin.
Product Positioning and Competitiveness
Darifenacin targets a niche within the broader antimuscarinic class, distinguished by its notable selectivity for M3 receptors. This selectivity aims to optimize efficacy while minimizing side effects such as dry mouth and constipation—a common issue with less selective agents like oxybutynin. However, the drug faces intense competition from other pharmacologic options, including:
- Mirabegron: A beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonist, offering an alternative mechanism with fewer anticholinergic side effects.
- Other antimuscarinics: Tolterodine, solifenacin, fesoterodine, and trospium.
- Emerging therapies: Combination drugs and novel agents with improved safety profiles.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Darifenacin’s patent life is nearing expiry or has expired in multiple jurisdictions, prompting the entry of generics. Patent expirations generally erode brand revenues, exposing the market to price competition and heightened generic penetration. Regulatory authorities’ approval of generic versions in the US and Europe has intensified price competition, compressing profit margins for originators.
Market Dynamics Influencing Financial Trajectory
Demand Trends
The global OAB market exhibits consistent growth, driven by aging populations and increasing awareness among healthcare providers and patients. According to Research and Markets, the global OAB therapeutics market is projected to reach USD 4.4 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of approximately 4.5% [2]. Darifenacin, as a branded alternative, benefits from brand loyalty but faces shrinking market share as generics and new therapies emerge.
Pricing and Reimbursement
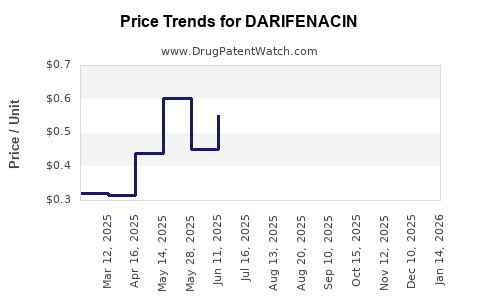
Pricing strategies are pivotal in shaping financial trajectories. The high cost of branded darifenacin constrains uptake where reimbursement policies favor lower-cost generics. Payers’ preference for cost-effective treatments pressures manufacturers to lower prices or develop value-added indications. In markets with strict price controls, such as parts of Europe and Asia, revenue prospects diminish accordingly.
Pipeline and Formulation Innovations
Innovation can rejuvenate market interest. Recent developments include formulations with extended-release profiles, combination therapies, or formulations targeting patient compliance. However, as of now, darifenacin’s pipeline remains limited, restricting future revenue growth unless new indications or formulations are developed.
Impact of Competition and Biosimilars
The entry of generic darifenacin significantly alters the economic landscape. Generics typically reduce per-unit revenue by 70-80% within the first year of market entry [3]. Biologics and biosimilars are less relevant here due to the small molecule nature of darifenacin but remain a disruptive consideration in broader therapeutic areas.
Regulatory and Patent Disputes
Patent litigation and regulatory hurdles can alter financial trajectories. For instance, patent challenges or disputes over formulation patents can expedite generic entry, suppress prices, and diminish revenues. Conversely, successful patent extension strategies or regulatory exclusivities can bolster revenue streams temporarily.
Financial Performance and Trajectory
Historical Revenue and Profit Trends
Historical data indicate that darifenacin experienced robust revenues during early years post-launch, with peak sales occurring around 2007-2010. Post-patent expiry, revenues declined sharply, a common trend among branded drugs facing generic competition.
Current Market Share and Revenue Projections
In mature markets, branded darifenacin’s market share has eroded significantly, often confined to niche segments or specialist settings. Based on recent estimates, global sales in 2022 hovered around USD 200 million, reflecting a downward trend from peak years [4].
Future Outlook
Forecasts suggest a continued decline in global revenues attributable to:
- Increased generic penetration.
- Shift towards alternative therapies like mirabegron.
- Pricing pressures from payers.
- Potential saturation in primary markets.
However, strategic repositioning, such as developing novel formulations or expanding indications (e.g., neurogenic bladder), could introduce revenue growth avenues. The adoption of digital health tools and remote monitoring may also enhance therapeutic adherence, indirectly supporting sales.
Key Drivers of Financial Success or Decline
- Patent strategies and exclusivity periods directly influence revenue lifespan.
- Market acceptance hinges on efficacy, safety, and tolerability relative to competitors.
- Pricing dynamics significantly impact profit margins amid rising healthcare cost containment efforts.
- Pipeline development and clinical positioning can restore growth potential, especially if novel indications or formulations are successfully developed.
Regulatory and Market Challenges
The primary challenges include:
- Patent expirations leading to generic erosion.
- Pricing pressures from payers and government agencies.
- Emergence of alternative therapies with favorable profiles.
- Regulatory hurdles in approving new formulations or indications.
Overcoming these hurdles requires pharmaceutical companies to innovate beyond the molecule, emphasizing value-based healthcare models, and exploring strategic partnerships or licensing agreements.
Conclusion
The financial trajectory of darifenacin reflects typical patterns seen in specialty pharmaceuticals: initial rapid growth, subsequent plateau or decline post-patent expiry, and a need for strategic repositioning. The market remains competitive, with the rising prominence of novel therapies and generics shaping future revenues. Successful adaptation depends on innovation, regulatory intelligence, and strategic marketing to sustain profitability and expand indications.
Key Takeaways
- Demand stability exists, driven by the high prevalence of overactive bladder, but market share for branded darifenacin is declining due to generics and alternative treatments.
- Patent expiration significantly impacts revenues; generics eroded the market share, emphasizing the importance of patent strategies and innovation.
- Pricing pressures and reimbursement policies influence profitability; cost-sensitive markets favor generic formulations.
- Future growth potential hinges on developing new formulations, expanding indications, or leveraging digital health tools.
- Market competition, including emerging therapies like mirabegron, necessitates ongoing differentiation and adaptation.
FAQs
1. What factors predominantly influence darifenacin’s market success?
Market success depends on patent protection duration, competitive landscape (especially generic entry), pricing strategies, regulatory approvals for new indications, and acceptance by healthcare providers and patients.
2. How has patent expiry affected darifenacin's revenues?
Patent expiry led to a surge in generic versions, causing a significant decline (estimated 70-80%) in brand revenue, as generic competition drives prices down and market share shifts.
3. Can darifenacin regain market share with new formulations?
Potentially. Developing extended-release formulations, combination therapies, or securing approval for additional indications can rejuvenate demand and market presence.
4. How is the rise of alternative therapies impacting darifenacin?
Therapies such as mirabegron, which offer different mechanisms and fewer side effects, are gaining popularity, often replacing antimuscarinic agents like darifenacin, thereby affecting its sales.
5. What strategic actions can manufacturers take to sustain long-term profitability?
Investing in pipeline development, exploring new indications, optimizing formulations, negotiating favorable reimbursement terms, and establishing strategic partnerships are key to maintaining profitability.
References
[1] M. M. Stewart, et al., "The Epidemiology of Overactive Bladder," Urology, 2018.
[2] Research and Markets, "Global Overactive Bladder (OAB) Therapeutics Market," 2022.
[3] IMS Health, "Impact of Generic Entry on Market Revenues," 2021.
[4] EvaluatePharma, "Pharmaceutical Market Trends," 2022.