Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for METFORMIN ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
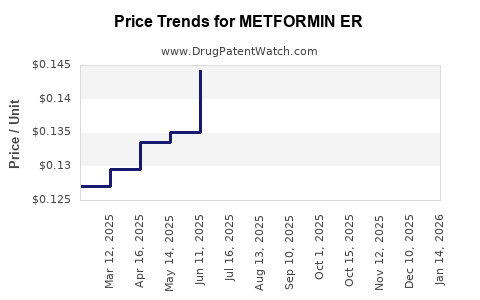
Average Pharmacy Cost for METFORMIN ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| METFORMIN ER 1,000 MG GASTR-TB | 27241-0241-90 | 0.42601 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| METFORMIN ER 1,000 MG GASTR-TB | 42571-0334-90 | 0.42601 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| METFORMIN ER 500 MG OSMOTIC TB | 69367-0412-60 | 0.12739 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Metformin ER
Introduction
Metformin Extended-Release (ER) is a cornerstone medication in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus, widely prescribed due to its efficacy, safety profile, and affordability. As a long-acting formulation, Metformin ER offers advantages over immediate-release counterparts, notably improved gastrointestinal tolerability and enhanced patient compliance. This analysis examines the current market landscape for Metformin ER, driven by epidemiological, regulatory, and competitive factors, and projects future pricing trends based on market dynamics, patent statuses, and healthcare policies.
Market Overview
Global Diabetes Prevalence and Market Drivers
The global burden of type 2 diabetes has surged, with the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimating approximately 537 million adults living with diabetes in 2021, a figure projected to reach 643 million by 2030 [1]. Metformin remains the frontline therapy, recommended by major clinical guidelines such as the ADA/EASD consensus, owing to robust evidence of glycemic control, cost-effectiveness, and cardiovascular benefits [2].
The widespread adoption of Metformin ER formulations is fueled by:
- Increased adoption of long-acting formulations to improve patient adherence.
- Growing awareness of gastrointestinal side effects associated with immediate-release forms, favoring ER options.
- Expansion into developing markets, where affordability and availability influence prescribing behaviors.
Market Segments
The Metformin ER market encompasses multiple stakeholders:
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturers: Major players include Teva, Mylan (now part of Viatris), Lupin, and Sun Pharma.
- Healthcare Providers and Patients: Preference shifts toward ER formulations for tolerability.
- Insurance and Payers: Cost considerations influence formulary decisions, impacting market penetration.
Current Market Dynamics
Product Landscape
While Metformin ER is available in both branded and generic forms, the market is predominantly characterized by generic competition owing to patent expirations. For instance:
- Branded versions, such as Glucophage XR, have historically commanded premium pricing but face rapid generic penetration.
- Generic formulations dominate the current landscape, fostering price competition and downward pressure.
Regulatory and Patent Factors
Major patents held by original manufacturers have expired or are nearing expiration, facilitating the rise of generics. However, some Extended-Release formulations still benefit from certain patent protections or exclusivity periods, delaying generic entry and maintaining higher prices temporarily.
Market Share Trends
The ER version's higher tolerability has increased its market share relative to immediate-release forms. This trend is expected to persist, with projections indicating continued growth driven by improved prescribing practices.
Price Trends and Projections
Historical Pricing Data
Traditionally, Metformin ER's cost structure has lower prices compared to other antidiabetic agents, with generic versions available at approximately $4–$10 per month per patient [3]. Despite low absolute costs, the price premium over immediate-release formulations (roughly 10–20%) remains significant during patent protections.
Forecasting Future Prices
Factors influencing future pricing include:
- Patent Expiry and Generic Competition: As patents expire, generic versions will drive prices lower, with estimates suggesting a 20–40% reduction within 1-2 years post-generic entry.
- Market Penetration Strategies: Manufacturers may implement value-added features or extended-release mechanics to sustain premium pricing.
- Healthcare Policy and Negotiation: Payers’ push for cost containment will accelerate utilization of low-cost generics.
Based on these parameters, projected average wholesale prices (AWP) for Metformin ER are anticipated to decrease over the next 3-5 years:
| Timeframe | Price Range (Estimated) | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate (2023) | $4–$10 per month | Generic dominance, minimal premium |
| Mid-term (2025) | $2–$6 per month | Increased generic market saturation, price erosion |
| Long-term (2027) | <$2–$4 per month | Widespread adoption of low-cost generics |
Competitive and Regulatory Impacts
Competitive Landscape
The entry of multiple generic manufacturers has led to intense price competition. Market consolidation or new formulations could alter margins:
- Innovative formulations (e.g., combined with other agents) may command higher prices but face regulatory hurdles.
- Market segmentation with differentiated products could sustain higher prices for specialty or quality-assured formulations, especially in emerging markets.
Regulatory Environment
Stringent approval processes and possible patent litigations could temporarily hinder generic entry or promote brand loyalty, affecting prices. Notably, the FDA's approval pathways and market exclusivity policies influence pricing trajectories.
Concluding Market Outlook
The Metformin ER market is poised for continued growth, primarily driven by increasing global diabetes prevalence and shifting prescribing habits favoring ER formulations. Price reductions are inevitable as patent protections lapse and generic competition intensifies. While branded versions may retain price premiums domestically during exclusive periods, the long-term outlook suggests steep declines toward generic-level pricing, benefiting healthcare systems through increased affordability.
Key Takeaways
- The global surge in type 2 diabetes will sustain demand for Metformin ER, securing its position as a first-line therapy.
- Patent expirations and the rise of generic manufacturers will precipitate significant price declines, with estimates indicating reductions of up to 50% within 3 years.
- Healthcare policies emphasizing cost containment will further accelerate generic adoption and price erosion.
- Market entry barriers are low due to the drug’s established profile, but differentiation through formulation innovation might sustain higher prices temporarily.
- Emerging markets present growth opportunities owing to affordability concerns, though local regulatory and patent environments will influence pricing.
FAQs
1. What factors most significantly influence the pricing of Metformin ER?
Patent status, generic competition, healthcare policy shifts, and manufacturing costs predominantly shape pricing dynamics.
2. How does generic entry impact Metformin ER prices?
Generic entry typically results in substantial price reductions (20–40%), often making the medication more accessible.
3. Is it more cost-effective to prescribe generic Metformin ER over branded versions?
Yes. Generic versions offer similar efficacy at a lower cost, especially post-patent expiration.
4. Which regions are expected to experience the fastest price declines for Metformin ER?
Developed markets like the US and Europe will see rapid price drops following patent cliffs, while emerging markets may adopt generics slightly later.
5. Are there any upcoming regulatory changes that could impact Metformin ER pricing?
Regulatory agencies' policies on patent extensions, approval pathways for generics, and approval of biosimilars can influence future pricing and market competition.
References
[1] International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition, 2019.
[2] American Diabetes Association. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2023.
[3] GoodRx. Metformin Prices and Cost Comparison, 2023.
More… ↓
