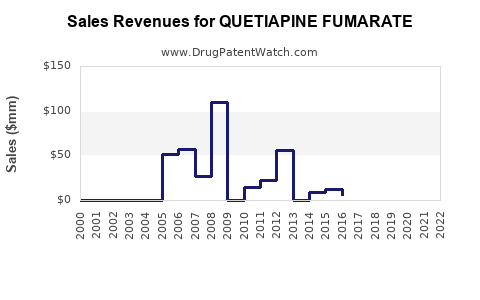
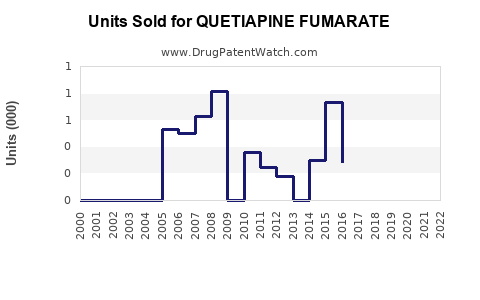
Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Quetiapine fumarate, marketed primarily under the brand name Seroquel, is an atypical antipsychotic medication indicated for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. Since its approval in 1997, it has become a cornerstone in psychopharmacology, with global sales surpassing billions annually. This analysis evaluates current market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and projected sales trajectories for Quetiapine fumarate over the next five years.
Market Overview
Global Market Size
The global antipsychotic market, valued at approximately $15 billion in 2022, continues to expand driven by increasing prevalence of psychiatric disorders and expanding treatment guidelines [1]. Quetiapine accounts for a significant share, estimated at 20-25%, owing to its versatility and broad indications. The drug’s large market share is underpinned by its approval for multiple psychiatric conditions, extensive formulary adoption, and entrenched prescribing habits.
Key Therapeutic Segments
- Schizophrenia: Approximately 21 million people worldwide suffer from schizophrenia, with treatment adherence challenges elevating the demand for effective long-term medications.
- Bipolar Disorder: An estimated 45 million globally, with lithium and atypical antipsychotics like quetiapine being first-line therapies.
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Quetiapine extended-release has gained approval as adjunctive therapy for MDD, further expanding its market penetration.
Market Drivers
- Rising Prevalence: Increasing mental health awareness and diagnostic rates.
- Off-label Uses: Off-label prescribing for insomnia and anxiety, although not officially indicated, contribute to sales.
- Expanded Formulations: Development of extended-release formulations enhances patient compliance and widens therapeutic applications.
- Aging Population: B2B demand driven by elderly populations with neuropsychiatric comorbidities.
Market Challenges
- Generic Competition: Patent expiration and the entry of generics globally have prompted pricing pressures.
- Side Effect Profile: Risks such as metabolic syndrome, weight gain, and sedation could influence prescribing patterns.
- Regulatory Restrictions: Labeling restrictions and warnings on side effects may impact market share.
Competitive Landscape
Major Players
- Eli Lilly and Company: Original developer and key holder for Seroquel.
- Teva Pharmaceuticals: Prominent generic manufacturer.
- Mylan (now part of Viatris): Significant generics supplier.
- Other Biopharmaceuticals: Innovative atypical antipsychotics like aripiprazole and lurasidone are competitors.
Market Share Dynamics
While Eli Lilly retains a significant portion of the brand-name market, generics dominate the volume sales, especially post-patent expiration in many jurisdictions. The shift from branded to generic versions impacts revenue streams, although innovator brands maintain residual profits through listing exclusivity in certain markets.
Regulatory Environment
- FDA and EMA Approvals: The drug is approved globally with varying indications.
- Off-label Use Regulations: Strict regulations impact the extent of off-label prescribing.
- Pricing and Reimbursement Policies: Healthcare policy changes influence sales; countries with comprehensive reimbursement schemes support higher utilization.
Sales Projections (2023-2028)
Methodology
Estimates derive from historical sales data, market growth rates, patent expiry timelines, and competitive shifts. Modelling incorporates an annual compound growth rate (CAGR), adjusted for regional variations and potential market saturation.
Forecasted Sales Trends
- 2023: Approximately $3.2 billion globally, considering steady growth following patent expiry in key markets.
- 2024-2025: Post-patent erosion accelerates, leading to a CAGR of around 4-6%, with generic proliferation reducing per-unit prices but increasing total volume.
- 2026-2028: Market stabilization as generic penetration reaches near saturation, but sustained demand in off-label and expanded indications supports ongoing revenues.
Regional Variations
- North America: Largest market, projected to decline slightly due to generics but offset by off-label uses and new formulations.
- Europe: Rising awareness and increased reimbursement favor sustained sales.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid growth driven by expanding mental health infrastructure and increasing recognition of psychotropic treatments, forecasted at 6-8% CAGR.
Future Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities
- New Formulations: Development of long-acting injectables and novel delivery systems.
- Expanded Indications: Approvals for adjunctive therapy in depression or for behavioral disturbances.
- Personalized Medicine: Pharmacogenomic profiling to optimize dosing and reduce side effects.
- Emerging Markets: Increased adoption in low- and middle-income countries.
Risks
- Patent Challenges: Patent cliffs could accelerate generic substitution.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Warnings regarding metabolic syndrome could impact prescribing.
- Market Saturation: Slowdown due to high existing penetration.
- Competitive Drugs: New atypical antipsychotics with better safety profiles.
Conclusion
Quetiapine fumarate’s market remains robust, driven by its multi-indication profile and entrenched positioning. While patent expiries and generic competition pose revenue pressures, expanding off-label use, regional growth, and formulation innovation offer avenues for sustained sales growth. Strategic focus should include pipeline expansions, geographic diversification, and safety profile enhancements to capitalize on evolving market dynamics.
Key Takeaways
- Market Potential: The global antipsychotic market, with Quetiapine fumarate as a leading product, is projected to grow modestly at a CAGR of 4-6% over the next five years.
- Patent and Generic Impact: Expirations are driving volume increases but suppressing unit prices; strategic differentiation is essential.
- Regional Growth: Asia-Pacific presents significant growth opportunities, with anticipated CAGR of 6-8%.
- Innovation Drivers: Formulation advances and new indications can mitigate competitive pressures.
- Regulatory and Safety Factors: Side effect management and regulatory compliance are crucial to maintaining market share.
FAQs
-
What is the primary therapeutic use of Quetiapine fumarate?
Quetiapine fumarate is primarily used for treating schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and as an adjunct in major depressive disorder.
-
How does patent expiry affect Quetiapine sales?
Patent expiration introduces generic competition, leading to lower prices but increased volume, impacting overall revenue depending on market penetration.
-
What regions are expected to drive future sales growth?
The Asia-Pacific region is projected for rapid growth, supported by expanding mental health infrastructure and rising awareness.
-
What are the main risks to Quetiapine’s market stability?
Risks include adverse side effect profiles, regulatory restrictions, and the emergence of competing drugs with improved safety or efficacy.
-
Are off-label uses significant for Quetiapine’s revenue?
Yes, off-label prescribing for insomnia and anxiety significantly contributes to sales, even though not officially indicated.
References
[1] GlobalData. “Antipsychotic Drugs Market Size & Share, 2023-2028,” 2023.