Start working smarter.
See how companies in more than 70 countries are using DrugPatentWatch.
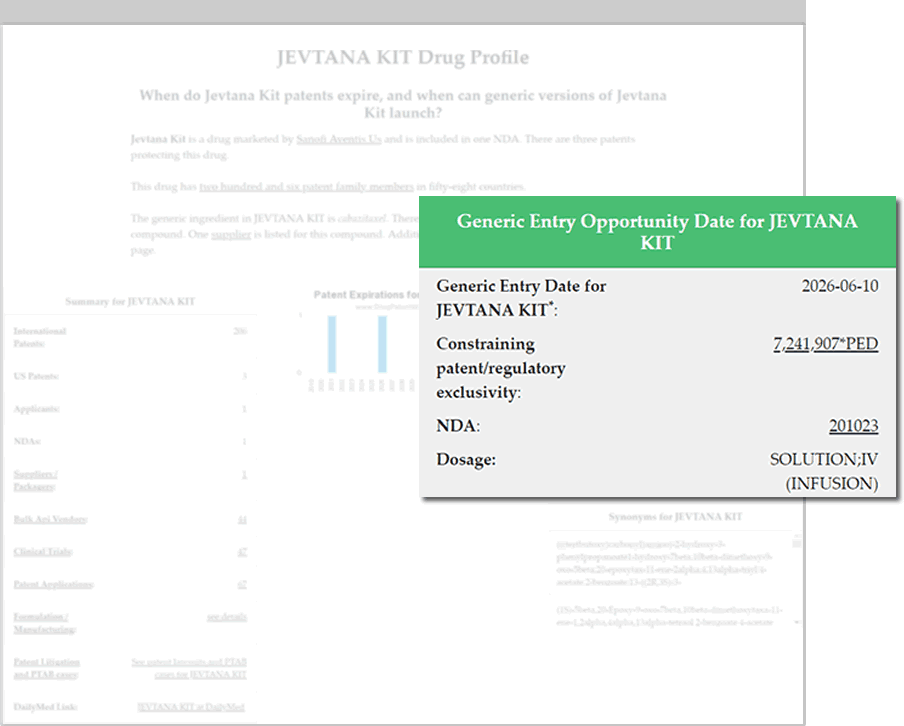
Global Biopharmaceutical Business Intelligence
- Identify and evaluate commercial opportunities
- Branded and generic drug pipeline forecasting
- Anticipate future revenue events
- Identify API and finished drug product suppliers
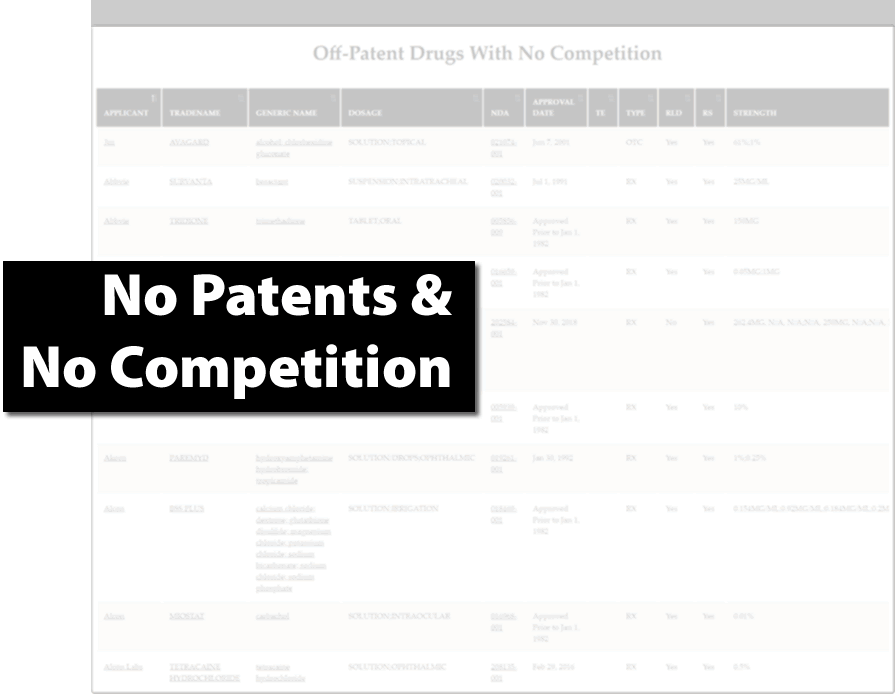
Find Generic Drug Entry Opportunities
- Inform portfolio management decisions
- Sector landscaping and due diligence
- Track investigational drugs and explore new indications for existing drugs

Get Confidential Royalty and Settlement Terms
- Study failed patent challenges to develop a better strategy
- Collect competitive intelligence by examining contractual disputes
- Track litigation to anticipate early generic entry
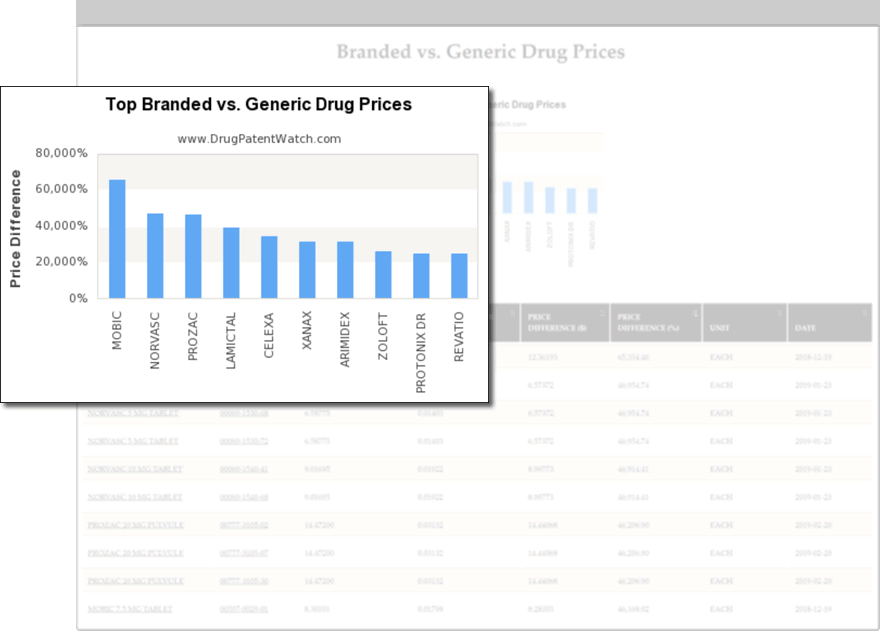
Find and Evaluate Business Opportunities
- Assess levels of generic competition
- Use drug price ranges to evaluate price elasticity
- Determine optimal prices before launch
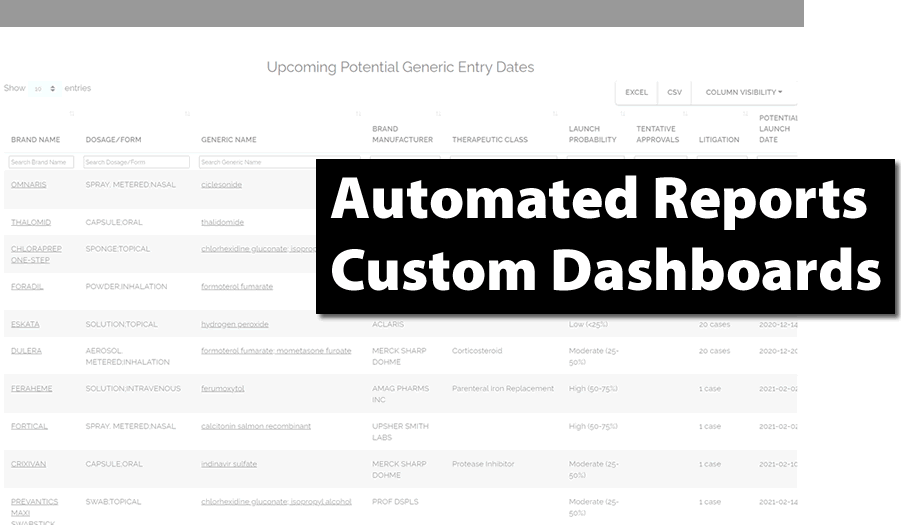
Automated Reports & Custom Dashboards
- Do more with less staff
- Take the load off your team
- Automate processes and focus on growing your business
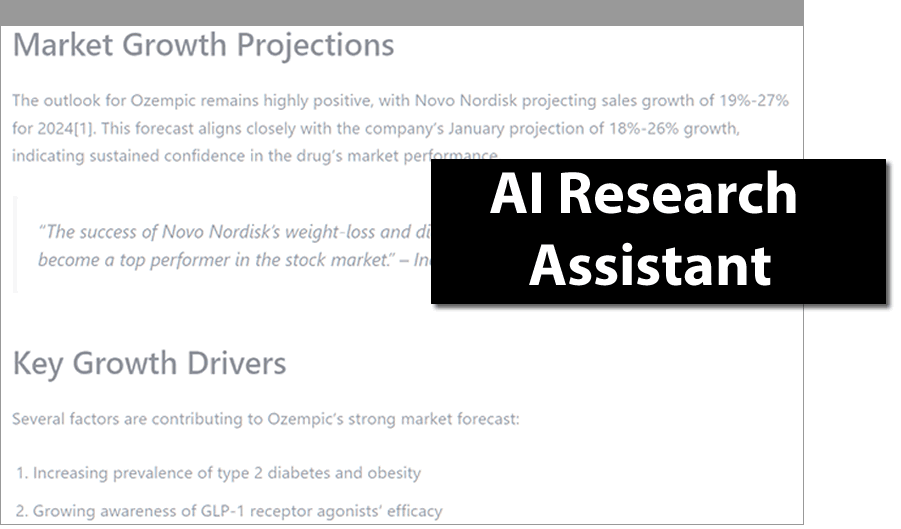
AI Research Assistant
- Quickly find answers beyond the scope of DrugPatentWatch
- Pull together comprehensive information from disparate sources
- Precise answers, with full citations for accuracy and reliability
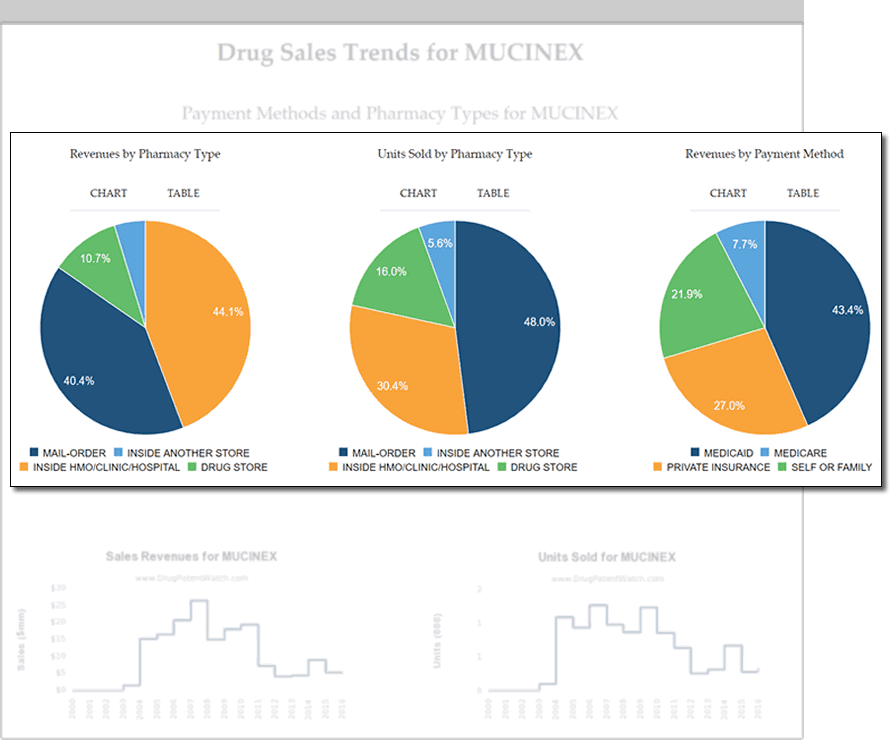
Refine Your Market-Entry Strategy
- Assess market potential through historic sales figures
- Evaluate buyer power with data on reimbursement segmentation
- Align distribution methods with information on where and how drugs are purchased
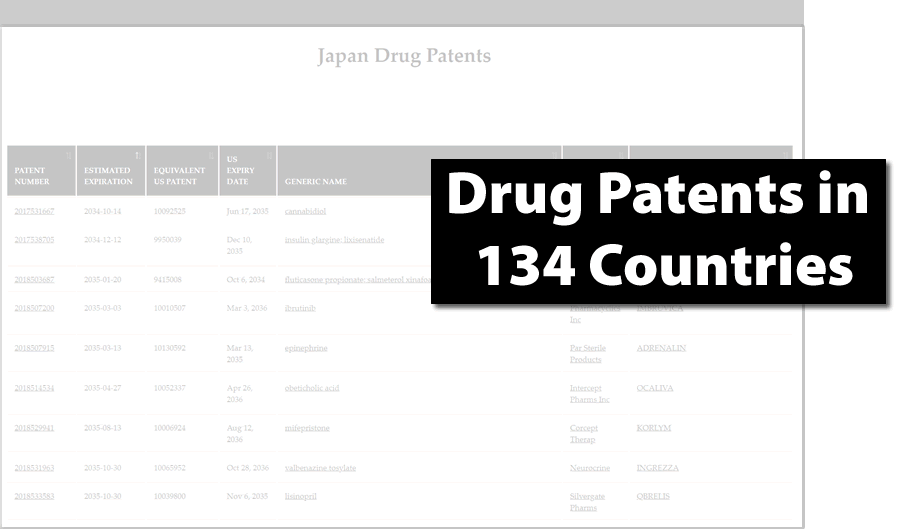
Global Drug Patents
- Drug Patents in 134 Countries
- Evaluate branded and generic market opportunities globally
Monitor biosimilar and 505(b)(2) activity
- Anticipate 505(b)(2) and biosimilar approvals
- Track OTC-switches, new formulations, biosimilars, and other drug improvements
- Strengthen new formulation patents by studying prior claims and litigation