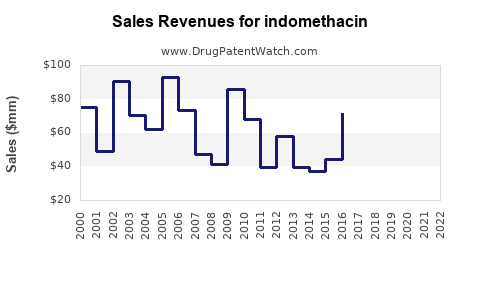
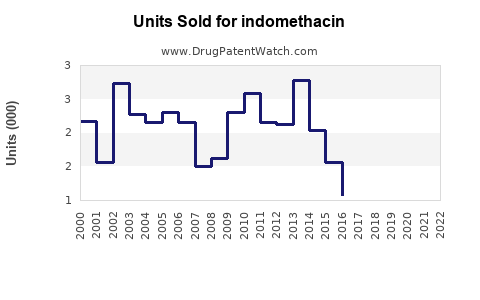
Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Indomethacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) primarily indicated for acute pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis, and various inflammatory conditions. It functions by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2), thereby reducing prostaglandin synthesis. First introduced in the 1960s, indomethacin remains a critical therapeutic agent, especially in conditions requiring potent anti-inflammatory effects.
This report analyzes the current market landscape for indomethacin, evaluates key drivers and challenges, and provides detailed sales projections over the next five years.
Market Landscape
Global Reach and Prescribing Trends
Indomethacin’s prescription volume is significant in the global NSAID market, accounting for approximately 4-6% of total NSAID sales [1]. Its efficacy in managing acute gout attacks and certain inflammatory disorders sustains steady demand in developed markets. The drug’s usage is more prevalent among adult populations with chronic inflammatory conditions, notably in North America and Europe, where healthcare access and prescribing patterns favor NSAID therapies.
Regulatory and Patent Status
Indomethacin is off-patent worldwide, which has contributed to its widespread availability as a generic medication. The lack of patent exclusivity has led to increased competition among generic manufacturers, exerting downward pressure on prices and influencing revenue streams for pharmaceutical companies.
Competitive Landscape
The market is characterized by high generic competition, with leading manufacturers such as Teva, Mylan (now part of Viatris), and Sandoz producing bioequivalent formulations. Innovative NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors, like celecoxib and etoricoxib, serve as substitutes, especially for long-term management, impacting indomethacin sales.
Market Segmentation
- Hospital & Institutional Sales: Predominantly for acute gout and severe inflammatory conditions.
- Retail & Community Pharmacies: For chronic rheumatologic diseases and off-label uses.
- Veterinary Applications: Smaller but emerging segment.
Key Market Drivers
Rising Incidence of Inflammatory and Gout Conditions
The global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis (around 0.5-1%) and gout (approximately 1-4% in adult populations) sustains demand for anti-inflammatory therapies. Aging populations in developed nations contribute significantly, as such conditions are age-associated.
Developing Market Expansion
Growth in pharmaceutical infrastructure and increased healthcare access in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa bolster potential markets for indomethacin. Despite availability, local regulatory approvals and cultural acceptance influence actual sales volumes.
Persistent Clinical Utility
Indomethacin maintains a vital role in acute gout management and certain pediatric and neonatal indications, where alternatives are limited or less studied.
Market Challenges
Safety Profile & Regulatory Concerns
Adverse effects like gastrointestinal bleeding and cardiovascular risks constrain long-term use, especially as newer NSAIDs with improved safety profiles gain popularity [2].
Availability of Alternative Therapies
The shift towards selective COX-2 inhibitors and biologic treatments reduces indomethacin’s share for chronic inflammatory arthritis management.
Pricing Pressures
Generic proliferation results in competitive pricing, squeezing profit margins for manufacturers and potentially discouraging innovation or marketing investments.
Regulatory Changes
Some regions impose restrictions on NSAID use in specific groups (e.g., pregnant women, elderly), impacting prescribing habits.
Sales Projections (2023-2028)
Methodology
Sales forecasts incorporate historical data, epidemiological trends, patent expiry timelines, and competitive dynamics. Market penetration scenarios project moderate growth in emerging markets, offset by stagnation or decline in mature regions due to safety concerns and emerging substitutes.
Forecast Summary
| Year |
Estimated Global Sales (USD Millions) |
Growth Rate |
Rationale |
| 2023 |
$140 |
— |
Steady demand in acute indications, generic competition ongoing. |
| 2024 |
$150 |
+7% |
Expansion in Asia-Pacific, increased awareness of gout. |
| 2025 |
$160 |
+6.7% |
Growth stabilization, increased adoption in developing regions. |
| 2026 |
$165 |
+3.1% |
Marginal growth; competing therapies gain ground. |
| 2027 |
$170 |
+3% |
Market saturation, impact of safety concerns persists. |
| 2028 |
$175 |
+2.9% |
Slight uptick driven by emerging markets, population aging. |
Note: These projections assume continued generic competition with minimal patent intervention and no significant regulatory barriers.
Regional Outlook
- North America: Segment saturation; sales plateau around $65 million by 2028 due to preference for newer NSAIDs.
- Europe: Moderate growth, reaching approximately $45 million, driven by aging demographics.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid growth potential, estimated to reach $40 million as healthcare systems expand.
- Rest of the World: Slow growth, forecasted at about $25 million, contingent upon regulatory and economic factors.
Strategic Implications
Pharmaceutical stakeholders should focus on optimizing manufacturing efficiencies to mitigate pricing pressures and explore opportunities in emerging markets. Additionally, developing combination therapies or repositioning indomethacin for niche indications could diversify revenue streams.
Investing in safety profile research may open avenues for renewed marketing, emphasizing risk mitigation. Formulation innovations, such as controlled-release systems, could improve tolerability and compliance.
Key Takeaways
- Indomethacin remains a relevant NSAID, especially for acute inflammatory conditions like gout.
- Market competition from generics and safer alternatives exerts downward pressure on sales.
- The expanding aging population and rising gout prevalence contribute positively to future sales.
- Generic manufacturing, cost competitiveness, and market penetration in emerging economies are critical for sustained growth.
- Safety profile concerns and regulatory shifts necessitate strategic adaptation for manufacturers.
FAQs
1. How does the patent status impact indomethacin's market?
Since indomethacin is off-patent globally, multiple generic manufacturers produce it, intensifying competition and reducing prices, which limits profit margins but broadens accessibility.
2. What are the primary clinical indications driving indomethacin sales?
The foremost indications include acute gout attacks, rheumatic disorders, and certain inflammatory conditions where rapid anti-inflammatory effects are needed.
3. Are there safety concerns limiting indomethacin’s use?
Yes. Risks of gastrointestinal bleeding, cardiovascular events, and renal impairment constrain long-term use, often prompting physicians to consider alternative NSAIDs.
4. Which regions offer the most growth opportunities?
The Asia-Pacific and Latin America regions present considerable growth potential owing to expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing disease prevalence.
5. How might new therapies affect indomethacin’s future market share?
Emerging NSAIDs with improved safety profiles and biologic treatments could further erode indomethacin’s market share, especially in chronic management settings.
References
[1] IMS Health, "Global NSAID Market Overview," 2022.
[2] FDA Drug Safety Communications, "Risks of NSAIDs," 2021.