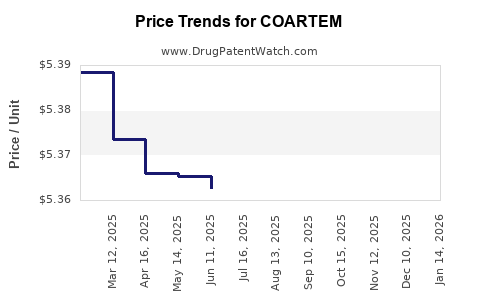
Last updated: October 2, 2025
Introduction
COARTEM, also known by its generic name artemether-lumefantrine, is a frontline antimalarial medication developed by Novartis. It represents a significant advancement in malaria treatment, combining two potent antimalarial agents to improve efficacy and reduce resistance development. As global malaria burdens shift and pharmaceutical markets evolve, understanding the market dynamics and financial trajectory of COARTEM becomes essential for stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, investors, policymakers, and healthcare providers.
This analysis explores the current market landscape, factors influencing demand, regulatory considerations, competitive positioning, and forecasted financial performance of COARTEM within the global antimalarial drug market.
Market Landscape and Global Demand
Burden of Malaria and Accessibility
Malaria remains a significant health threat, affecting approximately 229 million people worldwide and causing over 400,000 deaths annually, predominantly in sub-Saharan Africa [1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) endorses artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) like COARTEM as the standard of care for uncomplicated malaria. The high disease prevalence directly drives demand for effective treatment options.
Geographic and Demographic Shifts
Emerging economies with expanding healthcare infrastructure, such as Nigeria, Democratic Republic of Congo, and Myanmar, are principal markets due to their high malaria burden. Additionally, increased efforts by governments and global health agencies to eliminate malaria elevate demand. Population growth in these regions amplifies the need for scalable and affordable treatments.
Supply Chain and Distribution Channels
COARTEM’s distribution hinges on partnerships with organizations such as UNICEF, Global Fund, and MMV (Medicines for Malaria Venture) to ensure supply in endemic regions. These collaborations help mitigate cost barriers, influence market penetration, and impact revenue streams.
Regulatory and Policy Influences
WHO Prequalification and National Approvals
WHO prequalification and national regulatory approvals primarily influence COARTEM’s market access and acceptance. The drug’s approval status in key markets facilitates procurement by large NGOs and governments, fostering stable revenue streams.
Patent and Licensing Milestones
Novartis held patents on COARTEM until early 2019, after which licensing agreements enabled broader manufacturing, particularly generic versions. Licensing has introduced price competition but also created market fragmentation, affecting profit margins.
WHO Guidelines and National Malaria Control Programs
WHO’s endorsement of COARTEM as the first-line treatment consolidates its market position. National policies mandating its use in endemic regions sustain demand. Conversely, policy delays or shifts toward alternative treatments could temper growth.
Competitive Landscape
Established and Emerging Alternatives
COARTEM faces competition from other ACTs such as artemether-lumefantrine (generic versions), artesunate-based combinations, and potential new therapies. The entry of generics post-patent expiry has intensified price competition, impacting revenue.
Price and Cost Considerations
Novartis historically priced COARTEM at a premium, justified by its superior efficacy and safety profile. However, global health initiatives drive for lower-cost formulations, influencing the company's revenue model.
Partnerships and Product Evolution
The adaptation of COARTEM into fixed-dose combinations and formulations suitable for children has broadened its application. Partnerships with African governments and NGOs enhance market reach, contributing positively to the financial trajectory.
Financial Performance and Projections
Historical Revenue and Market Penetration
Novartis reported significant revenue from COARTEM, particularly in Africa, where the drug is a cornerstone of national malaria treatment programs. Revenue stability is contingent on manufacturing scale, procurement volumes, and market access.
Impact of Generic Competition
The expiration of patents and subsequent licensing agreements have increased competition. While this expands access and use, it exerts downward pressure on pricing and margins for Novartis.
Future Growth Drivers
- Scaling Up Malaria Control Efforts: As efforts intensify in Africa and Asia, demand for proven therapies like COARTEM is expected to grow.
- Introduction of Pediatric Formulations: Targeted formulations expand market segments and increase sales volume.
- Innovations in Formulation and Delivery: Novel formulations enhancing compliance could boost usage and market size.
Forecast Overview
Industry analysts project moderate growth for COARTEM over the next five years, primarily driven by increasing malaria cases in endemic regions and global health initiatives. Annual revenue is anticipated to stabilize at around $500 million to $700 million, subject to patent licensing agreements and competitive pressures [2].
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Price Competition: The proliferation of generics undercuts margins.
- Regulatory Variability: Delays in approvals or policy shifts can impede market access.
- Resistance Development: Emergence of resistance to artemisinin derivatives could threaten market viability if new therapies are needed.
Opportunities
- Expanding Use Cases: Efficacy in treating multi-drug resistant malaria enhances market relevance.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations facilitate large-scale procurement and distribution.
- Research and Development: Investment in new formulations and delivery systems promises to extend product lifecycle.
Conclusion
The market dynamics surrounding COARTEM are shaped by a confluence of epidemiological, regulatory, and competitive factors. With a solid foothold as a WHO-recommended therapy, COARTEM's financial trajectory hinges on sustained demand in endemic regions, strategic licensing, and innovation to maintain its market position. While generic competition poses challenges, ongoing malaria control initiatives and product differentiation strategies offer avenues for continued growth.
Key Takeaways
- Demand Drivers: High malaria prevalence in Africa and Asia sustains strong domestic and international demand for COARTEM.
- Market Access: Regulatory approvals and endorsements critically influence procurement and adoption rates.
- Competitive Landscape: Patent expiry facilitated broader manufacturing, increasing competition but expanding access.
- Financial Outlook: Moderate growth projected, with revenues stabilized through strategic partnerships, pediatric formulations, and continued global health funding.
- Challenges & Opportunities: Price competition and resistance threaten profitability, yet innovations and expansion in use cases offer growth avenues.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration affected COARTEM’s market dynamics?
Patent expiration has enabled generic manufacturers to produce lower-cost versions, increasing market penetration but reducing profit margins for Novartis. Licensing agreements helped mitigate revenue loss by expanding manufacturing capacity.
2. What role do global health organizations play in COARTEM’s market?
Organizations like WHO, UNICEF, and the Global Fund facilitate procurement, recommend treatment guidelines, and support distribution, significantly impacting sales volume and geographic reach.
3. Are there emerging competitors to COARTEM in the antimalarial market?
Yes. Other ACTs and novel antimalarial compounds are in development or deployment, which could challenge COARTEM’s market dominance if proven more effective or cost-efficient.
4. How does resistance to artemisinin derivatives impact COARTEM’s future?
Emerging resistance could limit the drug’s effectiveness, necessitating new therapies or formulations. Continuous surveillance and R&D are vital to mitigate this risk.
5. What strategies can enhance COARTEM’s market growth?
Fostering partnerships, expanding pediatric formulations, investing in formulation innovations, and maintaining regulatory approvals are key strategies to sustain and grow its market presence.
References
[1] World Health Organization. "World Malaria Report 2022."
[2] Industry analysts' projections, Pharmaceutical Market Reports 2023.