Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Methamphetamine, a potent central nervous system stimulant, remains a significant concern within illicit drug markets globally. Despite stringent law enforcement measures and international control efforts, the drug's production, trafficking, and consumption persist, influencing market dynamics and pricing structures substantially. This analysis explores current market trends, factors shaping methamphetamine prices, and future price projection models rooted in socio-economic and regulatory variables.
Current Market Landscape
Global Production and Trafficking Trends
Methamphetamine's illegal manufacturing hubs are primarily situated in Southeast Asia (notably in Myanmar and Laos), North America (notably Mexico and the United States), and Australia. These regions benefit from access to precursor chemicals—primarily pseudoephedrine and ephedrine—which are regulated but still accessible through illicit channels[1].
Global trafficking networks are highly sophisticated, utilizing clandestine labs, concealed shipping routes, and digital facilitation. The global market saw an estimated annual consumption of over 35 million users in 2021, with the United States and Asia Pacific regions being the largest consumer markets[2].
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation reveals a dichotomy between high-purity, domestically produced methamphetamine and lower-purity, trafficked imports. The domestic production in North America and Asia yields high-grade product, commanding premium prices, while trafficked variants often serve regional markets at lower prices[3].
Pricing Dynamics
Price ranges and units
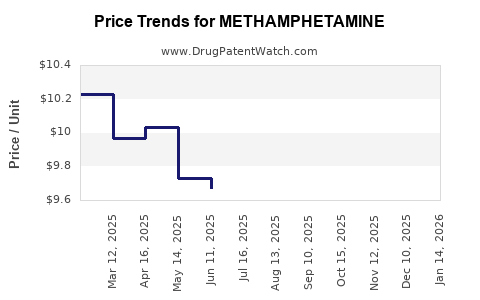
The street-level price of methamphetamine varies significantly across regions, purity levels, and supply chain factors. In North America, the price per gram ranges between $20 and $50, with purity levels exceeding 80% in domestically produced batches. Conversely, in parts of Southeast Asia, prices can be as low as $5-10 per gram but with variable purity[4].
Factors Influencing Price
Purity and Quality: Higher purity products fetch premium prices. Production methods and precursor quality impact purity levels.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Law enforcement crackdowns, interdiction efforts, and precursor chemical restrictions lead to supply shortages, typically inflating prices.
Regional Demand and Policy Environment: Regions with high demand and less stringent regulatory enforcement tend to maintain stable or rising prices. Conversely, aggressive interdiction efforts can temporarily reduce supply, impacting prices inwardly but possibly fostering illicit manufacturing.
Market Maturity: Mature markets with established distribution channels often see stabilized prices, while emerging markets experience volatility, mainly driven by law enforcement and social factors.
Regulatory and Enforcement Effects
International Control Measures
The international community, via the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), classifies methamphetamine as a Schedule II controlled substance under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. This classification imposes strict manufacturing and trafficking regulations, yet enforcement effectiveness varies regionally[5].
Impact on Prices
Stringent regulations tend to increase production costs and reduce supply, thus elevating market prices. Conversely, enhanced interdiction and chemical precursor control measures often lead to the emergence of small, clandestine manufacturing units, which can cause price fluctuations[6].
Future Price Projections
Market Drivers
-
Precursor Chemical Control: Tightening restrictions on pseudoephedrine and ephedrine is likely to increase production costs, pressuring prices upward.
-
Emerging Markets: New consumption markets, particularly in Africa and Eastern Europe, may initially experience low prices due to demand elasticity and unregulated distribution channels but could escalate as markets mature.
-
Technological Developments: Advances in clandestine manufacturing techniques, such as the use of alternative chemicals or "one-pot" synthesis, could reduce production costs, thereby lowering prices or increasing supply.
-
Regulatory Evasion: Sophisticated smuggling and chemical diversion methods may sustain or increase supply, maintaining current low-price ceilings.
Projected Price Trends (2023-2030)
Based on current data, the following projections are plausible:
-
North American Market: Mild upward pressure, with prices stabilizing broadly between $20-$60 per gram, considering potential law enforcement effectiveness and interdiction efforts.
-
Asia-Pacific Markets: Potential premium increases of 5-10% over current prices, driven by regional regulatory tightening and demand growth.
-
Emerging Markets: Likely initial low prices (around $10-$15 per gram), with gradual increases as markets mature and regulation intensifies.
Overall, a modest increase in methamphetamine prices, averaging 3-7% annually over the next seven years, appears plausible. However, regional disparities and law enforcement actions could disrupt this trend.
Implications for Stakeholders
Law Enforcement: Efforts should focus on disrupting precursor chemical supply chains, which could sustainably impact production costs and prices.
Public Health: Rising prices may shift consumption patterns toward adulterated or alternative substances, with associated health risks.
Investors & Businesses: The illicit market's resilient nature necessitates cautious engagement and emphasizes the importance of interdiction and regulatory compliance in related sectors such as chemical manufacturing.
Key Takeaways
- The global methamphetamine market remains highly dynamic, influenced primarily by regional supply-demand factors and regulatory measures.
- Prices are currently quite variable, heavily dependent on purity, regional supply, and enforcement efficacy.
- Future trends project mild increases in prices, driven by stricter precursor chemical controls and regional market maturation.
- Market responses to law enforcement actions and technological shifts in clandestine manufacture could produce significant volatility.
- Stakeholders should monitor regulatory changes and interdiction efforts to anticipate market shifts effectively.
FAQs
1. How do precursor chemical regulations impact methamphetamine prices?
Stringent controls on precursor chemicals like pseudoephedrine increase manufacturing costs, which typically elevate market prices. Conversely, lax enforcement can sustain or lower prices by facilitating easier production.
2. What are the main factors causing regional price disparities?
Differences in production costs, purity levels, law enforcement intensity, demand, and the sophistication of trafficking networks mainly drive regional price disparities.
3. Could technological advances in clandestine synthesis affect future prices?
Yes. Innovations such as one-pot synthesis reduce production complexity and costs, potentially lowering prices or increasing supply.
4. How might emerging markets influence global methamphetamine prices?
Emerging markets with growing demand and minimal regulation might initially see low prices, which could rise as markets stabilize and enforcement intensifies.
5. What role do international agencies play in controlling methamphetamine prices?
Organizations like UNODC promote precursor controls and provide intelligence to countries for enforcement, aiming to reduce supply and influence prices indirectly.
References
[1] UNODC, World Drug Report 2022.
[2] United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, Global Synthetic Drug Assessment 2022.
[3] European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction, Drug Market Trends 2022.
[4] RAND Corporation, The Economics of Illicit Drug Markets, 2021.
[5] United Nations, Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971.
[6] US Drug Enforcement Administration, 2022 National Drug Threat Assessment.