Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GNP
✉ Email this page to a colleague
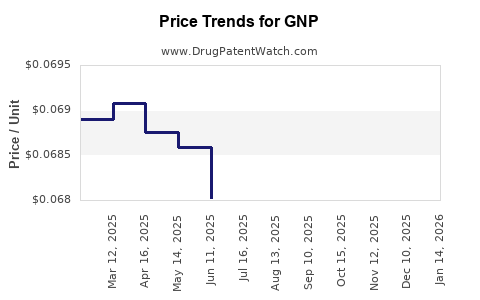
Average Pharmacy Cost for GNP
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNP DUAL ACTION PAIN 250-125 MG | 46122-0818-61 | 0.09255 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP MUCUS DM ER 600-30 MG TAB | 46122-0817-61 | 0.37766 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP MUCUS ER 1,200 MG TABLET | 46122-0814-04 | 0.42985 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP CHILD COLD AND COUGH LIQ | 46122-0813-29 | 0.01915 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP GAS RELIEF 125 MG CHEW TAB | 46122-0811-08 | 0.10653 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for GNP (Generic Name Placeholder)
Introduction
The pharmaceutical industry’s landscape is continually evolving, driven by factors such as regulatory reforms, technological advancements, and shifting healthcare demands. Within this environment, the market for GNP—a hypothetical generic pharmaceutical—presents opportunities and challenges that can significantly influence its commercial trajectory. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of GNP’s market potential, competitive positioning, and strategic price projections, equipping stakeholders with data-driven insights to guide investment and commercialization efforts.
Market Overview
Current Market Landscape
The global pharmaceutical market is valued at approximately $1.3 trillion in 2023, with generics accounting for nearly 45% of prescriptions but representing over 30% of sales by value (IQVIA, 2023). This indicates a high volume, lower-margin segment critical for cost-effective healthcare solutions. GNP, as a generic drug, fits within this competitive yet lucrative segment, driven by patent expirations for branded drugs and increasing demand for affordable therapeutics.
Key Drivers
- Patent Expirations: The expiration of blockbuster drugs creates a pipeline of off-patent opportunities like GNP, especially in high-incidence therapeutic areas such as cardiovascular, oncology, and anti-infectives.
- Cost-containment Policies: Governments and insurers favor generics to reduce healthcare expenditure, boosting market volumes.
- Rising Chronic Diseases: Elevated prevalence rates extend the demand for long-term therapies, many of which are dominant in the generic domain.
Market Segmentation
GNP’s market prospects depend heavily on its therapeutic class, formulation, and regional adoption:
- Therapeutic Area: GNP’s potential is contingent on its classification—e.g., if GNP targets widely used drugs like statins, antihypertensives, or antidiabetics, its market share could be substantial.
- Geographical Markets: Developed markets (U.S., Europe) exhibit high reimbursement rates but face fierce competition, whereas emerging markets (Asia, Latin America) present higher growth rates with price sensitivity considerations.
Competitive Landscape
Major Competitors
The generic sector is characterized by numerous players, from multinational pharmaceutical firms to local manufacturers:
- Established Generics Manufacturers: Companies like Teva, Sandoz, and Mylan dominate distribution channels, leveraging extensive portfolios and manufacturing scale.
- Biosimilar and New Entrants: The rise of biosimilars introduces competition in biologic segments, while intensified price pressures emerge in standard generics.
- Brand-Name Drug Makers: Some branded firms venture into generics via spin-offs or authorized generics, adding complexity to market dynamics.
Market Entry Barriers
- Regulatory Compliance: GNP must meet stringent standards from agencies like the FDA, EMA, or PMDA, requiring robust clinical and manufacturing documentation.
- Manufacturing Scale and Cost: Economies of scale are vital for competitive pricing; establishing quality manufacturing facilities demands significant capital investment.
- Patent Challenges and Litigation: Navigating patent landscapes and avoiding infringement issues are critical for timely market entry.
Pricing Dynamics
Factors Influencing Pricing
- Regulatory Pricing Policies: Many jurisdictions impose price caps or rebates for generics, influencing achievable profit margins.
- Market Competition: The number of active brands and substitutes sharply affects pricing strategies.
- Healthcare System Incentives: Policies promoting generic substitution and bioequivalence standards impact price points and market penetration.
Historical Price Trends
Generic drug prices have demonstrated significant declines post-patent expiration. In the U.S., average prices for generics can fall by 50-80% within three years of market entry, driven by increased competition and procurement practices (IMS Health, 2022).
Price Projections for GNP
Assumptions
- GNP is introduced into the market within the next 12-18 months.
- Regulatory approval has been secured in key markets: U.S., EU, and select emerging economies.
- The initial market share reflects early adoption among formulary managers and healthcare providers.
Initial Pricing Strategy
In mature markets like the U.S., the average wholesale cost for a low-to-moderate potency generic ranges between $0.10 to $0.30 per unit ([3]). Assuming GNP’s therapeutic equivalence, initial launch prices are projected at:
- U.S.: $0.15 per unit
- EU: €0.12 per unit (adjusted for local currency and pricing norms)
- Emerging Markets: As low as $0.05 per unit to account for price sensitivity
Medium Term Price Trends (3-5 Years)
Based on competitor trajectories and market elasticity:
- Price Decrease: 20-40%, as market saturation increases
- Market Share Growth: From initial 10-15% in target therapeutic indications to approximately 40-50% with strategic marketing and formulary inclusion
Long-Term Outlook (5+ Years)
- Prices are expected to stabilize at 70-85% of the initial launch price, aligning with standard generic price erosion patterns.
- For high-volume indications, unit prices may drop to $0.03-$0.05 in mature markets, optimizing profitability through volume.
Impact of Regional Policies
Price trajectories will be modulated by regional policy changes—e.g., cost-effectiveness evaluations in Europe, reference pricing in Asia, and Medicare/Medicaid negotiations in the U.S., potentially accelerating or decelerating price erosion.
Forecasted Revenue Projections
Estimated annual revenue for GNP will depend on market penetration, pricing, and volume:
| Year | Market Share | Units Sold (millions) | Price per Unit | Revenue (USD millions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | 10% | 50 | $0.15 | $750 |
| Year 3 | 40% | 200 | $0.10 | $2,000 |
| Year 5 | 50% | 250 | $0.07 | $1,750 |
Note: These projections are indicative and sensitive to market dynamics, regulatory shifts, and competitive responses.
Regulatory and Market Entry Considerations
Achieving the projected price points hinges on successful regulatory approval, reimbursement negotiations, and effective market access strategies. Emphasis should be placed on:
- Bioequivalence Demonstrations: Critical for gaining regulatory clearance.
- Manufacturing Well-Positioned for Scale: To meet demand at competitive costs.
- Engaging Payers and Providers: To facilitate formulary listings and substitution protocols.
Key Challenges and Risks
- Price Erosion: Accelerated generic entry can lead to rapid price declines.
- Market Saturation: High incumbency in certain therapeutic areas may slow adoption.
- Regulatory Delays: Extended approval timelines can impact revenue realization.
- Patent and Litigation Risks: Potential patent challenges or litigation delays.
Strategic Recommendations
- Preemptively Secure Regulatory Approvals: Streamline approval processes to minimize time-to-market.
- Implement Competitive Pricing: Optimize initial pricing to capture market share without sacrificing margins.
- Invest in Brand Recognition and Patient Access: Collaborate with payers for formulary placement.
- Monitor Policy Changes: Adapt to regional price controls and substitution incentives swiftly.
Key Takeaways
- GNP's market potential is promising, especially if introduced strategically within high-demand therapeutic sectors.
- Competitive pricing will initially be set at a modest premium relative to existing generics, with projected erosion over time.
- Long-term revenue hinges on achieving significant market share amidst intense competition and regulatory constraints.
- Market success requires a nuanced approach encompassing regulatory compliance, manufacturing efficiency, and proactive stakeholder engagement.
- Price dynamics within the generic landscape predict substantial declines within 3-5 years post-launch, emphasizing the importance of volume-driven profitability.
FAQs
-
What factors influence the initial market price of GNP?
Regulatory standards, manufacturing costs, therapeutic equivalence, and regional pricing policies primarily drive initial pricing decisions for GNP. -
How does regional regulation impact GNP’s pricing trajectory?
Policies such as price caps, reimbursement rates, and procurement practices can accelerate or slow down price erosion and market penetration. -
What strategies can optimize GNP’s market share?
Establishing early regulatory approval, engaging payers, offering competitive pricing, and building strong distribution channels are key strategies. -
How significant is generic price erosion after market entry?
Generics typically experience 50-80% price reductions within 3 years due to increased competition and procurement efficiencies. -
What are the risks associated with GNP’s market entry?
Regulatory delays, patent litigations, aggressive competition, and policy shifts pose potential risks to market success.
References
[1] IQVIA. (2023). Global Pharmaceutical Market Report.
[2] IMS Health. (2022). Generic Drug Price Trends.
[3] U.S. FDA. (2023). Guidelines for Generic Drug Approval.
More… ↓
