Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for PHENYTOIN SODIUM
✉ Email this page to a colleague
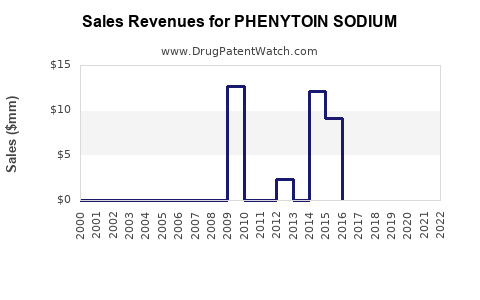
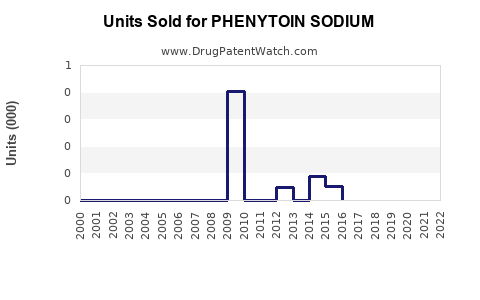
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for PHENYTOIN SODIUM
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHENYTOIN SODIUM | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| PHENYTOIN SODIUM | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| PHENYTOIN SODIUM | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Phenytoin Sodium
Introduction
Phenytoin sodium is a widely prescribed antiepileptic drug primarily used for controlling seizures, including tonic-clonic and complex partial seizures. Its long-standing clinical utility, coupled with broad regulatory approval worldwide, positions it as a key player within the antiseizure medication (ASM) market. As global healthcare systems increasingly prioritize neurological disorder management, understanding the market dynamics and sales forecasts for phenytoin sodium offers strategic insights for pharmaceutical stakeholders.
Market Overview
Phenytoin Sodium: Therapeutic Profile and Current Usage
Phenytoin sodium operates by stabilizing neuronal membranes and inhibiting abnormal neuronal firing, effectively preventing seizure episodes. Despite the advent of newer ASMs with improved side effect profiles, phenytoin remains a critical therapy, especially in resource-limited settings and for acute seizure management in hospital environments. Its pharmaceutical formulations include oral tablets, injectable solutions, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) formulations.
Regulatory Landscape and Global Approvals
Regulatory acceptance of phenytoin sodium spans over 70 countries, with major markets including the United States, European Union, and emerging economies in Asia-Pacific. Notably, in the United States, phenytoin is available generically with pivotal approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Its longstanding status as a generic drug underpins widespread use, but also constrains potential for branded sales growth.
Market Dynamics
Key Market Drivers
-
Prevalence of Epilepsy and Neurological Disorders: The World Health Organization estimates over 50 million people globally have epilepsy, with higher incidence rates in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). The chronic nature of epilepsy sustains steady demand for effective maintenance therapies like phenytoin sodium.
-
Healthcare Infrastructure and Access: In many developing nations, phenytoin’s affordability and established manufacturing make it an essential therapy within national essential medicines lists.
-
Clinical Guidelines and Prescribing Patterns: Many neurological and emergency protocols endorse phenytoin, especially for acute seizure control and status epilepticus, supporting robust demand.
Market Challenges
-
Side Effect Profile and Drug Safety Concerns: Phenytoin’s side effects—including gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, and neurological toxicity—prompt clinicians to escalate to newer third-generation ASMs, like levetiracetam or lamotrigine.
-
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (TDM): Requires regular blood level assessments, which can hamper adherence and increase healthcare costs in some settings.
-
Availability of Competitors: The rise of newer, better-tolerated drugs challenges phenytoin’s market share, particularly in Western markets with advanced healthcare infrastructure.
Regional Market Insights
- North America: Market penetration is mature, with extensive generic availability. Sales are stabilizing but sustain due to large epilepsy patient populations.
- Europe: Similar to North America, with increasing adoption of newer ASMs, yet phenytoin retains niche utility.
- Asia-Pacific: Emerging markets demonstrate significant growth potential driven by large population bases and cost-sensitive healthcare systems relying on older, affordable therapies like phenytoin.
- Latin America & Africa: High demand driven by limited access to newer medications; local manufacturing and supply chain ease bolster usage.
Market Size and Revenue Estimation
Historical Market Trends
The global anti-epileptic drug market was valued at approximately USD 4.4 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 3.8% from 2022 to 2030 [2]. A substantial segment of this market comprises generic phenytoin sodium formulations, translating into steady sales volumes historically.
Market Segmentation
- By Formulation: Oral tablets (~60%), injectable (~30%), and CSF formulations (~10%).
- By Region: North America (~35%), Europe (~25%), Asia-Pacific (~20%), Latin America (~10%), Africa (~10%).
Projected Sales Forecast (2023–2030)
Assuming the continued demand in existing markets and growth in emerging regions:
- 2023: Estimated global sales of USD 600 million.
- 2025: Expected to reach USD 720 million, driven by emerging markets.
- 2030: Projected sales could surpass USD 900 million, leveraging increasing epilepsy prevalence and expanding healthcare infrastructure in LMICs.
The growth is contingent on sustained manufacturing, regulatory stability, and minimal competition from newer ASMs in developed markets. The continued reliance on generics and healthcare disparities underpin the overall sales trajectory.
Opportunities and Strategic Considerations
- Development of Novel Formulations: Long-acting or depot formulations could enhance patient compliance and expand usage.
- Manufacturing Cost Optimization: Improving production efficiencies in emerging markets can enhance margins.
- Regulatory Approvals and Patent Expirations: Targeting prior-approved markets can facilitate rapid commercialization of new or biosimilar formulations.
- Market Expansion in LMICs: Strategic licensing and partnerships can tap into underserved populations, increasing global market share.
Risks and Limitations
- Competitive Pressure: Increasing market share of newer ASMs reduces growth potential.
- Regulatory Stringency: Evolving safety standards and post-market surveillance may restrict certain formulations.
- Market Saturation: Mature Western markets exhibit limited growth potential, emphasizing the importance of emerging markets.
Key Takeaways
- Steady but Limited Growth: Phenytoin sodium maintains a stable revenue base driven by global epilepsy prevalence and affordability, with projections indicating incremental sales growth.
- Emerging Markets as Growth Drivers: Rapid expansion of healthcare infrastructure and increasing epilepsy diagnoses in LMICs underpin future sales.
- Market Challenges: The shift toward newer, better-tolerated ASMs poses long-term risks; however, phenytoin's low cost and clinical necessity sustain current demand.
- Strategic Focus Areas: Developing improved formulations, expanding access in developing regions, and maintaining manufacturing efficiencies are critical for capitalizing on market opportunities.
- Regulatory and Competitive Monitoring: Continuous assessment of regulatory changes and competitor dynamics is essential to safeguard and grow market share.
FAQs
1. What is the primary therapeutic use of phenytoin sodium?
Phenytoin sodium is mainly prescribed for controlling partial and generalized tonic-clonic seizures, and it is often used during status epilepticus.
2. How does the market for phenytoin sodium compare to newer antiepileptic drugs?
While newer ASMs like levetiracetam and lamotrigine offer better tolerability, phenytoin’s low cost makes it indispensable in resource-constrained settings, ensuring steady market demand.
3. What regions present the greatest growth opportunities for phenytoin sodium?
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America offer significant growth potential due to expanding healthcare access and high epilepsy prevalence.
4. Are there significant regulatory challenges facing phenytoin sodium?
As a WHO essential medicine, phenytoin generally faces less regulatory hurdles; however, safety monitoring and formulation approvals continue to be critical considerations.
5. What are the main risks to sales growth for phenytoin sodium?
Shifts toward newer drugs with improved safety profiles, stricter regulatory requirements, and potential shortages or manufacturing issues could constrict sales growth.
References
- World Health Organization. (2019). Epilepsy Fact Sheet.
- Grand View Research. (2022). Anti-Epileptic Drugs Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report.
More… ↓
