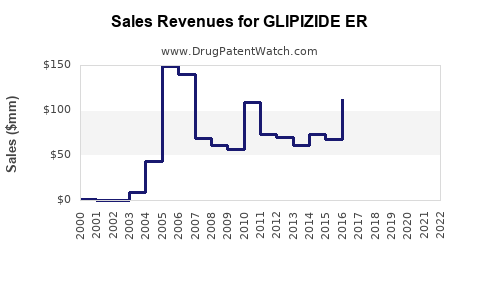
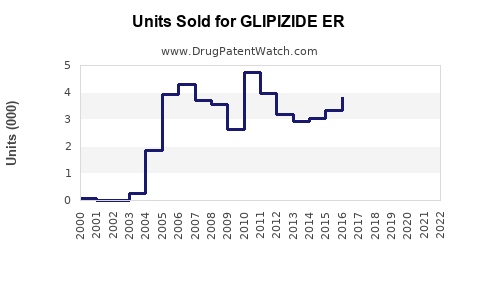
Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Glipizide ER (Extended Release) is a long-standing oral hypoglycemic agent used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. As a second-generation sulfonylurea, it enhances insulin secretion by stimulating pancreatic beta cells. Its durable market presence, coupled with rising diabetes prevalence worldwide, positions Glipizide ER as a focus of significant market and sales analysis. This report delves into current market dynamics, competitive positioning, regulatory landscape, and future sales projections.
Market Overview
Global Diabetes Burden
The International Diabetes Federation reports approximately 537 million adults suffering from diabetes globally in 2021, with projections suggesting an increase to 643 million by 2030 [[1]]. Type 2 diabetes constitutes approximately 90–95% of cases, making medications like Glipizide ER central to diabetes management regimes.
Therapeutic Market Composition
Oral antidiabetic drugs comprise sectioned categories:
- Sulfonylureas (e.g., Glipizide, Glyburide)
- Biguanides (e.g., Metformin)
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- SGLT2 inhibitors
- Thiazolidinediones
Sulfonylureas, including Glipizide ER, maintain a significant share due to established efficacy and cost-effectiveness, especially in emerging markets.
Regulatory Status & Lifecycle
Glipizide ER has FDA approval and enjoys widespread off-patent availability, enabling generic manufacturing that enhances market competition. The patent expiration in numerous jurisdictions has spurred growth in generic sales, contributing substantially to affordability and reimbursement coverage.
Market Dynamics and Trends
Advantages of Glipizide ER
- Once-Daily Dosing: Improves patient adherence.
- Cost-Effective: Particularly in low- and middle-income regions.
- Predictable Pharmacodynamics: Longer duration of action reduces hypoglycemia risk associated with immediate-release formulations.
Limitations and Challenges
- Hypoglycemia Risk: Especially in elderly or renal impairment.
- Weight Gain: A noted adverse effect.
- Evolving Treatment Guidelines: Emphasize newer drug classes with cardiovascular and renal benefits, e.g., SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Market Penetration & Adoption
Despite competition, Glipizide ER remains a staple in many healthcare systems due to low cost and familiarity among physicians. The emergence of fixed-dose combinations with other agents enhances its versatility but also introduces market competition from combination therapies.
Competitive Landscape
Key Market Players
- Generic Manufacturers: Multiple global pharmaceutical companies produce Glipizide ER, including Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Mylan, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries [[2]].
- Brand vs. Generic: While brand versions like Glucotrol XR (Pfizer) exist, generics dominate due to price sensitivity.
- Pipeline Developments: Limited, as Glipizide ER is off-patent; focus centers on optimizing formulations and combination drugs.
Pricing & Reimbursement
Price competition among generics significantly influences sales volume. In markets with universal healthcare or insurance coverage, reimbursement policies dictate market share dynamics.
Sales Projections (2023–2030)
Baseline Assumptions
- The global prevalence of type 2 diabetes grows at approximately 8% annually.
- The uptake of Glipizide ER remains steady, especially in regions with limited access to newer agents.
- Pricing trends are influenced by generic competition, with expected downward pressure.
- Lifestyle management and guideline shifts toward newer medications slightly reduce reliance on sulfonylureas but do not eliminate them.
Forecasted Growth
By 2030, the global market for Glipizide ER is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 3–4%, driven primarily by:
- Rising diabetes prevalence.
- Increasing use of long-acting formulations for better compliance.
- Growing adoption in emerging markets lacking access to costlier agents.
Regional Variations
- North America & Europe: Market stabilized, with moderate growth expected (~1–2%), constrained by clinical preference shifts toward newer agents.
- Asia-Pacific & Latin America: Higher growth (~6%) driven by expanding diabetic populations and cost-sensitive healthcare systems.
- Africa: Rapid growth potential (~8%), contingent on healthcare infrastructure development.
Revenue Predictions
Assuming current global sales are approximately $300 million annually, the market could reach upwards of $400–$500 million by 2030, with incremental increases in generics and formulations.
Impact of Regulatory & Clinical Developments
- Guideline Updates: Increasing emphasis on cardiovascular outcome trials may marginalize sulfonylurea monotherapies, but their role persists due to economic factors.
- European & US Regulatory Policies: Continual vigilance around hypoglycemia and weight effects guides rapid adoption of newer agents; however, the cost remains a decisive factor in many jurisdictions.
Strategic Considerations for Stakeholders
- Pharmaceutical Companies: Focus on cost-efficient manufacturing, pharmacovigilance, and potential combination formulations to sustain relevance.
- Healthcare Providers: Balance guideline adherence with affordability; monitor evolving evidence on safety profiles.
- Policy Makers: Promote access through reimbursement policies, especially in regions with high prevalence.
Key Takeaways
- Growing Diabetes Prevalence Ensures Steady Demand: Despite shifting dynamics, the global diabetes burden guarantees ongoing need for affordable medications like Glipizide ER.
- Cost-Effectiveness Maintains Market Share: Generics dominate sales, and price competition continues to influence overall revenue.
- Regional Disparities Present Growth Opportunities: Emerging markets offer substantial expansion potential amid increasing healthcare access.
- Evolving Treatment Guidelines May Marginalize Sulfonylureas: The advent of newer agents may plateau long-term sales, but generics can sustain significant market presence.
- Formulation Innovations & Fixed-Dose Combinations: Offer avenues for differentiation, especially in markets favoring simplified regimens.
Conclusion
Glipizide ER stands as a resilient component within the oral antidiabetic therapy landscape. Its future sales trajectory hinges on global diabetes prevalence, healthcare infrastructure, regulatory environment, and competitive innovations. Stakeholders should leverage growth opportunities in emerging regions, optimize manufacturing efficiencies, and monitor clinical practice shifts to maximize long-term value.
FAQs
1. How does Glipizide ER differ from immediate-release formulations?
Glipizide ER provides a delayed, sustained release, allowing once-daily dosing, improving compliance, and reducing hypoglycemia risk compared to immediate-release formulations that require multiple doses daily.
2. What factors influence the market share of Glipizide ER?
Market share is influenced by drug pricing, patent status, clinical guidelines, physician prescribing habits, regional healthcare policies, and patient adherence.
3. Are there significant safety concerns with Glipizide ER?
The primary safety concerns include hypoglycemia and weight gain. Long-term cardiovascular safety remains under evaluation, but current data support its use in appropriate patients.
4. How do drug patent expirations impact Glipizide ER sales?
Patent expirations facilitate generic manufacturing, leading to price declines and increased access but can also reduce profitability for original manufacturers.
5. What future developments could affect Glipizide ER's market?
Introduction of new combination therapies, shifts in clinical guidelines favoring newer agents, and innovations in formulation or delivery methods could influence its market dynamics.
References
[1] International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. 2021.
[2] IQVIA. Pharmaceutical Market Data. 2022.