Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR
✉ Email this page to a colleague
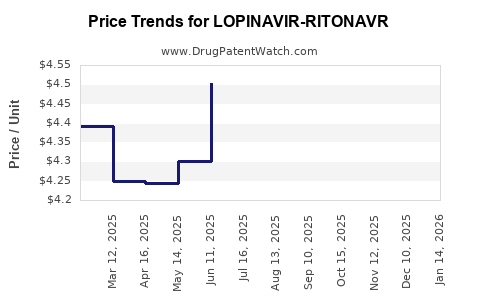
Average Pharmacy Cost for LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR 200-50 MG TB | 31722-0556-12 | 5.20028 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR 200-50 MG TB | 42385-0934-12 | 5.20028 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR 200-50 MG TB | 31722-0556-12 | 5.24272 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR 200-50 MG TB | 42385-0934-12 | 5.24272 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR 200-50 MG TB | 31722-0556-12 | 5.01811 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR 200-50 MG TB | 42385-0934-12 | 5.01811 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| LOPINAVIR-RITONAVR 200-50 MG TB | 31722-0556-12 | 4.85095 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Lopinavir-Ritonavir
Introduction
Lopinavir-ritonavir (brand name: Kaletra) is a combination antiretroviral medication primarily used to treat HIV/AIDS. It functions as a protease inhibitor, disrupting viral replication. Over the years, it has faced evolving market dynamics due to advancements in HIV therapies, patent landscapes, generic entry, and the ongoing development of broader antiviral agents. This report provides a comprehensive market analysis, examining historical trends, current positioning, and future price projections for Lopinavir-ritonavir in global health markets, with particular emphasis on key regions such as North America, Europe, and emerging markets.
Market Overview
Global HIV Treatment Landscape
The global HIV treatment market is mature, with antiretroviral therapies (ART) installed as standard care. According to UNAIDS, approximately 38 million people globally live with HIV, with sustained ART coverage. Lopinavir-ritonavir, first approved in 2000, was among the first protease inhibitors introduced. Its initial commercial success was driven by its efficacy and manageable safety profile. However, later development of integrase inhibitors and other novel agents has shifted treatment paradigms.
Current Market Position of Lopinavir-Ritonavir
Despite being a foundational drug historically, Lopinavir-ritonavir's market share has declined due to the availability of newer, more tolerable therapies with simplified dosing regimens. Nevertheless, it remains a component of second- and third-line treatment regimens, especially in resource-constrained settings. The drug is often favored in developing countries owing to its affordability and existing generic manufacturing infrastructure.
Patent and Regulatory Status
The original patent for Kaletra expired in many jurisdictions between 2018 and 2020, leading to widespread generic manufacturing. Several generic versions are now available, reducing average wholesale prices. Patent expirations have significantly impacted market dynamics, contributing to increased competition and pricing pressure.
Competitive Landscape
Lopinavir-ritonavir faces competition from other classes of HIV drugs, including integrase inhibitors (e.g., dolutegravir), nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and entry inhibitors. The newer agents often offer improved tolerability, fewer drug interactions, and simplified dosing schedules, making them preferred options where accessible.
Market Drivers and Constraints
Drivers
- Cost-effectiveness in Low-Income Countries: Generic availability and lower manufacturing costs make Lopinavir-ritonavir a vital option for resource-limited settings.
- Established Efficacy: Long-term safety and proven efficacy bolster its continued usage in salvage therapy.
- Global HIV Burden: Ongoing need for effective ART sustains demand, especially where newer agents are inaccessible.
Constraints
- Market Penetration of Newer Agents: Advances in HIV therapy have shifted prescribing patterns away from protease inhibitors.
- Side Effect Profile: Gastrointestinal disturbances and metabolic complications limit desirability compared to newer agents.
- Price Erosion: Patent expiry and generic proliferation cause significant price reductions, impacting revenue streams.
Price Trends and Projections
Historical Pricing Data
Pre-patent expiry, branded Lopinavir-ritonavir (Kaletra) had a list price exceeding $2000 per treatment year in high-income markets. Generic versions launched post-patent expiry rapidly reduced prices, with current wholesale costs in low-income countries reported to be below $100 per treatment year.
Current Market Prices
- High-Income Markets: Retail prices range from $1500 to $2500 annually, heavily influenced by insurance reimbursements and negotiated discounts.
- Emerging Markets: Government procurement prices often fall below $100–$200 per year per patient, driven by generic competition and purchasing volume.
Future Price Projections
Considering current patent expirations, the following price trajectory is anticipated over the next decade:
| Timeline | Price Range in High-Income Markets | Price Range in Low-Income Markets | Drivers and Assumptions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023–2025 | $1000–$2000 | $50–$150 | Continued generic penetration; supply chain stability |
| 2026–2030 | $700–$1500 | $40–$120 | Market saturation; further generic manufacturing efficiencies |
| 2031 and beyond | $500–$1000 | $30–$80 | Further patent expirations; potential biosimilar or alternative formulations |
In high-income regions, prices are expected to decline due to stricter formulary controls, insurance negotiations, and the preferential shift toward newer agents. In contrast, in low-income settings, prices may stabilize or decline marginally, maintaining affordability for government programs and NGOs.
Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities
- Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs): Enhancing adherence in resource-limited settings.
- Generic Production: Expansion in emerging markets sustains low-cost supply chains.
- Combination with New Agents: Potential for co-formulations to streamline regimens.
Risks
- Market Shrinkage: Shift toward integrase inhibitors reduces demand.
- Price Erosion: Global competition from generics and biosimilars accelerates revenue decline.
- Regulatory Barriers: Variations in approval processes across jurisdictions could delay market access.
Conclusion
Lopinavir-ritonavir remains a vital component of HIV therapy, particularly in resource-constrained environments. However, its market is under substantial pressure from newer, more tolerable treatment options and generic competition. Price projections indicate a continued downward trend, especially in high-income markets, driven by patent expirations and market evolution. The product's future in the global market will heavily depend on strategic positioning, manufacturing efficiency, and the ability to adapt to evolving treatment guidelines.
Key Takeaways
- The patent expiry of Lopinavir-ritonavir has catalyzed significant price reductions, especially in emerging markets.
- Its role is anticipated to decline further in high-income countries as integrase inhibitors dominate first-line therapies.
- Generics and biosimilars are likely to maintain the drug’s affordability and accessibility in low-income regions.
- Market growth is constrained, but the ongoing global HIV burden sustains essential demand, primarily in second-line and salvage therapy.
- Strategic diversification, such as developing fixed-dose combinations and co-formulations, can prolong product relevance.
FAQs
1. What factors most influence Lopinavir-ritonavir pricing in different markets?
Pricing is primarily affected by patent status, manufacturing costs, competition from generics, regulatory environments, and healthcare reimbursement policies across regions.
2. How has patent expiry impacted the global market for Lopinavir-ritonavir?
Patent expiration has facilitated the entry of generic manufacturers, leading to significant price reductions and increased accessibility, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
3. What is the outlook for Lopinavir-ritonavir in high-income countries?
Its use is declining due to the adoption of newer agents with better tolerability and simplified regimens; therefore, revenue and pricing are expected to decrease further.
4. Are there potential new formulations that could extend the lifecycle of Lopinavir-ritonavir?
Yes. Fixed-dose combinations, improved delivery options, and co-formulations with other antiretrovirals could sustain its relevance, particularly in resource-limited settings.
5. How does market competition affect future price projections?
Intense competition from generics and biosimilars, coupled with shifting treatment guidelines, will likely drive prices down over the next decade.
References
[1] UNAIDS. Global HIV & AIDS statistics — 2022 fact sheet.
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Kaletra (Lopinavir/Ritonavir) prescribing information.
[3] IQVIA. Global HIV market analysis reports, 2023.
[4] World Health Organization. Consolidated guidelines on HIV prevention, testing, treatment, service delivery and monitoring, 2021.
[5] WHO Essential Medicines List. Protease inhibitors including Lopinavir, 2022.
More… ↓
