Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for SM MOTION SICKNESS
✉ Email this page to a colleague
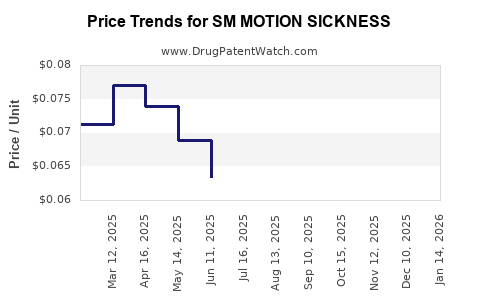
Average Pharmacy Cost for SM MOTION SICKNESS
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM MOTION SICKNESS 50 MG TAB | 70677-0022-01 | 0.05458 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| SM MOTION SICKNESS 50 MG TAB | 70677-0022-01 | 0.06092 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| SM MOTION SICKNESS 50 MG TAB | 70677-0022-01 | 0.06778 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for SM Motion Sickness
Introduction
The management of motion sickness remains a significant segment within the broader pharmaceutical gastrointestinal (GI) and neurovestibular markets. SM Motion Sickness (SM MS) likely refers to a proprietary or branded formulation targeting this condition. As the global travel industry rebounds post-pandemic and an increasing awareness of motion sickness management arises, understanding the market landscape and pricing strategies for such drugs becomes critical for stakeholders. This analysis examines the current market landscape, potential growth drivers, competitive environment, and future price projections for SM Motion Sickness, providing a comprehensive outlook to inform strategic decisions.
Market Overview
Global Incidence and Demand Drivers
Motion sickness affects an estimated 30-50% of the population across various age groups, with prevalence rising among frequent travelers, military personnel, and patients undergoing certain medical procedures. The global travel industry generated approximately $3.4 trillion in revenue in 2022, with mobile and maritime modes contributing significantly to motion sickness cases.[1] Post-pandemic, the resurgence of tourism and increased international mobility are expected to boost demand for effective prophylactic and symptomatic treatment options.
Existing Therapeutic Landscape
Current treatments predominantly include antihistamines (e.g., meclizine, dimenhydrinate), anticholinergics (e.g., scopolamine), and newer agents like promethazine. Over-the-counter (OTC) formulations dominate, with prescription options reserved for severe cases.[2] Despite the variety, unmet needs remain for drugs with improved safety profiles, minimal sedative effects, and rapid onset.
Market Segments and Opportunities
- OTC Market: Estimated to dominate due to accessibility and consumer convenience.
- Prescription Market: Gaining prominence in cases of severe or chronic motion sickness.
- Specialized Treatments: For military, athletes, and airline crews, where tailored formulations may command premium pricing.
The global anti-motion sickness market was valued at ~$1.5 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 4% through 2027.[3] A new entrant like SM MS could capture market share by offering superior efficacy or reduced side effects.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
Major pharmaceutical companies with proprietary formulations include Merck (Dramamine), Johnson & Johnson, and Pfizer (Lomotil variants used off-label), alongside OTC brands like Bonine and Dramamine II.
Innovative and Niche Players
Emerging companies focus on novel delivery systems (e.g., transdermal patches, nasal sprays) and formulations with fewer sedative effects. Biotech startups are exploring neurogenic pathways to mitigate motion sickness without compromising alertness.
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
Patented formulations and delivery mechanisms significantly influence market positioning and pricing power. Patent exclusivity typically spans 10-20 years, with expiry opening market segments to generics and biosimilars, strongly affecting future pricing.
Market Entry and Commercialization Strategies
Product Differentiation: SM MS could distinguish itself via faster onset, longer duration, fewer side effects, or unique delivery methods.
Pricing Strategy: Premium pricing can be justified if clinical data shows superior efficacy or safety; otherwise, competitive OTC pricing becomes necessary.
Regulatory Pathways: Accelerated approval routes (e.g., FDA’s Fast Track/Breakthrough Therapy) could expedite market entry, influencing initial pricing.
Price Projections and Future Outlook
Current Pricing Dynamics
- OTC formulations: Ranged from $8–$15 for a 20-30 dose bottle.
- Prescriptions: Typically range between $25–$50 per prescription, depending on formulation and insurance coverage.
- Premium formulations (e.g., patches): Can reach upwards of $50–$70 per treatment course.
Projected Pricing Trends
Near-term (1–3 years):
An innovative SM MS product with demonstrated clinical benefits could command a premium price of $30–$60 per treatment course for OTC formulations. If marketed as prescription-only with added benefits, prices could increase to $60–$120 per course.
Medium to Long-term (4–10 years):
As patent protections lapse and generics enter, prices will likely decline by 30–50%. Ballooning demand for personalized and non-sedating options may support premium pricing for specialized formulations. Market entry of biosimilars or new mechanisms could create price competition, depressing prices but expanding volume.
Pricing for Niche Markets:
Military and aviation sectors often pay higher prices (up to $150 per dose) for tailored, reliable formulations. SM MS targeting these sectors could maintain high prices through contractual agreements.
Factors Influencing Price Projections
- Regulatory Approval: Fast-track or breakthrough status can enable premium pricing.
- Clinical Efficacy: Superior efficacy and safety profiles justify higher prices.
- Market Penetration: Strategies that secure rapid adoption can sustain premium pricing longer.
- Patent Life and Competition: Patent expiry timelines influence long-term pricing.
Implications for Stakeholders
Pharmaceutical Companies:
Investing in clinical trials demonstrating superior efficacy can support higher initial pricing. Clear differentiation from existing treatments allows premium positioning.
Investors:
Early-stage valuation models should incorporate potential pricing premiums, patent life, and market share projections, with sensitivity to pending generic entry.
Healthcare Providers and Payers:
Reimbursement decisions hinge on cost-effectiveness. Demonstrating reduced side effects or enhanced compliance supports favorable reimbursement landscapes.
Key Market Growth Drivers
- Resurgence of global travel and tourism.
- Increasing prevalence of motion sickness in pediatric and elderly populations.
- Innovations in drug delivery improving compliance and efficacy.
- Expansion into niche markets, including military, aerospace, and sports.
Challenges and Risks
- Regulatory delays or rejections slowing market entry.
- High development costs reducing initial profitability.
- Competitive pressure from established brands and generics.
- Consumer preferences shifting toward non-pharmacological remedies.
Conclusion
The market for SM Motion Sickness holds promising growth potential driven by increased travel, technological innovations, and unmet clinical needs for safer, faster, and more convenient treatments. Pricing strategies must balance premium margins justified by product differentiation and broader market penetration pressures as generics emerge. Stakeholders capable of leveraging clinical advantages, securing patent protections, and understanding evolving consumer preferences stand to maximize profitability within this expanding segment.
Key Takeaways
- The global anti-motion sickness market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4%, with significant opportunities for innovative therapies like SM MS.
- Pricing for new formulations initially could command a premium ($30–$60 OTC, up to $120 prescription), decreasing as market competition intensifies.
- Differentiation through rapid onset, safety profile, and delivery system innovation enhances market positioning and pricing power.
- Patent protection and regulatory approval speed are critical determinants of initial pricing and market share.
- Emerging niche markets (military, aerospace) can sustain higher price points via specialized formulations and contractual agreements.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main factors influencing motion sickness treatment pricing?
Therapeutic efficacy, safety profile, delivery method, patent protection, and market competition significantly impact pricing. Premium formulations with demonstrated clinical advantages can command higher prices, especially in niche markets.
Q2: How will patent expiry affect the market for SM Motion Sickness?
Patent expiry typically leads to generic entry, exerting downward pressure on prices by 30–50%. Strategic patent extensions or formulation innovations can mitigate this effect temporarily.
Q3: What role do delivery systems play in pricing strategies?
Advanced delivery systems (patches, nasal sprays) often justify higher prices due to increased convenience, faster onset, and improved compliance, particularly in premium or niche markets.
Q4: Which markets are most promising for premium pricing of SM MS?
Aerospace, military, and specialized medical settings can sustain higher pricing due to the demand for reliable, non-sedating, and tailored therapies.
Q5: How does the resurgence in global travel influence market growth?
Increased travel volume correlates with higher motion sickness incidence, expanding both OTC and prescription markets, and encouraging innovation and premium offerings.
References:
[1] World Travel & Tourism Council. (2022). Travel Industry Economic Impact.
[2] Stewart, J. (2019). Pharmacologic treatments of motion sickness. Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery.
[3] MarketsandMarkets. (2022). Anti-Motion Sickness Market Forecast.
More… ↓
