Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for exemestane
✉ Email this page to a colleague
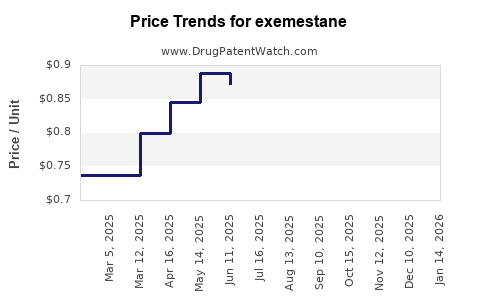
Average Pharmacy Cost for exemestane
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXEMESTANE 25 MG TABLET | 00832-0595-30 | 0.59712 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| EXEMESTANE 25 MG TABLET | 59651-0516-30 | 0.59712 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| EXEMESTANE 25 MG TABLET | 59762-2858-01 | 0.59712 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| EXEMESTANE 25 MG TABLET | 51991-0005-90 | 0.59712 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| EXEMESTANE 25 MG TABLET | 72603-0329-01 | 0.59712 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Exemestane
Introduction
Exemestane, marketed under brand names such as Aromasin, is an oral steroidal aromatase inhibitor primarily used in the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Since its approval by regulatory agencies, including the FDA in 1999, it has established a significant presence within the oncology pharmacological landscape. This comprehensive market analysis examines current market dynamics, competitive positioning, manufacturing and pricing trends, and offers projections for future pricing movements.
Market Overview and Clinical Demand
The global breast cancer therapeutics market was valued at approximately $20 billion in 2022, with endocrine therapies constituting a significant segment, driven principally by the prevalence of ER-positive breast cancer. Exemestane accounts for a substantial share within aromatase inhibitors (AIs), alongside anastrozole and letrozole.
Prevalence and Incidence Trends
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), breast cancer remains the most prevalent cancer among women worldwide, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases in 2020. The postmenopausal demographic increasingly accounts for the bulk of ER-positive cases, contributing to sustained demand for Exemestane. The continued aging population and improved screening practices further bolster market demand.
Pharmaceutical Usage and Adoption
Physician preference for Exemestane has been influenced by its unique steroidal mechanism, which confers advantages in some resistant cases, and its tolerability profile. Its use in adjuvant settings and metastatic diseases consolidates steady demand.
Market Segmentation and Key Players
Competitive Landscape
The primary competitors for Exemestane are other third-generation AIs, notably anastrozole (Arimidex) and letrozole (Femara). Major pharmaceutical companies, including Pfizer (partnered for Aromasin), Novartis, and AstraZeneca, control significant market shares.
Distribution and Pricing Strategies
While originator products maintain premium pricing, generic versions entered markets post-patent expiry, substantially reducing prices and increasing accessibility—especially in emerging economies.
Regulatory and Patent Status
Patent Lifecycles
Aromasin’s patent protections expired in key markets by 2013, paving the way for generics to enter. This has intensified price competition. However, patent distinctions and secondary patents sometimes sustain exclusivity in specific regions.
Regulatory Approvals
Expanded indications, including preventive therapy and combination regimens, have further expanded market potential, subject to regulatory approvals.
Manufacturing and Cost Factors
Production Dynamics
Exemestane’s synthesis involves complex steroidal intermediates, influencing manufacturing costs. Generic producers benefit from streamlined synthesis processes, resulting in cost reductions that translate into lower consumer prices.
Pricing Factors
Pricing is influenced by manufacturing costs, regulatory environment, market competition, and payer negotiations. Brand-name products typically command higher prices, but generic entries have driven down retail and institutional prices.
Current Pricing Landscape
Pricing in Developed Markets
In the U.S., the list price of branded Exemestane can exceed $250 for a 30-day supply (30 tablets of 25 mg), but actual out-of-pocket costs vary significantly due to insurance coverage. Generic versions list at approximately $70–$100 per month (per 30 tablets).
Pricing in Emerging Markets
In regions like India and Brazil, generics are available at substantially lower prices—often below $10 per month—making treatment more accessible.
Market Trends and Price Projections
Short to Medium-Term Outlook (Next 3–5 Years)
- Increased Generic Penetration: As patents expire or are circumvented, generics will dominate the price landscape, driving prices further down. This trend aligns with global shifts toward cost-effective cancer care.
- Price Stabilization in Branded Segment: The brand-name Exemestane’s premium pricing is likely to stabilize or decline slowly, as generic competition intensifies.
- Impact of Biosimilars and New Formulations: While biosimilars are less relevant for small-molecule drugs like Exemestane, new formulations or combination therapies could influence pricing patterns, particularly in personalized medicine approaches.
Long-Term Projections (Next 5–10 Years)
- Gradual Decrease in Average Price: Based on historical trends for oncology generics, prices are expected to decline by approximately 50–70% from current levels in mature markets.
- Evolving Market Dynamics: Market access policies, especially in cost-sensitive regions, and novel AI agents could influence the demand and, consequently, the price dynamics.
- Emerging Market Growth: As healthcare infrastructure improves, demand for affordable Exemestane will rise, potentially opening new markets and further reducing prices.
Regulatory and Policy Influences
Government pricing policies, reimbursement rates, and patent litigations significantly affect prices. Countries with strict price controls, such as those in Europe and parts of Asia, may see more stable or lower prices. Conversely, in markets with limited price regulation, premium pricing may persist until generic competition intensifies.
Implications for Stakeholders
- Pharmaceutical Companies: To optimize profits, companies must balance brand positioning with strategic generic launches. Innovations, such as combination therapies, may offer premium pricing opportunities.
- Healthcare Providers and Payers: Cost containment measures and formulary management are increasingly leaning towards favoring generics, influencing market prices.
- Patients: Affordable access depends heavily on national policies and the availability of generics, impacting adherence and outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- The expiration of Aromasin’s primary patents has catalyzed extensive generic competition, leading to significant price reductions.
- In mature markets like the US and EU, expect branded Exemestane prices to decline by approximately 20–30% over the next 3–5 years, with generics becoming the dominant, cost-effective options.
- Emerging markets represent growth opportunities due to expanding access and regulatory pathways favoring affordable generics, potentially leading to further price drops.
- Innovations in formulation, combination therapies, or patent extensions could temporarily influence pricing; however, the overarching trend favors decreasing prices driven by market competition.
- Policy shifts in healthcare reimbursement and patent law will continue to shape the pricing trajectory, emphasizing the importance of strategic planning for pharmaceutical stakeholders.
FAQs
1. What is the typical current price of Exemestane in developed markets?
In the US, branded Exemestane (Aromasin) typically costs over $250 per month, while generic versions are priced between $70 and $100 monthly, depending on pharmacy discounts and insurance coverage.
2. How has the patent expiry affected Exemestane’s market pricing?
Patent expiry has led to a surge in generic versions, significantly lowering prices—by up to 70%—and increasing market access, especially in price-sensitive regions.
3. Are there upcoming patent protections that could influence future prices?
While primary patents have expired, secondary patents or formulations might extend exclusivity temporarily, but these are often challenged or fall short in preventing generic competition.
4. What factors could slow down the decline in Exemestane prices?
Regulatory delays, patent litigations, supply chain constraints, and ongoing brand loyalty can temporarily slow price declines.
5. How do price projections differ between developed and developing markets?
Developed markets are characterized by stagnant or declining prices due to high generic competition, while emerging markets may see sharper reductions as access and manufacturing scale increase.
Conclusion
Exemestane’s market is undergoing a transformative phase characterized by diminishing prices driven primarily by patent expirations, increased generic penetration, and evolving healthcare policies. Stakeholders must continuously monitor regulatory developments and market entrants to optimize pricing strategies and ensure broader patient access without compromising sustainability. As a core component of breast cancer management, Exemestane remains integral to oncology therapeutics, with its pricing trajectory reflecting broader trends in drug affordability and market competition.
Sources:
[1] WHO. Breast Cancer Fact Sheet. 2020.
[2] U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). Aromasin (Exemestane) Approval Information. 1999.
[3] IQVIA. Global Oncology Market Reports. 2022.
[4] Bloomberg Intelligence. Oncology Drug Pricing Analysis. 2023.
[5] MarketWatch. Breast Cancer Therapy Market Trends. 2022.
More… ↓
