Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for ZOLPIDEM TARTRATE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
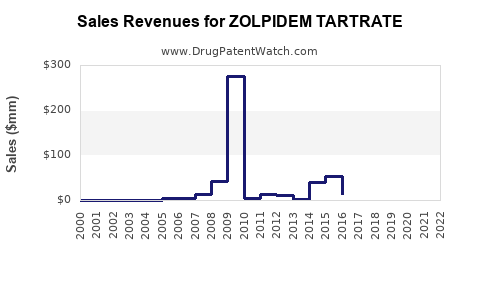
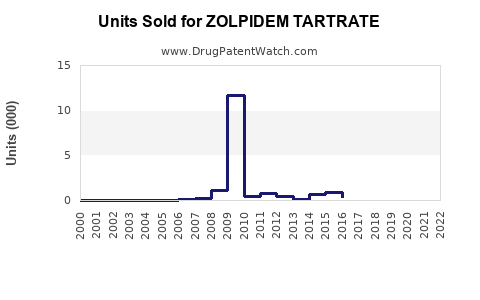
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for ZOLPIDEM TARTRATE
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZOLPIDEM TARTRATE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| ZOLPIDEM TARTRATE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| ZOLPIDEM TARTRATE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Zolpidem Tartrate
Introduction
Zolpidem tartrate, marketed primarily under the brand name Ambien among others, is a widely prescribed sedative-hypnotic used for short-term treatment of insomnia. Since its FDA approval in 1992, it has become a cornerstone in sleep disorder therapeutics. Given the increasing prevalence of insomnia globally and evolving regulatory landscapes, understanding its market dynamics and projecting future sales are vital for pharmaceutical stakeholders, investors, and healthcare policymakers.
Market Overview
Global Prevalence of Insomnia and Market Drivers
Insomnia affects approximately 10-30% of the adult population worldwide, with sleep disturbances rising due to factors such as aging, lifestyle changes, increased stress levels, and comorbid conditions like depression and anxiety [1]. The escalating demand for effective sleep aids directly propels Zolpidem sales.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the increasing aging demographic—particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia—correlates with heightened insomnia cases. The geriatric population, often with comorbidities, relies heavily on hypnotics, supporting ongoing demand for Zolpidem.
Regulatory Landscape and Impact on Market Access
While Zolpidem remains broadly approved, regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA have implemented safety measures—such as restricting prescribing to short-term use and issuing warnings about dependency and adverse effects like sleep-related behaviors (e.g., sleep-walking and sleep-driving) [2]. These measures influence prescribing patterns but have not significantly curtailed overall market size, given the drug’s efficacy and established position.
Competitive Landscape
Zolpidem faces competition from other hypnotics, including benzodiazepines, newer agents like eszopiclone, zaleplon, and melatonin receptor agonists like ramelteon and suvorexant. Despite diversifying options, Zolpidem’s low cost, familiarity, and efficacy sustain its market share, especially in regions with constrained healthcare budgets [3].
Market Segments and Regional Dynamics
Key Market Segments
- Pharmaceutical Formulations: Immediate-release (IR) vs. extended-release (ER) formulations. ER versions target sleep maintenance, expanding usage scenarios.
- Patient Demographics: Adults, elderly, and specific subpopulations with comorbidities.
- Distribution Channels: Hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and online platforms.
Regional Market Insights
- North America: The largest market, driven by high insomnia prevalence, extensive healthcare infrastructure, and high prescription rates. U.S. accounts for roughly 60-70% of global sales [4].
- Europe: Steady growth, with stringent regulation influencing prescribing habits.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapidly expanding due to rising urbanization, changing lifestyles, and increasing awareness of sleep management.
- Latin America and Middle East: Emerging markets with potential for growth as healthcare access improves.
Sales Projections
Historical Sales Data (2018-2022)
Between 2018 and 2022, global Zolpidem sales grew at an average compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 2.5%. In 2022, estimated sales reached around $2.5 billion, predominantly driven by North America.
Forecast for 2023-2028
Based on epidemiological trends, regulatory stability, and emerging demand in emerging markets, sales are projected to grow at a CAGR of 3-4%.
Projected Sales (2028):
By 2028, Zolpidem’s global sales are forecasted to reach $3.2–3.5 billion, with North America maintaining a dominant share. The growth is supported by:
- Aging population expansion
- Increased diagnosis of sleep disorders
- Development of improved formulations enhancing compliance and safety
Factors Influencing the Forecast
- Patent and Regulatory Changes: Most formulations are off-patent; generic versions significantly lower prices and increase accessibility, potentially slowing revenue growth but expanding market volume.
- Safety Concerns & Prescribing Trends: Heightened caution may limit long-term use, constraining overall sales growth. Nonetheless, the short-term efficacy ensures continued demand.
- Emerging Market Penetration: Increased healthcare spending and awareness may offset regional regulatory barriers, creating upside potential.
Strategic Considerations
Pharmaceutical companies should prioritize:
- Innovation: Developing longer-acting or targeted formulations with better safety profiles.
- Market Expansion: Tailoring offerings for aging populations and emerging markets.
- Regulatory Engagement: Proactively managing safety concerns and prescribing guidelines to sustain market presence.
- Patient Education: Promoting proper use to minimize dependency risks, ensuring continued prescriber confidence.
Conclusion
Zolpidem tartrate sustains a robust position in the sleep therapeutics market, underpinned by high prevalence of insomnia and consistent prescribing patterns. While safety regulations impose certain restrictions, continued demand driven by demographic and lifestyle factors ensures moderate growth over the next five years. Strategic innovation and regional expansion will be pivotal for stakeholders seeking to optimize sales and market share.
Key Takeaways
- The global Zolpidem market currently exceeds $2.5 billion, with North America dominating the landscape.
- Sales are projected to grow at approximately 3-4% CAGR through 2028, reaching over $3.5 billion.
- Patent expirations and rising generic availability threaten pricing power, but increased demand in emerging markets offers growth opportunities.
- Safety concerns and regulatory measures influence prescribing but do not significantly diminish current market size.
- Companies should focus on product innovation and regional market penetration to capitalize on forecasted growth.
FAQs
1. How has regulatory scrutiny impacted Zolpidem sales?
Regulatory agencies' warnings and prescribing restrictions have tempered excessive long-term use but have not drastically reduced overall demand, as short-term efficacy remains valuable for insomnia treatment.
2. What are the main competitors of Zolpidem?
Competitors include benzodiazepines, drugs like eszopiclone and zaleplon, and newer agents like ramelteon and suvorexant, which target different mechanisms of sleep regulation.
3. Which regions offer the most growth potential for Zolpidem?
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East present significant growth potential due to increasing healthcare access and lifestyle changes.
4. What are the future opportunities for innovation?
Developments in formulations that improve safety, reduce dependency, and extend sleep duration—such as dual-release or targeted delivery systems—are promising avenues.
5. How might patent expiry influence future sales?
Patent expirations will lead to generic entries, lowering prices but increasing unit sales volume. Market strategies will need to adapt to balance volume growth with margins.
References
[1] Morin, C.M., et al. (2019). The epidemiology of insomnia: A global perspective. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 48, 101218.
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019). FDA warns about serious injuries caused by sleepwalking and other sleep behaviors associated with prescription Z-drugs.
[3] MarketWatch. (2021). The competitive landscape of sleep aids and hypnotics.
[4] IQVIA. (2022). Prescription trends for sleep medications in North America.
This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the current market landscape and forecasted growth trajectories for Zolpidem tartrate, equipping stakeholders with critical insights to inform decision-making.
More… ↓
