Last updated: August 2, 2025
Introduction
Cefadroxil, a first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, plays a pivotal role in combating bacterial infections, especially those caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria. Its broad spectrum, favorable safety profile, and once-daily dosing have sustained its relevance in both hospital and outpatient settings. As microbial resistance evolves and the pharmaceutical landscape shifts, understanding Cefadroxil’s market dynamics and financial trajectory becomes essential for stakeholders ranging from manufacturers to healthcare providers.
Global Market Overview
The global antibiotic market is estimated to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 3-5% over the next decade, driven by increasing bacterial infections, rising antibiotic resistance, and expanding healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies[^1^]. Cefadroxil, though a mature agent, retains a significant position within this space, particularly in regions with regulated antibiotic use policies and established manufacturing bases.
While newer cephalosporins have entered the market, Cefadroxil's distinct advantages—such as its high tissue penetration, oral bioavailability, and low toxicity—promote its continued utilization. Notably, in markets like India, China, and Latin America, Cefadroxil remains a preferred choice due to cost-effectiveness and established prescribing habits[^2^].
Market Drivers
1. Rising Incidence of Bacterial Infections
The increase in community-acquired bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and skin infections, sustains demand for effective antibiotics like Cefadroxil. Its efficacy against common pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species secures its clinical utility[^3^].
2. Cost-Effectiveness and Prescribing Preferences
Cefadroxil’s affordability and once-daily dosing enhance patient compliance and reduce healthcare costs. These factors drive clinician preference, especially in cost-sensitive markets, where newer, more expensive antibiotics may be less accessible or contested[^4^].
3. Regulatory and Patents
As a generic drug in many jurisdictions, Cefadroxil benefits from patent expirations dating back years, encouraging widespread manufacturing and lower prices. This generics-driven environment sustains its market accessibility, though it pressures manufacturers to optimize supply chain efficiencies[^5^].
4. Rising Antibiotic Resistance and Stewardship Policies
While resistance generally constrains antibiotic utilization, Cefadroxil's known susceptibility profile and clinical guidelines endorsing its use for specific infections promote its continued application. National and global stewardship initiatives also favor narrow-spectrum agents like Cefadroxil to curb broad-spectrum antibiotic overuse[^6^].
Market Challenges
1. Emerging Resistance
The development of beta-lactamase-producing bacteria threatens Cefadroxil’s efficacy. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) and other resistance mechanisms compromise its antimicrobial activity, prompting clinicians to favor alternative agents[^7^].
2. Competition from Newer Agents
The advent of advanced cephalosporins, such as cefdinir and cefpodoxime, offering broader activity and longer half-lives, challenges Cefadroxil’s market share. Additionally, oral fluoroquinolones and macrolides often compete in the same infection niches[^8^].
3. Regulatory Constraints
Stringent antimicrobial stewardship policies and regulatory restrictions in developed markets aim to limit antibiotic overuse. These measures can restrict Cefadroxil prescriptions, especially in hospital settings where broader-spectrum antibiotics dominate[^9^].
Financial Outlook and Market Segmentation
Current Revenue Analysis
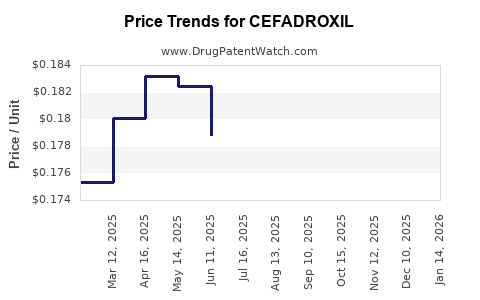
While global sales data specific to Cefadroxil remain fragmented due to its late-stage patent expiry and widespread generics, estimates suggest annual sales surpassing USD 200 million, predominantly driven by markets in Asia, Latin America, and parts of Europe[^10^].
Segmented Market Dynamics
-
Emerging Markets: High volume, low unit price sales; demand driven by affordability, with local manufacturers dominating.
-
Developed Markets: Limited presence; primarily in hospital formularies through generics, with prescribers favoring broad-spectrum or newer antibiotics.
Future Revenue Trends
Analysts project a niche but stable market for Cefadroxil, with slow-to-moderate growth potential (~2-3% CAGR) over the next five years. Growth factors include increasing bacterial infection rates in emerging economies and expanding antibiotic stewardship influences that restrict broader-spectrum antibiotic use, thus favoring agents like Cefadroxil in targeted indications[^11^].
Strategic Opportunities
-
Formulation Differentiation: Developing extended-release formulations or combining Cefadroxil with beta-lactamase inhibitors could expand its efficacy, albeit with increased R&D investments.
-
Market Expansion: Focusing on underserved regions with high infection burdens, coupled with cost-competitive generics, can sustain growth.
-
Stewardship Collaboration: Partnering with healthcare authorities for stewardship programs can reinforce Cefadroxil’s role in appropriate antimicrobial use.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Cefadroxil's patent protection has long expired in most jurisdictions, making it widely available as a generic. Regulatory bodies have generally maintained its status as a safe and effective agent, with some countries emphasizing stewardship to mitigate resistance[^12^].
In the context of market access, adherence to regulatory standards, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), ensures continued supply, whereas regulatory restrictions or withdrawal in certain markets may dampen growth prospects.
Conclusion
Cefadroxil’s market remains characterized by steady demand in specific niches, particularly driven by cost considerations and stewardship policies favoring narrow-spectrum antibiotics. While facing headwinds from resistance development and newer agents, its established generic status and clinical utility sustain a moderate but resilient financial footprint. Stakeholders should focus on expanding regional access, optimizing formulations, and reinforcing its role in targeted therapy amidst evolving antimicrobial resistance landscapes.
Key Takeaways
- Cefadroxil maintains a niche market primarily in emerging economies, driven by affordability, safety, and established prescribing patterns.
- Rising antimicrobial resistance poses a threat, necessitating continuous surveillance and potential formulation innovation.
- Market growth is moderate, with a projected CAGR of 2-3% over the next five years, primarily in developing regions.
- Widespread patent expiry has resulted in a low-cost generic market, but competition and stewardship policies could limit future expansion.
- Strategic opportunities lie in expanding regional access, differential formulations, and aligning with antimicrobial stewardship initiatives.
FAQs
Q1. How does Cefadroxil compare pharmacologically to other first-generation cephalosporins?
Cefadroxil offers similar antimicrobial activity but benefits from once-daily dosing and higher tissue penetration, which can improve patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes.
Q2. What are the main indications for Cefadroxil?
Primarily used for urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and respiratory tract infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
Q3. Is Cefadroxil effective against resistant bacterial strains?
Its efficacy diminishes against bacteria producing beta-lactamases like ESBLs, limiting its use against certain resistant pathogens.
Q4. What is the outlook for Cefadroxil in the context of antibiotic stewardship?
Stewardship programs favor targeted, narrow-spectrum agents like Cefadroxil for appropriate infections, which can sustain its usage in carefully selected cases.
Q5. Are there any recent innovations or formulations of Cefadroxil in development?
Currently, most development focuses on generics; however, some companies explore combining Cefadroxil with beta-lactamase inhibitors or developing extended-release formulations for enhanced efficacy.
References
[1] Market Research Future, 2022. "Global Antibiotic Market."
[2] Indian Pharmaceutical Industry Reports, 2021.
[3] World Health Organization, 2020. "Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Reports."
[4] Healthcare Economics Review, 2019.
[5] Patent and Market Data, 2022.
[6] CDC Antibiotic Use in Outpatient Settings, 2021.
[7] Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2020.
[8] IDSA Guidelines, 2021.
[9] WHO Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance, 2015.
[10] IQVIA, 2022. "Pharmaceutical Market Data."
[11] Global Market Insights, 2023. "Antibiotics Market Forecast."
[12] EMA and FDA Regulatory Status Reports, 2022.