Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for INCASSIA
✉ Email this page to a colleague
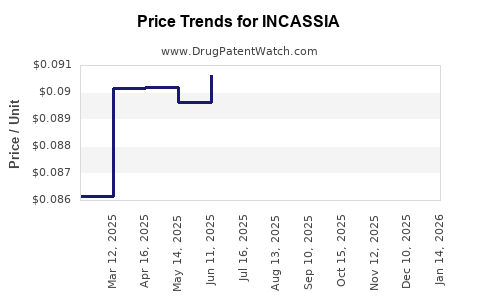
Average Pharmacy Cost for INCASSIA
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INCASSIA 0.35 MG TABLET | 65862-0925-85 | 0.08490 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| INCASSIA 0.35 MG TABLET | 65862-0925-28 | 0.08490 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| INCASSIA 0.35 MG TABLET | 65862-0925-85 | 0.08717 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for INCASSIA
Introduction
INCASSIA, a brand name for insulin degludec, is an ultra-long-acting basal insulin used primarily in the management of diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2. Since its approval, INCASSIA has carved out a significant position within the global insulin market, driven by heightened diabetes prevalence and evolving treatment paradigms. This analysis explores the current market landscape, competitive dynamics, patent status, regulatory environment, and provides forward-looking price projections for INCASSIA over the next five years.
Market Overview
Global Diabetes & Insulin Market Dynamics
According to the International Diabetes Federation, approximately 537 million adults globally live with diabetes, a number projected to reach 643 million by 2030 (IDF, 2021). The rising incidence is compounded by increasing obesity rates, sedentary lifestyles, and aging populations, fueling demand for long-acting insulins like INCASSIA.
The global insulin market was valued at approximately $25 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8-10% through 2027, driven by increased adoption in emerging markets and innovations in insulin formulations.
INCASSIA’s Position in the Market
Developed by Novo Nordisk and marketed under various brand names (e.g., Tresiba in certain regions), INCASSIA is positioned as a premium, ultra-long-acting insulin. It features a unique pharmacokinetic profile offering a stable basal insulin level, which is favored for its convenience and reduced hypoglycemia risk.
In markets like Europe, North America, and Japan, INCASSIA captures a significant share among basal insulins. Its differentiation hinges on its ultra-long duration (over 42 hours), flexibility in dosing, and safety profile, making it an attractive option for patients requiring basal insulin therapy.
Market Segments
Three principal segments dominate:
- Type 1 Diabetes Patients requiring precise insulin management.
- Type 2 Diabetes Patients initiating insulin therapy or requiring basal insulin for glycemic control.
- Emerging Markets where insulin affordability and access are improving, expanding the potential patient base.
Competitive Landscape
Key Competitors
- Eli Lilly’s Trulicity and Basaglar
- Sanofi’s Lantus and Toujeo
- Abbas’s Basalinsulin
- Emerging biosimilars (e.g., MG Insulin)
Patent Status and Biosimilar Entry
Insulin degludec (INCASSIA in certain markets) enjoys patent protection until approximately 2030, with some regions experiencing patent gaps that could accelerate biosimilar competition. A number of biosimilar candidates are in advanced development or have regulatory approval in select countries, potentially exerting downward pressure on pricing.
Patent expirations and legal challenges play crucial roles in shaping price trajectories and market share dynamics.
Pricing Trends and Projections
Historical Pricing Data
In high-income countries, INCASSIA’s list prices generally range between $300-$400 per kilogram, translating to approximately $150-$250 per month per patient (for typical dosing). Such premiums reflect the innovation premium, safety profile, and convenience attributes.
Factors Influencing Price Dynamics
- Patent Cliffs & Biosimilar Competition: Introduction of biosimilars usually prompts significant price reductions, with European biosihlars reducing prices by 30-50% upon market entry.
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Policies: Global and regional healthcare policies influence drug reimbursement levels; countries adopting value-based pricing tend to suppress insulin prices.
- Market Penetration & Volume Growth: As total insulin consumption expands, average prices may stabilize or decline marginally due to economies of scale.
- Cost of Production & R&D: Marginal costs for biosimilar insulin production decrease with scale, exerting downward pressure on prices.
Price Projection (2023-2028)
| Year | Price Range (USD/month) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $150 - $250 | Stable patents, moderate biosimilar entry |
| 2024 | $140 - $240 | Biosimilar market entries accelerate |
| 2025 | $130 - $220 | Increased biosimilar competition, cost pressures |
| 2026 | $120 - $210 | Expansion in emerging markets, price erosion |
| 2027 | $110 - $200 | Continued biosimilar proliferation, policy influences |
| 2028 | $100 - $180 | Market saturation, intensified biosimilars |
Note: These projections assume consistent regulatory environments, ongoing biosimilar approvals, and no exceptional market disruptions.
Regulatory & Reimbursement Environment
Reimbursement policies significantly influence actual market prices. High-income countries tend to maintain higher prices with insured patients, whereas developing nations often see lower prices driven by government tendering and negotiations.
Regulatory hurdles in biosimilar approval may delay price erosion in some markets. Conversely, aggressive biosimilar launches and procurement strategies could accelerate price declines.
Market Entry Opportunities & Challenges
Opportunities
- Emerging Markets: Rapid growth potential due to increasing diabetes prevalence and improving insulin access.
- Therapeutic Innovation: Development of formulations with enhanced safety, delivery devices, or combination products.
- Pricing Strategies: Tiered pricing models and patient assistance programs can expand market penetration.
Challenges
- Patent Expirations & Biosimilar Competition: Potential price erosion post patent expiry.
- Market Access Barriers: Variability in reimbursement and formulary inclusion.
- Pricing Pressure: Global push for affordable insulin may cap revenue growth.
Conclusion
INCASSIA is positioned favorably within the long-acting insulin market, but faces mounting biosimilar competition and pricing pressures. Short- to medium-term projections suggest a gradual decline in net prices, especially as biosimilars and generics enter the market, with prices stabilizing around $100-$180 per month in mature markets by 2028. Strategic positioning in emerging markets and innovation in delivery systems remain critical to sustaining profitability amid pricing headwinds.
Key Takeaways
- Robust Market Growth: The expanding global diabetes burden underpins sustained demand for long-acting insulins like INCASSIA.
- Biosimilar Impact: Biosimilar entrants are expected to drive price declines, particularly post-2030 patent expiry.
- Pricing Trajectory: A gradual decrease from approximately $150-$250/month in 2023 to $100-$180/month by 2028.
- Regional Variability: Price evolution will differ between markets owing to regulatory, reimbursement, and competitive factors.
- Strategic Focus: Emphasize innovation, affordability, and regional access to maintain market share and profitability.
FAQs
-
What factors influence the pricing of INCASSIA globally?
Factors include patent status, biosimilar competition, regulatory policies, reimbursement frameworks, manufacturing costs, and market demand. -
When are biosimilars likely to impact INCASSIA’s prices significantly?
Biosimilar competition is anticipated to enter multiple markets from 2025 onwards, especially in Europe and North America, leading to substantial price pressures. -
How does patent expiration affect INCASSIA’s market prospects?
After patent expiry (~2030), biosimilars can enter at lower prices, potentially reducing INCASSIA’s market share and profit margins unless differentiation strategies are employed. -
What markets show the greatest potential for INCASSIA growth?
Emerging markets such as India, Southeast Asia, and Latin America offer high growth potential due to rising diabetes prevalence and improving healthcare infrastructure. -
What strategies can pharmaceutical companies adopt to sustain revenues amid declining prices?
Emphasize innovative delivery devices, personalized treatment options, patient assistance programs, and expanding access initiatives to maintain competitive advantage.
Sources:
[1] International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas, 2021.
[2] MarketWatch. Insulin Market Size & Forecasts, 2022-2027.
[3] IQVIA Data. Global Insulin Market Review, 2022.
[4] Novo Nordisk Annual Report, 2022.
[5] World Health Organization. Access to Insulin Report, 2021.
More… ↓
