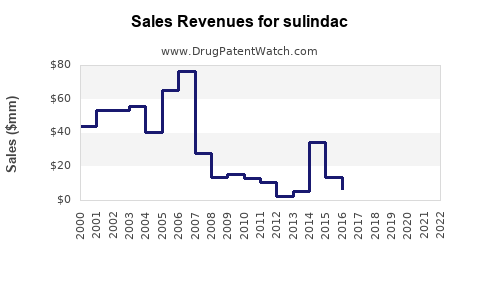
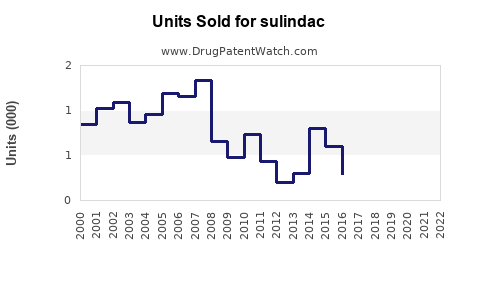
Last updated: July 30, 2025
rket Analysis and Sales Projections for Sulindac: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Sulindac is an established non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) primarily used for managing inflammation, pain, and reducing the risk of colon polyps. Approved by the FDA in the 1970s, it has a long-standing presence in therapeutics, especially for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). This analysis evaluates the current market landscape, emerging therapeutic developments, competitive dynamics, and future sales projections for Sulindac.
Product Profile and Therapeutic Positioning
Sulindac's mechanism centers on cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme inhibition, decreasing prostaglandin synthesis responsible for inflammation and pain. Its unique profile includes potential anticancer properties, particularly in preventing colorectal polyps, which enhances its therapeutic appeal beyond conventional anti-inflammatory use.
Despite its age, Sulindac maintains relevance due to its efficacy, safety profile, and the ongoing exploration of repurposing opportunities. However, newer NSAIDs with improved safety margins and targeted therapies pose competitive challenges.
Market Landscape Overview
Indications and Usage Trends
Sulindac’s primary indications include:
- Chronic inflammatory conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis.
- Polyposis conditions: Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP).
Recent clinical investments focus on its chemopreventive potential, especially for colorectal cancer (CRC) and adenomatous polyps, which could expand its market beyond traditional applications.
Market Size and Geographic Distribution
The global NSAID market is projected to reach approximately $27 billion by 2025, with Sulindac constituting a small but stable segment, mainly in niche indications. North America dominates this market, driven by high prevalence of inflammatory and colorectal conditions, along with strong healthcare infrastructure supporting prescription NSAID use.
In the colorectal polyposis space, Sulindac's market penetration is particularly notable due to FDA-approved use for FAP where it is indicated specifically, allowing it to command premium pricing.
Competitive Landscape
Key competitors include other NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib, along with targeted therapies like aspirin for colorectal chemoprevention. Novel agents and biologics for inflammatory diseases and colorectal cancer are emerging, potentially limiting growth for older NSAIDs.
The primary competitive advantage of Sulindac remains its established safety profile and specific indication for FAP, supported by clinical evidence. However, newer drugs with better safety profiles and targeted mechanisms threaten its market share.
Regulatory and Patent Status
Sulindac, being generic and off-patent for decades, faces limited intellectual property protection, constraining pricing power and market exclusivity. This situation emphasizes the importance of clinical positioning and expanding indications to maintain sales.
Ongoing research into new therapeutic applications, such as colorectal cancer chemoprevention, may result in regulatory changes or new labeling, temporarily boosting sales within defined niches.
Market Drivers and Barriers
Drivers:
- Aging population: Increased incidence of arthritis and colorectal neoplasms.
- Colorectal cancer prevention focus: Rising awareness and screening programs amplify demand for chemopreventive agents like Sulindac.
- Longstanding clinical familiarity and established safety profiles foster clinician confidence.
Barriers:
- Safety concerns: NSAID-related gastrointestinal (GI) and cardiovascular (CV) adverse events limit use, especially in high-risk populations.
- Generic competition: Price erosion due to multiple generic manufacturers reduces profitability.
- Emergence of targeted therapies: Biologics with better safety profiles challenge NSAIDs' dominance.
Sales Projections (2023-2030)
Base Scenario
Limited to niche markets like FAP management and ongoing research for chemoprevention, annual sales are projected to remain modest but stable, averaging $50–$70 million globally. The key factor is sustained demand within FAP indications, with some growth potential from expanded chemopreventive research.
Optimistic Scenario
If new clinical trials demonstrate compelling evidence for colorectal cancer prevention and regulatory support, sales could see a significant uptick—potentially doubling to $150 million annually—driven by expanded indications and increased physician adoption.
Pessimistic Scenario
Safety concerns, market saturation, and aggressive competition could lead to declining sales below $30 million, especially if newer agents overshadow Sulindac in key markets.
Emerging Opportunities
- Repurposing for colorectal cancer chemoprevention: Continued research may facilitate approval or off-label use expansion.
- Combination therapies: Sulindac combined with targeted agents may increase efficacy and broaden indications.
- Personalized medicine: Genetic profiling might identify patients who benefit most, enhancing market penetration.
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
Sulindac’s future sales trajectory hinges upon successful demonstration of its chemopreventive value, manageable safety profile, and the ability to carve out niche markets amid competition. Its long history of clinical use provides a stable base, but growth prospects will depend on ongoing research, regulatory dynamics, and the evolving landscape of colorectal cancer management and inflammatory disease treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Market remains niche but stable, with primary sales driven by FAP treatment and potential chemopreventive indications.
- Generic status limits pricing but provides widespread accessibility.
- Emerging clinical evidence on colorectal cancer prevention can spur future sales growth.
- Safety concerns and generic competition pose ongoing challenges.
- Strategic focus on expanding indications and combination therapies could unlock new revenue streams.
FAQs
Q1: How does Sulindac compare to other NSAIDs in terms of safety?
A: Sulindac has a well-established safety profile, but like other NSAIDs, it carries risks of gastrointestinal and cardiovascular adverse events, particularly with long-term use or in high-risk groups.
Q2: What are the main drivers for Sulindac’s sales growth?
A: Increased research into colorectal cancer chemoprevention, expanding indications like FAP, and growing awareness of NSAIDs’ potential in oncology contribute to sales opportunities.
Q3: Is there a competitive advantage for Sulindac in the colorectal cancer prevention market?
A: Its longstanding clinical use and FDA approval for FAP confer credibility, but newer targeted therapies threaten to capture market share unless compelling evidence for chemoprevention is established.
Q4: How does the patent landscape affect Sulindac’s market strategy?
A: Being off-patent limits exclusivity, so long-term growth relies on expanding indications, clinical research, and market positioning rather than patent protections.
Q5: What are the key risks for Sulindac’s future sales prospects?
A: Safety concerns, market saturation with generics, and the rise of targeted therapies present significant risks, which could inhibit growth or cause sales declines.
References
[1] Market research reports on NSAIDs, 2022.
[2] FDA drug approval database for Sulindac.
[3] Clinical studies on Sulindac’s role in colorectal cancer prevention.
[4] Competitive analysis of NSAIDs and chemopreventive agents.
[5] Industry insights on genetic and targeted therapies in colorectal disease.